Compound Microscope: Parts, Use, and Magnification
advertisement

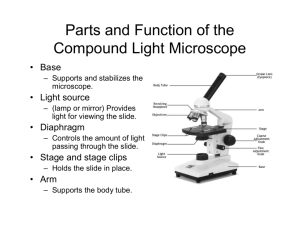
The Mi croscope Compound Microscope (lesson objectives) • Be able to identify the parts and functions of the compound microscope. • Be able to explain the procedures to making a wet mount slide. • Be able to calculate total magnification. COMPOUND MICROSCOPE • Compound = 2 lenses – Ocular Lens (10x) – Objective Lens (4x,10x,40x) Image is spun upside-down and backwards. Microscope Parts Eyepiece/Ocular Coarse Adjustment Fine Adjustment Arm Stage Clips Body Tube Nose Piece Low Power Objective High Power Objective Stage Diaphragm Base Light Functions 1. OBJECTIVE LENSES 2. EYEPIECE (Ocular) 3. DIAPHRAGM 4. STAGE 5. COARSE ADJUSTMENT 6. FINE ADJUSTMENT Using the Microscope!! HOW TO USE 1. Set the microscope to the lowest power objective. 2. coarse adjustment Lower the stage all the way using the ____________________. 3. Place the ____________ slide on the ________________. stage 4. Use the ________ coarseadjustment to bring the stage all the way up. 5. Then focus on the object using the coarse adjustment. 6. Then use the ____________ fine adjustment to focus better. 7. Find what you are looking for and place it in the center of the field of view. 8. stage by using the __________ Lower the ____________ adjustment. coarse 9. Switch to the ___________ high power objective. fine adjustment 10. Then focus, using only the _______________________. Rules 1. Always use lowest power to scan the slide for the specimen. Rules 2. Never use coarse adjustment with high power objective! Finding Total Magnification Ocular Lens X Objective Lens LP= 150x HP= 450x What is the lowest possible magnification that can be obtained using the microscope shown? 1. 2. 3. 4. 20x 200x 10x 100x Field of View • The area that can be seen through the microscope. 100x 400x • Is the field of view larger or smaller under high power? FOV • The lower the magnification, the Larger the Field of view. • The higher the magnification, the smaller the field of view. What do you notice about the amount of light when you switch from low power to high power? • There is less light. • You need to adjust the diaphragm. Field of View • Under high power: The FOV is SMALLER and DARKER! Depth of Field: the level you are focused on A Paramecium moves to different levels of depth when it swims Depth of field • Use the fine adjustment knob to get to the depth that you want to see. How to make a wet mount • 1. Place specimen on a glass slide. • 2. add a drop of water • 3.Lower glass cover slip on an angle to avoid air bubbles. • 4. examine under low power. • Note: if stain is to be used, place drop of stain on one side of slide and pull it through using a paper towel. Note: if stain is to be used, place drop of stain on one side of slide and pull it through using a paper towel. • Two common stains which are commonly used are: • METHELYNE BLUE IODINE How to Make a Wet Mount To avoid air bubbles under your slide, touch the coverslip to the drop then lower it slowly, squeezing the drop. Microscope Lab Examine the functions and magnification of your microscope. Microscope Lab A. B. C. D. E. Get to know the microsope. Wet Mount of “e”. Wet Mount of colored paper. Look at 2 hairs. 2 more slides. e The diagram represents a hydra as viewed with a compound light microscope. If the hydra moves to the right of the slide preparation, which diagram below best represents what will be viewed through the microscope? The diagram to the left represents the letter "h" as seen in the low power field of view of a compound light microscope. Which diagram below best represents the field of view if the slide is not moved and the objective is switched to high power?