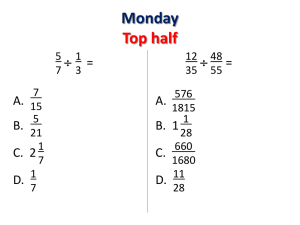
Powerpoint
advertisement

Diagnostic Laboratory Procedures Microscope Use • Objective lenses 4x, 10x, and 40x • Oil-immersion is used occasionally • A mechanical stage is necessary to view slides thoroughly Microscope Use •Viewing area = field Microscope Use • To scan a slide use 4x to focus, then move to 10x • Scan back and forth overlapping each field Microscope Use Scanning pattern Microscope Use • Debris can be closely examined under high power Sample Collection • The animal owner will most often collect the stool sample. Sample Collection • The sample should be fresh since some parasite eggs become unrecognizable as the feces ages. Sample Collection • If a fresh sample cannot be obtained, one can be refrigerated, but for no longer than 24 hours. Methods 1.Gross exam - used to observe outward characteristics of the sample. Methods 1.Gross exam - Several abnormalities can be seen with the naked eye. Methods 1.Gross exam - observe and record • color and consistency • blood and mucus • age of sample • presence of adult parasites Methods 2. Direct smear - the fastest and simplest method of diagnosing parasitism. Methods 2. Direct smear - A small amount of feces is mixed with water and applied directly to a slide. Methods 2. Direct smear -The main disadvantage of this technique is that a small sample may not contain any parasite eggs. Methods 2. Direct smear - This method also leaves debris on the slide. Methods 3. Floatation - the most commonly used procedure for diagnosing parasitism. Methods 3. Floatation - techniques using this method: - simple floatation - use of a centrifuge - Fecalyzer Methods 3. Floatation Fecalyzer - uses a solution (zinc sulfate or sodium nitrate) that has a specific gravity greater than the specific gravity of most parasite eggs Methods 4. Sedimentation - is commonly used for eggs that have a high specific gravity Methods 4. Sedimentation - The high specific gravity of these eggs makes it difficult to use floatation techniques without distorting them. Methods 4. Sedimentation - Sedimentation allows eggs to sink to the bottom. Debris • may be easily confused with parasite eggs. Common Debris: • hair • plant material • air bubbles •fat •epithelial cells •pollen grains