Review+class+for+quiz2
advertisement

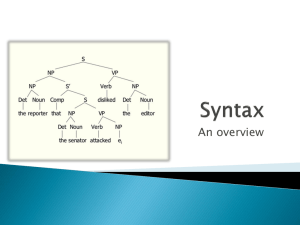
Quiz 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The boy found the ball. The boy found quickly. The boy found in the house. The boy found the ball in the house. Lisa slept the baby. Lisa slept soundly. Sentences are not random strings of words. They must conform to specific patterns. What is the purpose of studying syntax? To investigate word order and sentence structure. To be able to consciously articulate our unconscious knowledge of English. The knowledge of sentences and their structure. Syntactic rules include: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ The grammaticality of sentences Word order Hierarchical organization of sentences Grammatical relations such as subject and object Whether different structures have different meanings or the same meanings Grammaticality judgments do not depend on having heard the sentence before: Enormous crickets in pink socks danced at the party. Grammaticality judgments do not depend on meaning: Colorless green ideas sleep furiously. *Furiously sleep ideas green colorless Major word classes Nouns Verbs Adjectives Adverbs Sentence with only major word classes: Adjectives ◦ Modify nouns My favorite dog is hungry. Adjectives can have a predicative function or an attributive function. Adverbs Often considered the ‘garbage’ category Unfortunately, some students drive very quickly and create extremely dangerous roads. unfortunately: sentence adverb quickly: manner adverbs very: degree adverbs Phrasal category Form Function NP Headed by a noun Subject of sentence VP Headed by a verb Predicate of sentence VP NP det adj The friendly person NP N V det asked a N question The man with the toupee shocked the woman at the bar. Sentence (S) Subject (NP) Predicate (VP) The man with the toupee shocked the woman at the bar Hierarchical constituent structure Meaning (1)A big sale of stereos Big stereo sale (2) a sale of big stereos Big stereo sale S VP NP NP PP NP NP det adj The tipsy N man V finished det N P det N the drink in one minute Every NP has a grammatical relation to some other element in sentence. NP: ‘the tipsy man’ relationship with ‘finished’= SUBJECT NPs to left of verbs = subject (dominated by S) NP: ‘the drink’ = direct object NPs to right of verbs and dominated directly by VP = direct object Other NP not related directly to verb but to preposition (dominated directly by PP) = object of a preposition Test 1: “stand alone” test If a group can stand alone, they form a constituent Set of word that can answer a question: What did you pass? “the Linguistics class” “passed the” The student passed the Linguistics class. Test 2: “replacement by a pronoun” test ◦ Pronouns can substitute for natural groups. Pronoun that can answer a question: ◦ When did you pass the Linguistic class? “I passed it last trimester” Do can also substitute for the whole predicate passed the Linguistics class. Som passed the Linguistics class and Boss did too. Test 3: “move as a unit” test ◦ If a group of words can be moved, they form a constituent. The student passed the Linguistics class It was the Linguistics class that the student passed. The Linguistics class was passed by the student. S NP VP CP S NP VP NP det The N professor V said C that det the N student V passed det N the exam. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. S = NP = VP = VP = VP = PP = VP = CP = NP + VP Det + N V + NP V V + PP P + NP V + CP C+S The woman laughed. The meaning of language Why does a certain set of words mean something and a similar set mean something very different? When do two different sentences mean the same thing? How can one sentence mean more than one thing? What is meaning? In our society, many people feel that the dictionary definition of a word more accurately represents a word’s meaning than an individual speaker’s understanding of the word. But descriptivists arrive at their definitions by studying the ways speakers of the language use different words. The meaning of a word or expression is not just a definition composed of more words in the same language, since ultimately the meaning of some words would have to be known in order to understand the definitions. Meaning is provided by a community of language speakers, not by some special authority like a dictionary or grammar book. Mental image Reference Sense Synonyms Antonyms Homonyms (homophones) Hyponyms mother PARENT ADULT woman father bachelor boy MALE Incorrect “matching” of the semantic features of different elements of a sentence can result in ungrammatical (but syntactically sound) sentences: The man [-female] was pregnant [+female]. I sawed [+solid] the water [-solid]. The ideas [-living] are sleeping [+living]. The importance of context is concerned with the interpretation of meaning in context. 2 contexts: Linguistic context (discourse) Situational context (anything non-linguistic) What’s the concept of deixis? Holding texts together Cohesion Grammatical Reference Substitution Lexical Ellipsis Repetition Synonyms Superordinates Reference Using referring expressions to refer to referents in the context. Commonly used reference: pronouns Substitution Little boxes on the hillside, Little boxes made of ticky-tacky, Little boxes, little boxes, Little boxes, all the same. There’s a green one and a pink one And a blue one and a yellow one And they’re all made of ticky-tacky And they all just look the same. (Reynolds, 1963) Substitution Similar function as pronouns Using a word to substitute for its referent Ellipsis Omitting words and phrases mentioned earlier Purpose to avoid repetition Martin loves his wife, and so do I. Repetition Repeated words/phrases to exploit its stylistic effect ◦ “Little boxes” Synonyms To avoid repetition another word with the same meaning is used. At 75 cm across and capable of cracking open a coconut with its claws, the landdwelling coconut crab is your beach lounger’s worst nightmare. Fortunately for the sunbather, the world’s largest terrestrial arthropod has been confined to tropical islands across the Pacific and Indian oceans only. (adapted from Cutting, 2002) Superordinates Similar to hyponomy The great white shark can grow up to 8m long. It is one of the more dangerous predators in the sea.