White Board Review #2 - Marion County Public Schools
advertisement
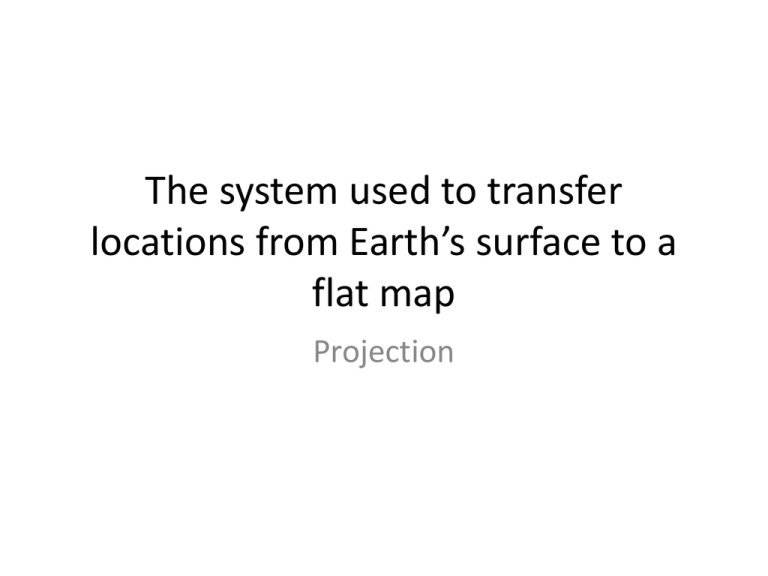
The system used to transfer locations from Earth’s surface to a flat map Projection A collection of languages related through a common ancestor that existed several thousands years ago Language branch A follower of a polytheistic religion in ancient times Pagan Belief that objects, such as plants and stones, or natural events, have a discrete spirit and conscious life Animism Another name for slash-and-burn agriculture Shifting cultivation A flooded field for growing rice sawah A market center for the exchange of services by people attracted from the surrounding area Central place The maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service range In the U.S., a central city of at least 50,000 population, the county within which the city is located, and the adjacent counties Metropolitan statistical area (MSA) A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings Burgess Concentric zones model The level of development that can be maintained in a country without depleting resources to the extent that future generations will be unable to achieve a comparable level of development Sustainable development Fuel that derives from plant material and animal waste Biomass fuel The sustainable use and management of a natural resource through consuming it at a less rapid rate than it can be replaced Conservation A resource that has a theoretically unlimited supply and is not depleted when used by humans Renewable energy Commercial agriculture characterized by the integration of different steps in the foodprocessing industry, usually through ownership by large corporations Agribusiness Harvesting twice a year from the same field Double cropping A journey to a place considered sacred for religious purposes Pilgrimage A religion that does not have a central authority but shares ideas and cooperates informally Autonomous religion Dialect spoken by some African Americans Ebonics A boundary that separates regions in which different language usages predominate Isogloss When the first Industrial Revolution happened in Britain Late 1700s When the first Agricultural Revolution happened Over 10,000 years ago (earliest crop domestication) When the Green Revolution happened? 1970s-1980s A country that is at a relatively early stage in the process of economic development LDC Eight international development goals that all members of the UN have agreed to achieve by 2015 Millennium Development Goals 1.eradicate extreme poverty and hunger, 2. achieve universal primary education, 3. Promote gender equality/empower women 4. Reduce child mortality 5. Improve maternal health 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, etc. 7. Ensure environmental sustainability 8. Global partnership for development Most countries have achieved relatively high levels of development are located above 30 degrees north latitude Wallerstein’s Core-Periphery Model Western Europe’s most important and most centrally located industrial area that produces iron and steel manufacturing because of its proximity to large coalfields Rhine-Ruhr Valley The leading industrial area in the U.S. outside of the northeast when they have the largest clothing and textile production, 2nd largest furniture production and major food-processing center Southern California Name the countries who currently still hold these colonies: 1. Greenland 2. Easter Island 3. Puerto Rico 4. Cayman Islands 5.Hong Kong 1. Denmark 2. Chile 3. U.S. 4. U.K. 5. China Where the Green Line Border exists Israel and the West Bank and Gaza Strip