The Articles of Confederations
advertisement

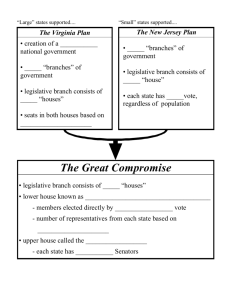
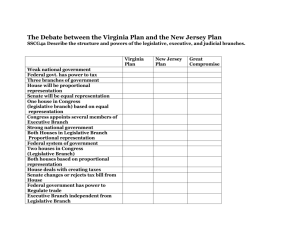
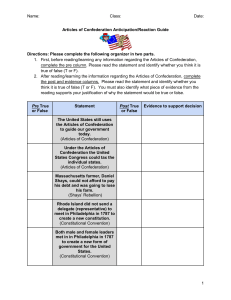
The Articles of Confederation and the Constitutional Convention The First Laws of the United States • Immediately following the Declaration of Independence, several states started chartering their own new laws and documents • Chiefly among these were two documents: 1. The Virginia Declaration of Rights (written by George Mason), which reiterated that basic human rights should not be violated by government 2. The Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom (written by Thomas Jefferson), which said that the government could not support one specific church or Christian sect Background • Provided for a weak national government • Gave Congress no power to tax or regulate commerce among the states • Provided for no common currency • Gave each state one vote regardless of size • Provided for no executive or judicial branch Why would American leaders agree on this limited government? Outline of the Articles • After the Revolution, the economy of the newly formed United States struggled • Poor farmers in Massachusetts eventually formed a rebellion to overthrow the national government • The rebellion was quickly put down, but it drew national attention to the fact that something needed to be done to fix the problems of the Articles of Confederation • Representatives from every state met in Philadelphia for the Constitutional Convention in 1787 in order to make changes Problems • The Virginia Plan – drafted by James Madison • This plan called for a bicameral legislative (two houses) branch • Representation in both houses would be determined by the size of the state – favored larger states • Also called for a national government with three branches • The New Jersey Plan – drafted by William Paterson • Opposed the Virginia Plan • Called for a unicameral legislative (one house) branch • Representation in the house would be equal, one vote per state – favored smaller states Plans to fix the Articles • Essentially combined both the Virginia and New Jersey Plans • Created two legislative houses: The House of Representatives would be based on population (favored large states) and the Senate would have two representatives from each state (favored small states) • The Three-Fifths Compromise addressed the population of slaves in the states, stating that each slave would count as 3/5 of a person in regards to population The Great Compromise