Definition
advertisement

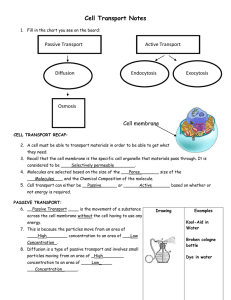
Parts of the Cell Membrane Outside of cell Proteins Carbohydrate chains Cell membrane Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Go to Section: Protein channel Double Fat Layer Homeostasis • Maintenance of a stable internal condition • Balance Vocab • Vesicle: – Membrane-covered compartments that forms when part of the cell membrane surrounds an object and pinches off Diffusion Definition: Movement of small particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, like oxygen Diffusion Definition: Movement of small particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, like oxygen Diffusion High Low Definition: Movement of small particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, like oxygen Diffusion High Low Definition: Movement of small particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, like oxygen Diffusion Requires NO ATP (energy), moves only small particles High Low Definition: Movement of small particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, like oxygen Osmosis: the diffusion of water Diffusion Requires NO ATP (energy), moves only small particles High Low Passive Transport Definition: the movement of medium particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a protein channel Passive Transport Definition: the movement of small & large particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a protein channel Passive Transport Requires NO ATP (ENERGY) Just like diffusion but through a protein Definition: the movement of medium particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a protein channel Passive Transport Requires NO ATP (ENERGY) Definition: the movement of med. particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Just like diffusion but through a protein High Passive Transport Requires NO ATP (ENERGY) Low Definition: the movement of med. particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Just like diffusion but through a protein High Passive Transport Requires NO ATP (ENERGY) Low Active Transport Definition: the movement of medium particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration through a protein channel Active Transport Definition: the movement of med. particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration through protein channel Active Transport Requires ATP (ENERGY) Similar to Passive Transport but requires energy Definition: the movement of med. particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration through a protein channel Active Transport Requires ATP (ENERGY) Definition: the movement of med. particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration Similar to Passive Transport but requires energy Low Active Transport Requires ATP (ENERGY) High Definition: the movement of sm. & lg. particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration Similar to Passive Transport but requires energy Low Active Transport Energy Requires ATP (ENERGY) High ENDOCYTOSIS ENDOCYTOSIS Definition: the cell taking in particles by surrounding the particle and enclosing it in a vesicle ENDOCYTOSIS Definition: the cell taking in particles by surrounding the particle and enclosing it in a vesicle Step 1: the cell comes into contact with a particle ENDOCYTOSIS Definition: the cell taking in particles by surrounding the particle and enclosing it in a vesicle Step 1: the cell comes into contact with a particle ENDOCYTOSIS Definition: the cell taking in particles by surrounding the particle and enclosing it in a vesicle Step 1: the cell comes into contact with a particle Step 2: the cell membrane begins to wrap around the particle ENDOCYTOSIS Definition: the cell taking in particles by surrounding the particle and enclosing it in a vesicle Step 1: the cell comes into contact with a particle Step 2: the cell membrane begins to wrap around the particle ENDOCYTOSIS Definition: the cell taking in particles by surrounding the particle and enclosing it in a vesicle Step 1: the cell comes into contact with a particle Step 2: the cell membrane begins to wrap around the particle Step 3: once the particle is completely surrounded, a vesicle pinches off ENDOCYTOSIS Definition: the cell taking in particles by surrounding the particle and enclosing it in a vesicle Step 1: the cell comes into contact with a particle Step 2: the cell membrane begins to wrap around the particle Step 3: once the particle is completely surrounded, a vesicle pinches off Endocytosis EXOCYTOSIS EXOCYTOSIS Definition: Vesicles formed by the Golgi carry particles to the cell membrane to be removed EXOCYTOSIS Definition: Vesicles formed by the Golgi or ER carry particles to the cell membrane to be removed Step 1: large particles that must leave the cell are packaged in vesicles EXOCYTOSIS Definition: Vesicles formed by the Golgi or ER carry particles to the cell membrane to be removed Step 1: large particles that must leave the cell are packaged in vesicles EXOCYTOSIS Definition: Vesicles formed by the Golgi or ER carry particles to the cell membrane to be removed Step 1: large particles that must leave the cell are packaged in vesicles Step 2: the vesicle travels to the cell membrane and fuses with it EXOCYTOSIS Definition: Vesicles formed by the Golgi or ER carry particles to the cell membrane to be removed Step 1: large particles that must leave the cell are packaged in vesicles Step 2: the vesicle travels to the cell membrane and fuses with it EXOCYTOSIS Definition: Vesicles formed by the Golgi or ER carry particles to the cell membrane to be removed Step 1: large particles that must leave the cell are packaged in vesicles Step 2: the vesicle travels to the cell membrane and fuses with it Step 3: the cell release the particles into its environment EXOCYTOSIS Definition: Vesicles formed by the Golgi or ER carry particles to the cell membrane to be removed Step 1: large particles that must leave the cell are packaged in vesicles Step 2: the vesicle travels to the cell membrane and fuses with it Step 3: the cell release the particles into its environment Review Transportation Through a Membrane • • • • • • Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis