Name Date Hour ______ Electron Configuration & Electromagnetic
advertisement

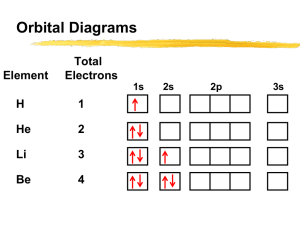
Name ___________________________________________ Date _____________________________ Hour ___________ Electron Configuration & Electromagnetic Spectrum Review 1. Write the electron configuration for tin using the noble gas notation. How many valence electrons does the atom tin have? 2. Write the noble gas electron configuration for the ion Sr+2. How many valence electrons does the ion strontium have? 3. Write the noble gas electron configuration for the ion Se-2. How many valence electrons does the ion selenium have? 4. Draw an orbital diagram for Mn. 5. Identify the element below and write its name in the space provided. Answer the three questions about the element by writing the letter of your choice by the correct description. The element is ______________________ a. 1s22s22p63s23p65p1 b. 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 c. 1s22s22p63s23p7 Which of the above electron configurations is the element’s ground state configuration? __________ Which of the above electron configurations is the element’s excited state configuration? __________ Which of the above electron configurations is an impossible configuration? __________ 6. As the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation increases, the frequency ____________________. 7. The speed of light for ALL electromagnetic radiation is _________________________. 8. Three rules (principles) define how electrons are arranged in orbit around an atom’s nucleus. a) ____________________ states that each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available. b) ____________________ states that single electrons with the same spin must each occupy an equal-energy orbital before additional electrons with different spins can occupy the same orbitals. c) ____________________states that a maximum of two electrons may occupy a single atomic orbital but only if they spin in opposite directions. 9. An X-ray has a wavelength of 1.81 x 10-12 m. What is the energy of a photon from this x-ray? The energy of a photon is equal to Plank’s constant (h) times the frequency of the wave (ν). Ephoton = h x ν (Plank’s constant, h = 6.626 x 10-34 J.s) The speed of light (c) is equal to the wave’s wavelength (λ) times the wave’s frequency (ν) c = λ . ν (c = 3.00 x 108 m/s) Show all your work and don’t forget units.