File
advertisement

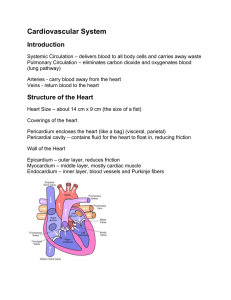
Ch 13 Notes •Name the structures composing the cardiovascular system. Heart Vessels Arteries Capillaries Veins •Identify the function of the cardiovascular system. Transport Oxygen Nutrients Waste Particularly CO2 Journal 4/28 - Sketch a frontal section view of the heart and label the following: Right atrium Aortic valvle Left atrium Pulmonary valve Right ventricle Aorta Left ventricle Vena cavae (2) Tricuspid valve Pulmonary veins Mitral (bicuspid) valve Pulmonary artery •Distinguish between the coverings of the heart... Fibrous pericardium Perietal pericardium Pericardial cavity Visceral pericardium ...and layers that compose the wall of the heart Epicardium Myocardium Endocardium •Identify and locate the major parts of the heart, and discuss the functions of each. Right atrium Aortic valvle Left atrium Pulmonary valve Right ventricle Aorta Left ventricle Vena cavae (2) Tricuspid valve Pulmonary veins Mitral (bicuspid) valve Pulmonary artery Trace the pathway of blood through the heart and the vessels of coronary circulation. Vena cava -> right atrium -> tricuspid valve -> right ventricle -> pulmonary valve -> pulmonary artery -> capillaries in the lungs -> pulmonary veins -> left atrium -> mitral (bicuspid) valve -> left ventricle -> aortic valve -> aorta -> body cells Trace the pathway of blood through the heart and the vessels of coronary circulation. Pulmonary vs Systemic Pulmonary = anything having to do with the lungs. Purpose: to oxygenate the blood and get rid of waste Systemic = the rest of the body Purpose: to carry oxygen to the rest of the body The heart’s own blood supply. The heart itself needs blood in addition to the blood that’s flowing through it for the rest of the body. Coronary arteries – branch directly from the aorta; feed the heart with oxygenated blood Coronary veins – drain unoxygenated blood into the coronary sinus. Coronary sinus – collects unoxygenated blood and pushes it back into the right atrium. •Describe the cardiac cycle... See page 567 Atrial systole – blood moves from atria to ventricles. AV valves are open. *AV valves close. “lubb” Atrial and Ventricular diastole – both are relaxed, and all valves are closed as atria refill with blood Ventricular systole – blood moves from ventricles to aorta and pulmonary trunk. Semilunar valves are open. *Semilunar valves close. “dubb” ...and the cardiac conduction system. ...and the cardiac conduction system. SA node, AV node, AV bundle and branches, and Purkinje fibers are located in the myocardium of the heart wall. Identify the parts of a normal ECG pattern and discuss the significance of this pattern. P – depolarization of atria QRS – depolarization of ventricles T – repolarization of ventricle See pg 567 Video Explain the control of the cardiac system. Heart rate is controlled in medulla oblongata in coordination with the cerebrum and hypothalamus. Factors that influence heart rate Physical activity Emotional upset – either increases or decreases Temperature changes Potassium and calcium ions. Journal 4/29 Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Start with un-oxygenated blood End with it going out to the body Compare the structures and functions of the major type of blood vessels. Together, they form a closed tube that carries blood away from the heart, to cells, and back again. Arteries – carry blood away from the heart. Arterioles – smaller branches off of the arteries. Blood is moved by blood pressure Compare the structures and functions of the major type of blood vessels. Capillaries – Transfer oxygen to the cells and moves blood to the veins. Venules – Connect to capillaries and carry blood to veins. Veins – Carry un-oxygenated blood back to the heart No blood pressure; must be “pushed” through. Valves keep blood from moving backward. Describe how substances are exchanged between blood in capillaries and the tissue fluid surrounding body cells. Oxygen and nutrients coming from the arteries diffuse into the tissue and fluids that need them based on pressure differences. Carbon dioxide and other wastes diffuse from the tissue and fluids into the blood base on pressure differences as well. Other materials are exhanged through filtration and osmosis. Explain how blood pressure is produced and controlled. Blood pressure = the force of blood against the inner walls of any blood vessels. What we refer to as “blood pressure” is really arterial pressure. Rises and falls with ventricular systole and diastole. Surge of blood that occurs during ventricular systole is a pulse. Describe the mechanisms that aid in returning venous blood to the heart. Contractions of skeletal muscles. Differences in thoracic and abdominal pressure.