Organelles PPT
advertisement

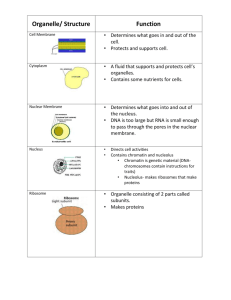
Cells and Their Amazing Organelles Cells can be … Prokaryotic no membrane bound organelles Eukaryotic membrane bound organelles Eukaryotic cells include … Plant Cell Animal Cell Why are cells so small? • As cell size increases the volume increases much faster than the surface area. • Cells obtain nutrients, gain information and rid waste through their plasma membrane. Ratio of Surface Area:Volume As cell size increases, it’s ability to exchange materials with its environment becomes limited by the amount of membrane area that is available for exchange. Cell Membrane • Outer boundary of all cells . • Described as being a fluid mosaic. • Semi-permeable: controls what enters and leaves the cell. Fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure How molecules cross the plasma membrane Vesicles • Membranous structures that derive from other membranous cellular parts. • Carry substances from one part of the cell to another. • Bind to the correct region if protein receptors are compatible. Cytoplasm • Consists of the cytosol (liquid) and all of the organelles within cell . The Nucleus • Controls most activities in the cell by controlling protein production. • Contains all genetic information in the form of DNA. • Nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope - a double membrane • The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores that control entry and exit of materials The Nucleolus • A darkened region where ribosomes (ribosomal RNA) is synthesized Ribosomes • Composed of a large and small sub-unit of RNA • Make proteins in the cell. • May be free-floating in cytoplasm or attached to endoplasmic reticulum. Free Floating Ribosomes Ribosomes on ER Endoplasmic Reticulum • Series of folded membranes that form sacs or tubes. • Rough ER has ribosomes attached. • Smooth ER doesn’t have ribosomes. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • The site for: - synthesis of steroids and other lipids, - Ca++ storage in muscle cells, - detoxification of drugs, toxins, alcohol (especially in liver cells) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • The site where proteins are made to be used inside or outside of cell. • Once proteins are made they are packaged into vesicles to be “shipped” to Golgi apparatus. Golgi Apparatus • Saclike membranes used for storing, modifying and packaging of proteins and other chemicals. Endomembrane System Proteins made by Rough ER are shipped to Golgi Apparatus in vesicles where they are modified. From here they move to the cell membrane in secretory vesicles which release them externally. nucleus nucleolus rough ER ribosomes smooth ER vesicle lipids Golgi apparatus vesicle cell membrane Lysosomes • Formed in Golgi bodies • Contain hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes to break down unwanted particles • Help white blood cells to destroy bacteria Mitochondria • Produce ATP through cellular respiration • Mitochondria replicate by binary fission similar to prokaryotic cell division Mitochondrial Structure - have double membrane structure - inner membrane folded into inward projections called cristae - two spaces within the mitochondrion - the matrix and the intermembrane space Chloroplasts • sites of photosynthesis in nearly all plants and some protists. • trap light energy and convert it into chemical energy Chloroplast Structure - have double membrane structure -Within the stroma (fluid) are a series of stacks of flattened -membranous structures called thylakoids (stacks of these are called grana) Cytoskeleton • Composed of proteins that maintain the cell’s structure, transport materials, and position and move organelles. • 3 cytoskeletal components: microtubules actin filaments intermediate filaments Actin Filaments • involved in cellular and organelle movement. • smallest components of the cytoskeleton. • “Motor” molecules Intermediate Filaments • involved in anchoring organelles in place and •holding cells together . Microtubules - hollow tubes made of proteins called tubulin dimers. -These are responsible for cell movement by changing in length by adding/taking away tubulin dimers polymerization/ depolymerization -Work with actin in the movement of organelles. - These are the largest components of the cytoskeleton. Cellular Work - Microtubules work with actin (and other motor molecules) in the movement of organelles and other cellular structures. - These are the largest components of the cytoskeleton. Cilia/Flagella Movement • A flagellum has pairs of microtubules in a 9+2 pattern each pair of tubules has short arms of dynein (a motor molecule) that pulls on neighboring tubules causing the structure to twist throughout. Back to Plant Cells Contain: • chloroplasts • A cell wall • A large central vacuole • No centrioles Check Out … www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model/htm