GASES,LIQUIDS & SOLIDS
advertisement
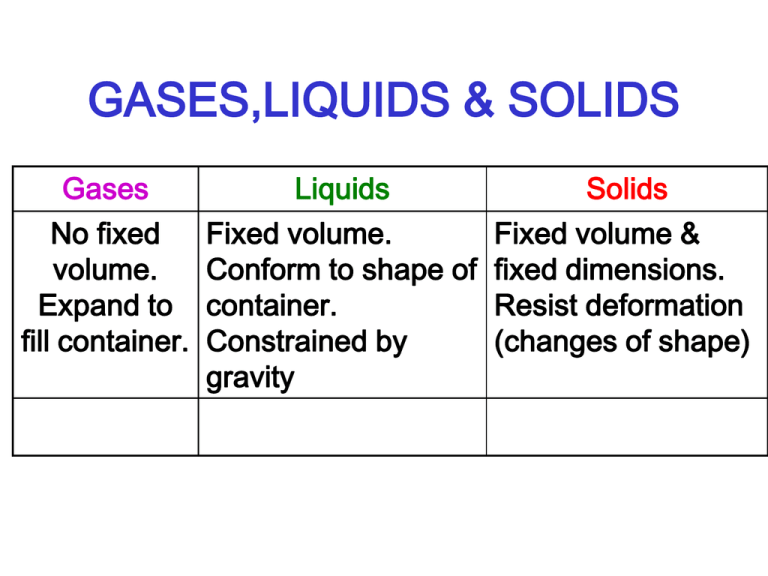
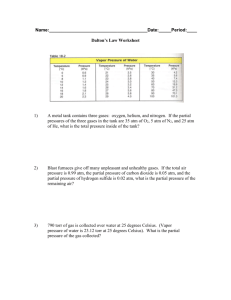
GASES,LIQUIDS & SOLIDS Gases Liquids Solids No fixed volume. Expand to fill container. Fixed volume. Conform to shape of container. Constrained by gravity Fixed volume & fixed dimensions. Resist deformation (changes of shape) COMPOSITION OF AIR: Minor Components Also, variable amounts of: H2O (0 – 7 %) CO2 (0.01 – 1 %) CO (0 – 0.000002 %) NO2 (0 - 0.000002 %) SO2 (0 - 0.0001 %) O3 (0 – 0.000007 %) COMPOSITION OF AIR: (contd.) • Greenhouse Gases: COMPOSITION OF AIR: (contd.) • Greenhouse Gases: CO2 & CH4 COMPOSITION OF AIR: (contd.) • Radon - Accumulates under houses COMPOSITION OF AIR: (contd.) • Radon - Accumulates under house • Arises from radioactive decay of traces of Actinides, typically found in Granite! NATURAL GAS • CH4 - FOUND WITH Oil deposits. • He - Up to 4 % in natural gas deposits WATER VAPOR • H2O from evaporation of water from surfaces of Lakes, Rivers, Oceans (80 % of Earth’s surface) GASES FROM HEATING SOLIDS • • • • CO2 O2 O2 NH3 CaCO3 4NaNO3 KClO4 NH4Cl CaO + CO2 Na2O + N2 + 5O2 KCl + 2O2 NH3 + HCl • Also: Gases (H2) from metals and acids, also from some metals and water (Li, Na). GAS PRESSURE • Results from gravitational force on Earth’s atmospheric gases (several miles deep). • Measure with Barometer. • P = Pressure = gdh – g = accel. due to gravity – d = density of liquid column – h = height of column PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS • • • • • • • 1 Atmosphere (atm.) = 760 mm Hg d H2O = 1.00 g cm-3 d Hg = 13.6 g cm-3 For same P (= 1 atm. = 760 mm Hg = 760 x 13.6 mm H2O = 10.336 m = 33.91 ft H2O PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS • Pressure usually meaured in: • (a) mm Hg (torr) 1 atm. – 760 mm Hg • (b) Pa (PASCALS) = N m-2 = kg m-1 s-1 • 1 Atm. = 101.325 kPa • 1 bar = 105 kPa = approx. 1 atm. • (= 0.9869 atm.) PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS • Common measure (engineering): – psi = Pounds per square inch psig= Pounds per square inch, gauge – ( add current atmospheric pressure to convert to Absolute pressure) – 1 atm. = 14.7 psi TEMPERATURE • C(elcius) vs. F(ahrenheit) • F = C x 9/5 + 32 • C = (F-32) x 5/9 • Absolute Temperature (K) • At 0K, all gases have 0 volume • K = 0C + 273.15 IDEAL GAS LAW • PV = Nrt • or P1V1 = P2 V2 n1 T1 n2 T2 AVOGADRO’S LAW • 1 L. of all gases contains the same no. of molecules at the same T & P • At STP (= 1 atmos. And 0 C), 1 mol. of any gas occupies 22.4 L Aso R= 1 atm. x 22.4 L 1 mol x 273.15K = 0.082057 L. atm.mol-1 K-1 UNIVERSAL GAS CONSTANT R = 0.082057 L. atm.mol-1 K-1 or R = 8.3145 J mol-1 K-1 GAS DENSITY & MOLAR MASS