lawyers

MERCANTILISM AND THE
CHANGING COLONIAL
CULTURE
Mercantilism
National power and prestige tied to wealth in Europe
Byproduct of imperialism
Creating colonies = Imperialism = Empire
Imperial nations control all commerce of their colonies
Commerce = business, trade, etc.
Colonies become necessary for economic growth
Provided cheap labor & resources and bought goods from Europe (mercantilism)
Brought wealth to colonies but also generated opposition because of restricted freedoms
Changing Culture
Mercantilism solidified the creation of an American
Aristocracy due to trade with England
North businessmen; ship builders
South plantation owners
Increased trade meant increased immigration
As immigration increased the citizens and culture became less and less English
Patriarchal Society
Men dominated all aspects of society in most colonies
Covertures – All of a woman’s possessions belonged to her husband
No inheritance rights
Patriarchal = Male
Matriarchal = Female
Birth of American Dream
Chance at social mobility for colonists
Headright System – 50-100 acres of land for immigrants
Indentured servants – Poor Europeans who volunteered to be a slave for 5-7 years
“Apprenticeship” or chance to own land
Most died of disease
By 1700 90% of 100,000 colonists in the
Chesapeake were indentured servants
55% of adult males could vote, higher than Europe
Mid-Atlantic Colonies: NY, PA, MD, DE, NJ
“Best Poor Man’s Country”
Increased Diversity; Irish & Germans after 1720
German “redemptioners” – indentured servants paid for sea voyage
New immigrants lived on the frontier
Violent life, heavy drinking
Hated Indians
Bacon’s Rebellion, 1676 (VA)
Poor frontier farms were being attacked, but Gov. did not respond against natives
Revealed a growing divide in colonies over class and if the govt. cared about all citizens or just rich
Young vs. Old, Rich vs. Poor, Coast vs. Frontier
Rebels sought to destroy all Indians left in VA
Burned the city of Jamestown to the ground
Formed a new House of Burgesses
Indentured servants, both black and white joined the rebellion, which terrified ruling elite
Led to future laws to encourage racial division
Discussion Questions
What is mercantilism? How did it encourage Britain’s fight for political and economic dominance over the New World?
What is the significance of Bacon’s Rebellion? How does it signify a greater problem in the relations of the socioeconomic classes in America?
Compare and contrast the roles of religion and economics in the early history of the New England colonies.
SLAVERY AND THE COLONIES
Labor Shortages
Native Americans got sick easily and able to run away easier
Indentured Servants problematic since they weren’t permanent
Africans - More resilient to European disease, and less likely to run away
1 st African slaves in VA 1619 as Indentured
Servants
Dutch
Slaves majority on sugar plantations in the
Caribbean by the 1650s
Outnumbered whites 4 to 1 by1713
Carolina
As the Caribbean population swelled and land dwindled many Europeans moved North with their slaves
Georgia and South Carolina economies focused on rice
Cash Crop
Rice harvesting required slave labor to be profitable
Slave majority by 1710
Carolina eventually divides over slavery
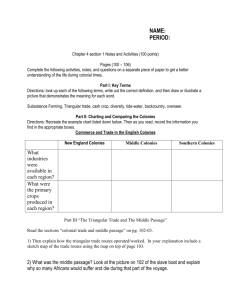
Triangular Trade
Colonial products sold in Europe
Money from Europe used to buy slaves in Africa
Slaves were traded for products in colonies
Middle Passage – Horrendous trip across the
Atlantic for slaves. “Amistad”
African slave trade reached its peak between
1730 and 1775
Life as a Slave
Task system – allowed to work for themselves after finishing their tasks, extra money
Gang system – worked until told otherwise, rule by fear, less freedom
Gang system became norm as workers produced more
Task system and increased freedom used to bribe slaves into supervisor positions
Stono Rebellion 9-9-1739
Was a Slave rebellion in South Carolina
Cato's Conspiracy or Cato's Rebellion
80 slaves rebelled and roughly 45 whites and 45 slaves were killed
In response SC legislature passed
Negro Act of 1740
Restricted slave assembly, education and movement.
Enacted a 10-year moratorium against importing
African slaves
Many rebel slaves were literate, Catholics from the
Congo
Established penalties against slaveholders' harsh treatment of slaves.
Required legislative approval for manumissions, which was previously handled by slaveholders
Setting slaves free
Discussion Questions
How did the economies of the southern colonies differ from those of the northern colonies, in the 1700s?
BUILDING THE ENGLISH
EMPIRE
English Control
First Navigation Act, 1651
Balance of trade favored England
Rules for English ports
Can only trade with English Ships
Navigation Act of 1660
All colonial trade only on English ships
Only certain goods could be bought from certain
English companies or colonies
Monopolies
Staple Act of 1663
Regulated goods going to colonies
Plantation Duty Act of 1673 – Trade only with
England
Navigation Acts forced the Dutch out and made
England the Atlantic power
Building an Empire
Lords of Trade and Plantation1675
Reinforced Navigation Acts and worked for total control of colonies
Crown sought to control governors and upper legislature houses
Elected by Colonists
Dominion of New England 1686 - 1689
England sought to combine NY, NH, MA, ME, CT into
1 colony
Increase tax revenue and control
Sir Edmond Andros Governor and Francis Nicholson
Lieutenant Governor
Both very unpopular
Failure to pay taxes resulted in loss of voting rights
Leisler’s Rebellion
NY militiamen rebelled against the Dominion of New
England in 1689 at Fort James
Lt. Gov. Nicholson
Issue of taxes and perceived Catholic attempts to control NY
Militia Captain Jacob Leisler given control of Fort who agrees to hold until King names new Governor
Leisler turns over fort to new governor in 1691
Leisler put on trial for treason and executed
Leisler becomes martyr to those fearing British control
Leisler posthumously pardoned by King
Completion of the Empire
Royal governments became the norm
Navigation Act, 1696
English system of vice admiralty courts brought to colonies
No jury, 1 judge; handled mostly business cases
Judge hired & paid by English King
Board of Trade established, 1696
System lasts until and fuels the American Revolution
Importance of Newspapers
Colonists relied on newspapers to learn about world affairs
Editors tended to support the needs of the colonies over Europe
John Peter Zenger criticized New York’s royal governor William Cosby
Seditious Libel – Crime for criticizing royal officials
Cosby had Zenger arrested and put on trial
Cosby appointed two royal judges and had
Zenger’s lawyers disbarred
Benjamin Franklin talked Andrew Hamilton into taking the case
Despite the judges telling the jury to ignore
Hamilton’s “lies” the jury found Zenger not guilty
Freedom of Speech
Colonial “Enlightenment”
Newspapers spread Enlightenment values through the colonies
Voltaire = Free Speech
Thomas Hobbes people give up some freedoms to govt. to create order
Social Contract Theory
John Locke if govt. fails in their duties then the people should form a new one
Democracy
Suffrage was more common in colonies than England
Most colonies, towns had elected assemblies
Clashes among colonial and royal leaders were common
Statutes = Laws
Duties = Taxes