Chapter 15
advertisement

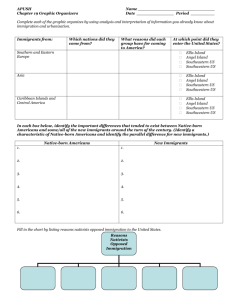
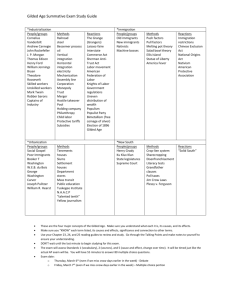
Chapter 15 Coming To America - Neil Diamond - YouTube Between 1870 and 1930 approximately 30 million immigrants came to America from all over the world. Europeans Flood into the U.S. . 1890's- 14 million-eastern and southern Europeans made up more than half of immigrants coming at that time - many were European Jews Reasons for coming: employment, few immigration restrictions, avoidance of military service, religious freedom, chance to move up social ladder How they came: most came by boat, steerage, 14 day trip, processed at Ellis island, NY (it is estimated that the ancestors of over 1/2 of all people living in the US passed through Ellis Island) -some sent back due to health problems YouTube - Immigration Ellis Island 1911 http://www.ellisisland.org/photoalbums/ell is_island_then.asp http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8RZbm eiYkJ0&feature=related Immigrant simulation A Boy's Journey -- Home Page- story of Seymour Rechtzeit Welcome to Immigration- interactive tour of Ellis Island Tenement Museum | From Ellis Island to Orchard Street with Victoria Confino Ethnic neighborhoods Most settled in cities among their same ethnic group, Most adjusted well, learned English, adapted to American culture English language classes at Ford Motor Co. Ellis island story Asian Immigrants Why did they come: severe unemployment, poverty, famine in China, the discovery of gold in California, the Taiping Rebellion in China, and demand for railroad workers Arrived in the West- San Francisco, Angel Island many waited months for permission to enter Worked as laborers, servants, skilled tradesmen, and merchants, laundries Japanese immigrants began to arrive due to industrialization in Japan Nativisim Italian immigrants Arguments for Immigrants Arguments against Immigrants Nativism Anti immigration feelings were focused on Asians, Jews, eastern Europeans, and Catholics Widespread hatred resulted in racial violence APA and Workingman’s Party of California A.P.A. Poem American Protective Association Come ye sons of Uncle Sam, Come join the gallant band, Come unite with us to fight our country's foe. For our God is with the right, We will conquer by His might, And the slick and wily Jesuit must go. Noble men are in our ranks -We are not a band of cranks -We are not a lot of bigots or of fools. But, ye Roman Catholic hordes, We will buckle on our swords, If you dare to meddle with our public schools. Dare to be an A.P.A., Dare to stand alone. Dare to work for Freedom's cause, Dare to make it known. Immigration Immigration numbers Impact of Anti-immigration Federal laws passed to curb the flow of people – 1882- banned convicts, paupers, and the mentally ill– also .50 tax on each head – Chinese Exclusion Act- law barred Chinese immigration for 10 years, and prevented those here from gaining citizenship rights – Chinese immigrants protested the law but it was enforced and made permanent in 1902 Not until 1943 was it repealed. Comparing Percentages of Immigrants Section 2 Objectives Discuss how political machines helped city dwellers in the late 1880’s. Describe what it was like to live in New York city during the 1880’s. People begin to move to the cities. What would motivate you to move to the cities? Impact on Cities -Housing and transportation needs changed due to influx of people mass transit was developed to move large numbers horse car- electric trolley, subways (elevated or underground railroads) -price of land went up so people began to build up--Skyscrapers---Louis Sullivan contributed to the design of these buildings Separation by Class wealthy- lived in cities- built elaborate homes middle class- tended to live away from the cities, Drs., lawyers, engineers, teachers working class- largest groupcity tenements- dark, crowded multi-family apartments Urban Problems Urban Politics – Rise of Political Machines-informal political group designed to gain and keep power Came about because cities were growing too fast to keep up with the influx of people, services etc. New city dwellers needed housing, food, heat, job etc.. They went to the party bosses for these items and the boss gave it to them in exchange for votes Tammany Hall- NY Democratic political machine William “Boss “Tweed (1860’s – 70’s) Bosses controlled city services, police dept. , Tweed- 3rd largest landowner in NY, House of Rep. Convicted of stealing $40 million through graft Party Bosses “ for dishonest graft one worked solely for one's own interests, while for honest graft one pursued the interests of one's party, one's state, and one's personal interests all together. “ George Plunkitt- New York party boss (pg 473) read excerpt Thomas Nast Political cartoonist Through his efforts Tweed was brought down and corruption was highlighted. Check for Understanding Discuss how political machines helped city dwellers in the late 1880’s. Describe what it was like to live in New York city during the 1880’s. Section 3 The Gilded Age Gilded Age (1870-1900) Time period characterized by new and amazing marvels – Skyscrapers, big cities, new inventions, electric lights, mansions, industrialization But what was underneath? – covered with gold on the outside but cheaper materials are underneath Corruption, poverty, crime, disparity b/w rich and poor Theory or movement Social Darwinism Laissez-Faire Gospel of Wealth Individualism Main Idea- Group Work Pick one of the terms and create a presentation to explain it to the class. – Presentations can be skits, songs, pictures, poems – Presentations should include the group and explain the main idea behind the philosophy. Individualism Strong American belief- no matter where you start you can rise up in society by working hard, and using your talents. Anyone can be successful. Horatio Alger- author of “rags to riches” stories Popular Culture Industrialization improved standard of living for many- had more money and leisure time Saloons- functioned as community centers, political centers, newspapers, baths, free toilets, water for horses, free lunch Other Amusements Amusement Parks- Coney Island Baseball stadiums- 1st modern World Series played in 1903 Boxing matches Football- mostly upper classes- started in private colleges Vaudeville-variety shows, singing, magicians, dog acts etc… YouTube - Who's on first? Abbot and Costello- vaudeville act Music Scott Joplin- “King of Ragtime- name of Ragtime” music that featured syncopated rhythms One of the most patterned after successful ragtime African American composers music, banjo, piano Maple Leaf Rag Played by Scott Joplin - YouTube Check for Understanding Why would Twain describe this era as the "gilded" age rather than the "golden" age? Imagine you are a Newspaper editor in the late 1880’s. Write an editorial in which you support or oppose the philosophy of Social Darwinism. Include reasons to support your position. Section 4- Rebirth of Reform Social Criticism Society problems needed to be fixed. But How? Many argued government should get more involved. Others said citizens needed to take care of those in need. Many argued for both to get more involved. Henry George Book, Progress and Poverty,1879 Argued that as more wealth was produced we were actually creating more poor too. Basic argument flawed- but it made people think about Laissez-faire and Social Darwinism Lester Frank Ward Book, Dynamic Sociology Argued for Reform Darwinism- humans are not like animals- we can make plans and think about the future, we succeed not due to competition but due to our ability to cooperate Competition was wasteful- govt. should regulate everything Edward Bellamy Book, Looking Backward 1888 Argued for socialism- young man falls asleep in 1887- wakes in 2000, US has become a perfect society, govt. Owns everything and shares the wealth equally with all of the citizens. All of these ideas helped bring about reform How to Help the Urban Poor Many churches began to get involved in efforts to improve their communities – Building gyms, providing daycare, medical care, social programs Salvation Army- 1878- offered practical and religious counseling to the poor YMCA- bible study, prayer meetings, citizenship training, low costs rooms, pools, gyms, libraries Settlement Houses Many believed it was their Christian duty to help those less fortunate. Jane Addams- Hull House, Chicago 1889 – medical care, recreation programs, English classes, hot lunches for factory workers Hull House Education Due to industrialization many jobs now required education and training. The demand for educated workers led to an increased emphasis on schools 1870- 6,500,000 1900- 17,300,000 Elementary and high schools were opened Many colleges opened too: – Land grant colleges– Private women’s colleges- Vassar, Wellesley, Smith Libraries Free public libraries opened to the masses Carnegie supported this effort by giving millions of dollars to library construction across the country Americanization Schools were where immigrant children learned about America, language, culture, history, work ethic and discipline Schools more prevalent in urban area Many African American did not have the same opportunity to attend schools Booker T. WashingtonTuskegee Institute 1881 Check for Understanding What problems had been created by changes in society? What programs did reformers start to try and solve societies problems? Changing roles and attitudes of women