Cornell Notes: Ch 14 Section 2 Part 1 THE AXIS

10.8 Students analyze the causes and consequences of WWII.
1. Warm Up Week
11
2. Cornell Notes:
Ch 14 Section 2
Part 1: The Axis
Advances (pg
12)
3. Q/S for C-Notes
4. Wrap Up
Questions and
Summary for C
Notes
Turn in your Ticket out the door from
Tues if you have not.
World Leader
Project is Due 4/14
(Monday)
Last Day to turn in
Extra Credit is
TOMORROW!
Eagles: Help your
Eaglets!!
Next Slide
10.8 Students analyze the causes and consequences of WWII.
1. Warm Up Week
11
2. Cornell Notes: Ch
14 Section 1: The
Axis Advances
3. Q/S for C-Notes
4. Wrap Up: Due
Today
Turn In Extra Credit
Questions and
Summary for C Notes
Turn in your Ticket out the door from Tues if you have not.
World Leader Project is Due 4/14 (Monday)
Eagles: Help your
Eaglets!!
Next Slide
Warm-Up
Who usually wins a war? Why? Explain your answer.
65 words minimum, use complete sentences
EQ: Which regions were attacked and occupied by the Axis powers and what was life like under their occupation?
Today’s Standard
10.8 Students analyze the causes and consequences of World War II.
3. Identify and locate the Allied and Axis powers on a map and discuss the major turning points of the war, the principal theaters of conflict, key strategic decisions, and the resulting war conferences and political resolutions, with emphasis on the importance of geographic factors.
Today’s Objectives
Identify and discuss the immediate causes of World War II by taking
Cornell notes and class discussion.
Identify the main theaters of conflict in
WWII and explain the significance of each area by taking Cornell notes and participating in class discussion.
Axis and Allies
Germany
Adolf Hitler
Great Britain -
Winston Churchill
Italy
Benito Mussolini
France
Charles de Gaulle
Japan
Emperor Hirohito
Prime Minister Tojo
Soviet Union
(USSR)
Joseph Stalin
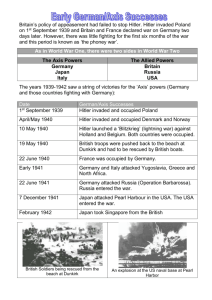
Blitzkrieg
(lightening
War ) invasion of Poland –
Sept. 1, 1939.
Germany Sparks New
European War
Germany Sparks New
European War
Sept. 3, Britain
& France declare war
“Phony War” –
7 month calm
Germany invades
Denmark &
Norway in April
1940; both surrender
One People,
One Empire,
One Leader!
Germany sweeps through Holland,
Belgium, &
Luxembourg
France invaded - May
1940
Allied troops escape from Dunkirk
Italy joins Germany & declares war on France
& Britain - June 10
France surrenders -
June 22
The Battle for France
Summer 1940 – May
10, 1941
Britain stands alone against
Nazis
RAF’s 2,900 planes to
Nazis 4,500
The Battle of Britain:
Sept. cities are bombed
(London)
Britain’s advantages: radar &
Enigma
Hitler calls off attacks
Allies learn:
Hitler’s advances could be blocked
The Battle of Britain
Germany &
Italy attack
N. Africa
They want
Oil & Egypt
(British)
Mediterranean Fighting
1941-1942
Erwin Rommel the “desert fox” led
German forces.
Pushed British back across the desert to
Cairo.
Mediterranean Fighting
Hitler takes
Balkans in April
1941 –
Yugoslavia
& Greece
The Eastern Front
The Eastern Front
10-year nonaggression pact with Stalin (U.S.S.R.) –
Aug. 23, 1939
Hitler invades
U.S.S.R. –
June 1941
Hitler penetrates
500 miles while Soviets
“slash & burn”
The Eastern Front
Leningrad
& Moscow repel Nazis
1 million
Russians die
500,000
German soldiers lost
The Eastern Front
Wrap Up
Who usually wins a war? Why? Explain your answer.
use complete sentences