The Effects of Blanket Attachment on Play
advertisement

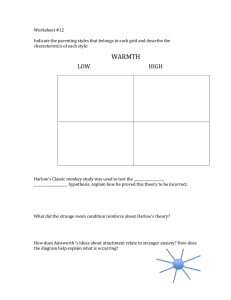
Attachment I. What are emotional attachments II. Theories of attachment A.Behaviorist approach 1.Dependency and drive reduction model 2.Operant conditioning model 3.Problems with the models B.Psychoanalytic approach 1.Freud’s theory 2.Erikson’s theory C.Cognitive-developmental approach D.Ethological approach 1.Background of the theory 2.The developmental course of attachment a. The “preattachment phase” b. The “attachment in the making phase” c. The phase of “clearcut attachment” d. The formation of a reciprocal relationship III.Measurement of attachment A.The “strange situation” B.Patterns of attachment 1.Secure 2.Insecure – avoidant 3.Insecure – resistant/ambivalent 4.Insecure - disorganized IV.Factors affecting attachment A.Maternal deprivation and institutionalization B.Quality of care-giving C.Infant characteristics Behaviorist Approach to Attachment The importance of feeding and drive reduction • Elicits positive responses • Mothers provide infants with additional comforts, such as warmth, vocalizations • All occur in single setting • Mom becomes source of reinforcement The Effects of Blanket Attachment on Play Blanket Attached Mean Duration of Play Blanket Non-Attached Mother Blanket Toy No Object Experimental Condition Behaviorist Approach to Attachment The importance of feeding and drive reduction • Elicits positive responses • Mothers provide infants with additional comforts, such as warmth, vocalizations • All occur in single setting • Mom becomes source of reinforcement Operant Conditioning model • Infants look, smile, and seek proximity because mom reciprocates with smiles, hugs • The greater number of behaviors that get reinforced by particular person, the more one is attached to that person Psychoanalytic Approach to Attachment Freudian approach • Similar to drive reduction • Become attached to person who satisfies basic biological drives (typically Mom) • Relationship with Mom then prototype for romantic relationships throughout life Erikson’s approach • 1st developmental stage: birth – 1 yr: Trust vs. mistrust • Children become attached to people who minister to needs • Importance of mother’s overall responsiveness Cognitive-Developmental Approach to Attachment Little to say about which people to whom one becomes attached • Suggests that attachment depends, in part, on level of cognitive development • Must be able to discriminate familiar persons from strangers • Must recognize that familiar persons have permanence – object permanence abilities, as discussed earlier • Thus, timing of attachment related to timing of development of cognitive ability Ethological Approach to Attachment Central feature of theory • Babies born with in-born set of behaviors • Behaviors elicit parent care, thus increase change of survival The developmental course of attachment • The preattachment phase • Behavior a matter of genetically determined reflexive responses with survival value • Promote physical contact • Attachment in the making • Orient and respond with preference towards mom • No specific attachment yet • The phase of clearcut attachment • Shows separation anxiety • Mom as a “safe haven” • Formation of a reciprocal relationship • Decrease in separation anxiety The Strange Situation Procedure Episode Persons Present Duration Description of Activity 1 Mother, baby and observer 30 sec Observer introduces mother and baby to experimental room, then leaves 2 Mother and baby 3 min Mother is nonparticipant while baby explores. If necessary, play is stimulated after 2 min. 3 Stranger, mother and baby 3 min Stranger enters, Min. 1: stranger silent; Min. 2: stranger talks with mother; Min 3: stranger approaches baby. After 3 min., mother leaves 4 Stranger and baby 3 min or less First separation episode. Stranger’s behavior is geared to that of baby 5 Mother and baby 3 min or more First reunion episode. Mother greets and comforts baby, then tries to settle baby into play. Mother then leaves, waves bye-bye 6 Baby alone 3 min or less Second separation episode 7 Stranger & baby 3 min or less Continuation of second separation. Stranger enters and gears behavior to that of baby 8 Mother and baby 3 min Second reunion episode. Mother enters, greets baby. Stranger leaves Patterns of Attachment Insecure – Avoidant • Little distress at separation • Avoids mother during reunion • About 20% of North-American infants Securely Attached Distressed during separation • Seeks out mother during reunion • About 65% of North-American infants Insecure – Ambivalent/Resistance • Distressed throughout, and during separation • Reunion a mixture of relief and anger • About 10% of North-American infants Insecure – Ambivalent/Resistance • Combination of avoidant and ambivalent/resistant • Confusion over whether to approach or avoid • During reunion may act dazed or freeze • About 5 - 10% of North-American infants