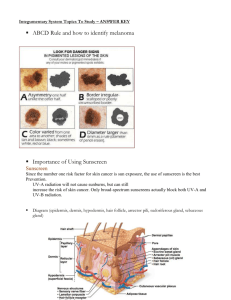
The Integumentary System * Epidermis/Dermis
advertisement

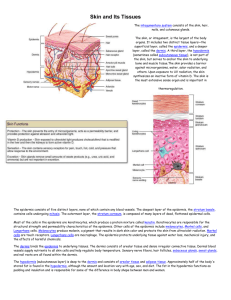
The Integumentary System – Epidermis/Dermis Human Anatomy & Physiology Integumentary System O The epidermis is a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium consisting of four distinct cell types and five distinct layers. It thickness varies over most of the body. O Its surface layer, consisting of dead cells, is rich in keratin, a protein which renders it dry and more or less waterproof, thus resisting surface evaporation and preventing excessive water loss. It also serves as a protective barrier against ultra-violet light, bacteria, many chemicals and abrasion. Integumentary System – Epidermis O The epidermal cells are: O - 1 - the keratinocytes: O 2 - the Merkel cells: sensory receptors (touch). They associate with a disc-like sensory nerve ending to form the Merkel disc. Integumentary System – Epidermis O 3 - the melanocytes: synthesize the melanin pigments which protect the skin against ultraviolet damage. O 4 - the Langerhans cells: macrophages used in the defense against microorganisms. Epidermis O The epidermis consists of several layers of cells. From the deepest to the most superficial we have: “Basic Skin Gets Lots of Care” Epidermis O 1 - the stratum basale (or stratum germinativum): is the deepest epidermal layer. It consists of one row of cuboidal to columnar shaped cells. Those cells are mostly stem cells that divide rapidly to produce new keratinocytes which push up toward the surface and become part of the more superficial layers O 10 to 25% of cells found here are melanocytes O Melanocytes that synthesize the pigment melanin. Epidermis O 2 - the stratum spinosum: is 8-10 layers thick. O Stratum basale and stratum spinosum are adjacent to the dermis and thus, contain the only epidermal cells that receive adequate nourishment (by diffusion of nutrients from the dermis). Epidermis O 3 - the stratum granulosum: here the keratinization process begins and the cells begin to die. O 4 - the stratum lucidum: is only found in thickened areas of the epidermis such as the sole of the feet. O 5 - the stratum corneum: is the outermost layer composed of dead, flat, keratinized cells Integumentary System Dermis O The dermis consists of two layers: O 1 - the Papillary layer - is the outer layer closest to the epidermis O Its superior region contains fingerlike projections called dermal papillae O Dermal papillae contain capillaries, Meissner corpuscles (pain and touch receptors: make us feel light touching) Integumentary System Dermis O 2 - the Reticular layer is the deeper layer and the thickest layer. It is made of dense connective tissue O The collagen fibers in the reticular region provides the skin with strength and extensibility O and elastic fibers provide its elasticity O The reticular layer is richly supplied with blood vessels and nerves, and contains sensory endings for touch (Pacinian corpuscle for sensing deep pressure Integumentary System Hypodermis O The Hypodermis (= subcutaneous tissue = superficial fascia) is NOT part of the skin. It consists mainly of adipose tissue plus some areolar tissue. "Beer belly" in man and thick thights and buttocks in female are due to too much fat stored in the hypodermis of these regions of the body. Integumentary System Hypodermis O Hypodermis shares the skin protective functions: it stores fat and thus helps prevent heat loss and acts as a shock absorber; it anchors the skin to the underlying structures allowing the skin to slide almost freely over them. This feature ensure that blows just glance of the body without injuring the tissues below.