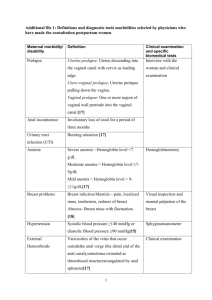
MCQs Prolapse [PPT]
advertisement
![MCQs Prolapse [PPT]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009919194_1-700829bcb6ca1de78812c42b927c23d6-768x994.png)
Which of the following regarding uterine descent is not correct? a) First degree descent implied the cervix descends below its normal Ievel on straining but does not protrude from the vulva b) First degree descent implied the cervix descends below its normal Ievel on straining and protrudes from the vulva c) Second degree descent implies the cervix reaches upto the vulva on straining d) Procidentia means whole of the uterus is prolapsed outside the vulva Answer • b Which of the following are etiologies of uterovaginal prolapse : a) b) c) d) e) f) Aging Estrogen deprivation Intrinsic collagen abnormalities Chronic increase in intraabdominal pressure Acute and chronic trauma of vaginal delivery All of above Answer • f All of the following are supports of the uterus except: a) b) c) d) e) Mackenrodt’s ligaments Uterosacral ligaments Broad ligament Pubocervical fascia Rectovaginal fascia Answer • c Following are the first level of support in DeLancy system a) b) c) d) e) Cardinal ligament Pubocervical fascia Rectovaginal fascia Pubo-urethral ligaments Perineal body Answer a Following is not a posterior vaginal wall defect a) b) c) d) Enterocele Rectocele Perineal body descent Perineal tear Answer • a Which of the following is false regarding the examination of a patient with prolapse? a) The maximal extent of prolapse is demonstrated with a standing straining examination when the bladder is empty b) Resting tone & voluntary contraction of the anal sphincters should be assessed during rectovaginal examination c) Women with prolapse and urinary incontinence should have stress testing performed with the prolapse reduction because this will mimic bladder and urethral function when the prolapse is treated d) Screening for presence of UTI or CIN is not needed at the time of examination Answer • d Which of the following is not an indication for use of pessary a) When future childbearing is intended in near future b) Refusal for operation by patient c) As a therapeutic test d) Prolapse with pregnancy e) Non healing decubitus ulcer Answer • e All of the following are complications associated with pessary except a) b) c) d) e) f) B.vaginitis, ulceration of vaginal wall Cervicitis Carcinoma of vaginal wall Impaction of pessary Reduction of prolapse Strangulation of prolapsed tissue Answer • e Following are true for management of prolapse except a) Any decision for surgical intervention should take account of how prolapse is affecting lifestyle b) Vaginal pessary can be used in elderly patients with prolapse with associated medical complications which contradict surgery c) Vaginal hysterectomy is the only treatment of prolapse in all women d) Sling surgeries are indicated in women desiring to retain reproductive function e) Assessment of SUI is must during examination of prolapse so that the same can be corrected during surgery Answer • c Managenent of 3rd degree prolapse in a 27yrs P1+0 can be all except a) b) c) d) Vaginal hysterectomy Fothergill’s surgery Sling surgery Ring pessary Answer • a