General Features of the Heart
advertisement

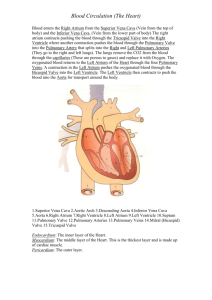
General Features of the Heart Created by: Sydney, Damon, and Jordy • The heart has four chambers. The two ventricles and the two atria Four Chambers • The Left Ventricle is the lower right part of the heart and receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium through the mitral valve, and pumps it into the aorta through the corresponding valve The Left Ventricle • The Right Ventrical is the lower right quarter of the heart and receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium through the tricuspid valve, and pumps it into the pulmonary artery through the pulmonary valve and trunk The Right Ventricle • The Right Atrium is the upper left part of the heart, has relatively thin walls, and receives blood that is returning through two large veins: the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. The Right Atrium • The Left Atrium is the upper right chamber of the heart and his job is to receive oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle which delivers it to the body. The Left Atrium • Pericardium: double-walled sac that surrounds the heart • Epicardium: layer of pericardium closest to the heart wall • Myocardium: muscles are arranged in spiral and circular bundles • Endocardium: connective tissue located on the inner surface of the myocardium Layers of the Heart Wall Layers of the Heart • • • • • • • • • • • Epicardium - the outer layer of the wall of the heart. Myocardium - the muscular middle layer of the wall of the heart. Endocardium - the inner layer of the heart. Atrioventricular Bundle - bundle of fibers that carry cardiac impulses. Atrioventricular Node - a section of nodal tissue that delays and relays cardiac impulses. Purkinje Fibers - fiber branches that extend from the atrioventricular bundle. Sinoatrial Node - a section of nodal tissue that sets the rate of contraction for the heart. Brachiocephalic Veins - two large veins that join to form the superior vena cava. Common iliac Veins - veins that join to form the inferior vena cava. Pulmonary Veins - transport oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. Vena Cava - transport de-oxygenated blood from various regions of the body to the heart. Inner and Outer Anatomy • Allow blood to flow from one chamber to another or allowing blood to flow out of the heart in only one direction • Control the flow of blood by opening and closing through contractions of the heart • Deoxygenated blood: right atrium -->tricuspid valve->right ventricle-->pulmonary valve-->lungs • Oxygenated blood: left atrium-->mitral valve-->left ventricle-->aortic valve-->aorta-->body’s organs Valves of the Heart Valves of the Heart • Prevents backflow of blood into the right atrium • Made up of 3 valve leaflets, annulus, supporting chordae tendineae, and papillary muscles • Located between right atrium and right ventricle • Atrioventricular valve • Leaflets are attached to papillary muscles that strengthen the movement of the leaflets • Opens when atrium contracts Tricuspid Valve • Prevents regurgitation of blood from the pulmonary artery back to the right ventricle • Formed by three cusps, supported by freestanding musculature • Divides right ventricle from pulmonary artery • Semilunar valve • Opens when right ventricle contracts Pulmonic/Pulmonary Valve • Connects left atrium to left ventricle • Sllows blood flow from LA to LV and then prevents backflow to the LA • 6 components • left atrial wall, annulus, 2 leaflets, chordae tendineae, papillary muscles, and left ventricular wall • Atrioventricular valve • Opens when atrium contracts Mitral Valve • Between left ventricle and ascending aorta • Forms centerpiece of heart • Prevents regurgitation of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle • Annulus, cusps, and commissures • Semilunar valve • Opens when ventricle contracts Aortic Valve • • • • • • • • • • • • http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1923232-overview http://surgery.about.com/od/beforesurgery/qt/HeartValves.htm http://heartdisease.about.com/cs/starthere/a/chambersvalves.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Left_ventricle http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Right_ventricle http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-the-coronary-sinus.htm http://www.innerbody.com/image_card01/card46-new2.html http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=26567 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chordae_tendineae http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aorta http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aortic_valve http://legacy.owensboro.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat2/notes/APIINotes5%20Anatomy %20of%20the%20Heart.htm • http://www.cts.usc.edu/hpg-valvesoftheheart-circulationofblood2.html Sources