8.3
advertisement

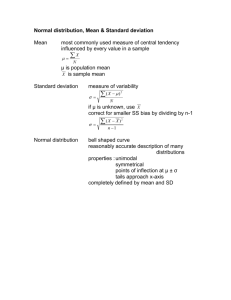
Section 8.3 You will need the equations from section 8.2 with the following… For this section we add two equations (that are very similar to one another): First, the definition formula for the variance…the equation is: 2 = ∑((X-)2 * P(X) ) Which means that you subtract the mean from each value of X, and then square that, and then that multiple each of the X’s in the probability distribution by its probability, and then add them up…giving you the variance. Second, the computing formula for the variance…the equation is: 2 = E(X2) - 2 Which means that you take the mean and square it, and then subtract that from the expected value of X-squared…giving you the variance. The standard deviation (which is ultimately what you really want to know is simply the square root of the variance (no matter how you get it). If you do not like equations, each will be done in a table as well… Problem #55 µ = 2*0.6 + 3*0.4 = 2.4 variance by definition formula: 2 = (2-2.4)2*0.6 + (3-2.4)2*0.4 = 0.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.24) = 0.4899 variance by computing formula: E(x2) = 22*0.6 + 32*0.4 = 6 2 = 6 - (2.4)2 = 0.24 (standard deviation) OR = sqrt(0.24) = 0.4899 variance by computing formula: x*P(x) x 2*0.6 = 1.2 2 3*0.4 = 1.2 3 1.2+1.2 = 2.4 P(x) 0.6 0.4 v2 4 9 v2*P(v) 4*0.6 = 2.4 9*0.4 = 3.6 2.4+3.6 = 6 (v-µ)2 0.16 0.36 (v-µ)2*P(v) 0.16*0.6 = 0.096 0.36*0.4 = 0.144 0.096+0.144 = 0.24 (variance) 2 = 6 - (2.4)2 = 0.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.24) = 0.4899 OR variance by computing formula: x*P(x) x P(x) 2*0.6 = 1.2 3*0.4 = 1.2 1.2+1.2 = 2.4 2 3 0.6 0.4 v-µ 2-2.4 = -0.4 3-2.4 = 0.6 (variance) 2 = 0.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.24) = 0.4899 Problem #56 µ = 1*0.3 + 2*0.4 + 3*0.3 = 2 variance by definition formula: 2 = (1-2)2*0.3 + (2-2)2*0.4 + (3-2)2*0.3 = 0.6 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.6) = 0.7746 variance by computing formula: E(y2) = 12*0.3 + 22*0.4 + 32*0.3 = 4.6 2 = 4.6 - (2)2 = 0.6 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.6) = 0.7746 OR variance by computing formula: y*P(y) y 1*0.3 = 0.3 1 2*0.4 = 0.8 2 3*0.3 = 0.9 3 0.3+0.8+0.9 = 2 P(y) 0.3 0.4 0.3 y2 1 4 9 y2*P(y) 1*0.3 = 0.3 4*0.4 = 1.6 9*0.3 = 2.7 0.3+1.6+2.7 = 4.6 2 = 4.6 - (2)2 = 0.6 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.6) = 0.7746 OR variance by computing formula: y*P(y) y P(y) 1*0.3 = 0.3 2*0.4 = 0.8 3*0.3 = 0.9 0.3+0.8+0.9 = 2 (variance) 2 1 2 3 0.3 0.4 0.3 y-µ 1-2 = -1 2-2 = 0 3-2 = 1 (y-µ)2 1 0 1 (y-µ)2*P(y) 1*0.3 = 0.3 0*0.4 = 0 1*0.3 = 0.3 0.3+0+0.3 = 0.6 = 0.6 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.24) = 0.7746 Problem #57 µ = 3*0.1 + 5*0.5 + 6*0.4 = 5.2 variance by definition formula: 2 = (3-5.2)2*0.1 + (5-5.2)2*0.5 + (6-5.2)2*0.4 = 0.76 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.76) = 0.8718 variance by computing formula: E(z2) = 32*0.1 + 52*0.5 + 62*0.4 = 27.8 2 = 27.8 - (5.2)2 = 0.76 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.76) = 0.8718 OR variance by computing formula: z*P(z) z 3*0.1 = 0.3 3 5*0.5 = 2.5 5 6*0.4 = 2.4 6 0.3+2.5+2.4 = 5.2 P(z) 0.1 0.5 0.4 2 = 27.8 - (5.2)2 = 0.76 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.76) = 0.8718 OR z2 9 25 36 z2*P(z) 9*0.1 = 0.9 25*0.5 = 12.5 36*0.4 = 14.4 0.9+12.5+14.4= 27.8 variance by computing formula: z*P(z) z P(z) 3*0.1 = 0.3 5*0.5 = 2.5 6*0.4 = 2.4 0.3+2.5+2.4 = 5.2 3 5 6 0.1 0.5 0.4 z-µ 3-5.2 = -2.2 5-5.2 = -0.2 6-5.2 = 0.8 (z-µ)2 4.84 0.04 0.64 (z-µ)2*P(z) 4.84*0.1 = 0.484 0.04*0.5 = 0.02 0.64*0.4 = 0.256 0.484+0.02+0.256 = 0.76 w2 0 1 w2*P(w) 0*0.4 = 0 1*0.6 = 0.6 0+0.6 = 0.6 (variance) 2 = 0.76 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.24) = 0.8718 Problem #58 µ = 0*0.4 + 1*0.6 = 0.6 variance by definition formula: 2 = (0-0.6)2*0.4 + (1-0.6)2*0.6 = 0.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.24) = 0.4899 variance by computing formula: E(w2) = 02*0.4 + 12*0.6 = 0.6 2 = 0.6 - (0.6)2 = 0.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.24) = 0.4899 OR variance by computing formula: w*P(w) w 0*0.4 = 0 0 1*0.6 = 0.6 1 0+0.6 = 0.6 (variance) 2 P(w) 0.4 0.6 = 0.6 - (0.6)2 = 0.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(0.24) = 0.4899 OR variance by computing formula: w*P(w) w P(w) 0*0.4 = 0 1*0.6 = 0.6 0+0.6 = 0.6 0 1 0.4 0.6 w-µ 0-0.6 = -0.6 1-0.6 = 0.4 (w-µ)2 0.36 0.16 (w-µ)2*P(w) 0.36*0.4 = 0.144 0.16*0.6 = 0.196 0.144+0.096 = 0.24 y2 4 4 y2*P(y) 4*0.6 = 2.4 4*0.4 = 1.6 2.4+1.6 = 4 (y-µ)2 2.56 5.76 (y-µ)2*P(y) 2.56*0.6 = 1.536 5.76*0.4 = 2.304 1.536+2.304 = 3.84 (variance) 2 = 0.24 (standard deviation) 2 = sqrt(0.24) = 0.4899 Problem #59 µ = -2*0.6 + 2*0.4 = -0.4 variance by definition formula: 2 = (-2-(-0.4))2*0.6 + (2-(-0.4))2*0.4 = 3.84 (standard deviation) = sqrt(3.84) = 1.9596 variance by computing formula: E(y2) = (-2)2*0.6 + 22*0.4 = 4 2 = 4 - (-0.4)2 = 3.84 (standard deviation) = sqrt(3.84) = 1.9596 OR variance by computing formula: y*P(y) y -2*0.6 = -1.2 -2 2*0.4 = 0.8 2 -1.2+0.8 = -0.4 P(y) 0.6 0.4 (variance) 2 = 4 - (-0.4)2 = 3.84 (standard deviation) = sqrt(3.84) = 1.9596 OR variance by computing formula: y*P(y) y P(y) -2*0.6 = -1.2 2*0.4 = 0.8 -1.2+0.8 = -0.4 -2 2 0.6 0.4 y-µ -2-(-0.4) = -1.6 2-(-0.4) = 2.4 (variance) 2 = 3.84 (standard deviation) = sqrt(3.84) = 1.9596 Problem #60 µ = -2*0.5 + 2*0.5 = 0 variance by definition formula: 2 = (-2-0)2*0.5 + (2-0)2*0.5 = 4 (standard deviation) = sqrt(4) = 2 variance by computing formula: E(y2) = (-2)2*0.5 + 22*0.5 = 4 2 = 4 - 02 = 4 (standard deviation) = sqrt(4) = 2 OR variance by computing formula: y*P(y) y -2*0.5 = -1 -2 2*0.5 = 1 2 -1+1 = 0 P(y) 0.5 0.5 y2 4 4 y2*P(y) 4*0.5 = 2 4*0.5 = 2 2+2 = 4 (y-µ)2 4 4 (y-µ)2*P(y) 4*0.5 = 2 4*0.5 = 2 2+2 = 4 (variance) 2 = 4 - 02 = 4 (standard deviation) = sqrt(4) = 2 OR variance by computing formula: y*P(y) y P(y) -2*0.5 = -1 2*0.5 = 1 -1+1 = 0 (variance) 2 -2 2 0.5 0.5 y-µ -2-0 = -2 2-0 = 2 =4 (standard deviation) = sqrt(4) = 2 Problem #61 µ = 0*0.5 + 4*0.3 + 6*0.2 = 2.4 variance by definition formula: 2 = (0-2.4)2*0.5 + (4-2.4)2*0.3 + (6-2.4)2*0.2 = 6.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(6.24) = 2.4980 variance by computing formula: E(w2) = 02*0.5 + 42*0.3 + 62*0.2 = 12 2 = 12 - (2.4)2 = 6.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(6.24) = 2.4980 OR variance by computing formula: w*P(w) w 0*0.5 = 0 0 4*0.3 = 1.2 4 6*0.2 = 1.2 6 0+1.2+1.2 = 2.4 P(w) 0.5 0.3 0.2 w2 0 16 36 w2*P(w) 0*0.5 = 0 16*0.3 = 4.8 36*0.2 = 7.2 0+4.8+7.2= 12 2 = 12 - (2.4)2 = 6.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(6.24) = 2.4980 OR variance by computing formula: w*P(w) w P(w) 0*0.5 = 0 4*0.3 = 1.2 6*0.2 = 1.2 0+1.2+1.2 = 2.4 0 4 6 0.5 0.3 0.2 (variance) 2 w-µ 0-2.4 = -2.4 4-2.4 = 1.6 6-2.4 = 3.6 = 6.24 (standard deviation) = sqrt(6.24) = 2.4980 Problem #62 µ = 2*0.1 + 6*0.5 + 10*0.4 = 7.2 (w-µ)2 5.76 2.56 12.96 (w-µ)2*P(w) 5.76*0.5 = 2.88 2.56*0.3 = 0.768 12.96*0.2 = 2.592 2.88+0.768+2.592 = 6.24 variance by definition formula: 2 = (2-7.2)2*0.1 + (6-7.2)2*0.5 + (10-7.2)2*0.3 = 6.56 (standard deviation) = sqrt(6.56) = 2.5612 variance by computing formula: E(x2) = 22*0.1 + 62*0.5 + 102*0.3 = 58.4 2 = 58.4 - (7.2)2 = 6.56 (standard deviation) = sqrt(6.56) = 2.5612 OR variance by computing formula: x*P(x) x 2*0.1 = 0.2 2 6*0.5 = 3 6 10*0.4 = 4 10 0.2+3+4 = 7.2 P(x) 0.1 0.5 0.4 x2 4 36 100 x2*P(x) 4*0.1 = 0.4 36*0.5 = 18 100*0.4 = 40 0.4+18+40= 58.4 2 = 58.4 - (7.2)2 = 6.56 (standard deviation) = sqrt(6.56) = 2.5612 OR variance by computing formula: x*P(x) x P(x) 2*0.1 = 0.2 6*0.5 = 3 10*0.4 = 4 0.2+3+4 = 7.2 (variance) 2 2 6 10 0.1 0.5 0.4 x-µ 2-7.2 = -5.2 6-7.2 = -1.2 10-7.2 = 2.8 = 6.56 (standard deviation) = sqrt(6.56) = 2.5612 (x-µ)2 27.04 1.44 7.84 (x-µ)2*P(x) 27.04*0.1 = 2.704 1.44*0.5 = 0.72 7.84*0.4 = 3.136 2.704+0.768+3.136 = 6.56 Problem #63(a) µ = 0*0.20+1*0.25+2*0.30 + 3*0.15 + 4*0.10 = 1.7 OR x*P(x) x P(x) 0*0.20 = 0 0 0.20 1*0.25 = 0.25 1 0.25 2*0.30 = 0.60 2 0.30 3*0.15 = 0.45 3 0.15 4*0.1 = 0.40 4 0.10 0+0.25+0.60+ 0.45+0.40 = 1.70 Problem #63(b) variance by definition formula: 2 = (0-1.7)2*0.20 + (1-1.7)2*0.25 + (2-1.7)2*0.30 + (3-1.7)2*0.15 + (4-1.7)2*0.10 = 1.51 variance by computing formula: E(x2) = 02*0.20 + 12*0.25 + 22*0.30 + 32*0.15 + 42*0.10 = 4.4 2 = 4.4 - (1.7)2 = 1.51 OR variance by computing formula: x*P(x) x 0*0.20 = 0 0 1*0.25 = 0.25 1 2*0.30 = 0.60 2 3*0.15 = 0.45 3 4*0.1 = 0.40 4 0+0.25+0.60+ 0.45+0.40 = 1.70 2 = 4.4 - (1.7)2 = 1.51 OR P(x) 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.15 0.10 x2 0 1 4 9 16 x2*P(x) 0*0.20 = 0 1*0.25 = 0.25 4*0.30 = 1.20 9*0.15 = 1.35 16*0.10 = 1.60 0+0.25+1.20+ 1.35+1.60 = 4.4 variance by computing formula: x*P(x) x P(x) 0*0.20 = 0 1*0.25 = 0.25 2*0.30 = 0.60 3*0.15 = 0.45 4*0.1 = 0.40 0+0.25+0.60+ 0.45+0.40 = 1.70 (variance) 2 0 1 2 3 4 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.15 0.10 x-µ 0-1.7 = -1.7 1-1.7 = -0.7 2-1.7 = 0.3 3-1.7 = 1.3 4-1.7 = 2.3 (x-µ)2 2.89 0.49 0.09 1.69 5.29 (x-µ)2*P(x) 2.89*0.20 = 0.578 0.49*0.25 = 0.1225 0.09*0.3 = 0.027 1.69*0.15 = 0.2535 5.29*0.10 = 0.529 0.578+0.1225+0.027 +0.2535+0.529 = 1.51 = 1.51 Problem #63(c) (standard deviation) = sqrt(1.51) = 1.2288 Problem #64(a) µ = (-3)*0.1 + (-1)*0.15 + 0*0.5 + 1(0.15) + 3(0.1) = 0 OR x*P(x) x P(x) -3*0.10 = -0.3 -3 0.10 -1*0.15 = -0.15 -1 0.15 0*0.50 = 0 0 0.50 1*0.15 = 0.15 1 0.15 3*0.1 = 0.30 3 0.10 -0.3 + (-0.15)+ 0 + 0.15 + 0.30 = 0 variance by definition formula: 2 = (-3-0)2*0.1 + (-1-0)2*0.15 + (0-0)2*0.5+ (1-0)2*0.15 + (3-0)2*0.1 = 2.1 (standard deviation) = sqrt(2.1) = 1.4491 variance by computing formula: E(x2) = (-3)2*0.1 + (-1)2*0.15 + 02*0.5+ (1)2*0.15 + 32*0.1 = 2.1 2 = 2.1 - (0)2 = 2.1 (standard deviation) OR = sqrt(2.1) = 1.4491 variance by computing formula: x*P(x) x -3*0.1 = -0.3 -3 -1*0.15 = -0.15 -1 0*0.5 = 0 0 1*0.15 = 0.15 1 3*0.1 = 0.3 3 -0.3+(-0.1)+0+ 0.15+0.3 = 0 P(x) 0.1 0.15 0.5 0.15 0.1 x2 9 1 0 1 9 x2*P(x) 9*0.1 = 0.9 1*0.15 = 0.15 0*0.5 = 0 1*0.15 = 0.15 9*0.1 = 0.9 0.9+0.15+0+ 0.15+0.9= 2.1 2 = 2.1 - (0)2 = 2.1 (standard deviation) = sqrt(2.1) = 1.4491 OR variance by computing formula: x*P(x) x P(x) -3*0.1 = -0.3 -1*0.15 = -0.15 0*0.5 = 0 1*0.15 = 0.15 3*0.1 = 0.3 -0.3+(-0.1)+0+ 0.15+0.3 = 0 (variance) 2 -3 -1 0 1 3 0.1 0.15 0.5 0.15 0.1 x-µ -3-0 = -3 -1-0 = -1 0-0 = 0 1-0 = 1 3-0 = 3 = 2.1 (standard deviation) = sqrt(2.1) = 1.4491 (x-µ)2 9 1 0 1 9 (x-µ)2*P(x) 9*0.1 = 0.9 1*0.15 = 0.15 0*0.5 = 0 1*0.15 = 0.15 9*0.1 = 0.9 0.9+0.15+0+ 0.15+0.9= 2.1 Problem #64(b) Since = sqrt(2.1) = 1.4491, then 2 = 2*1.4491 = 2.8982 So µ-2 = 0 – 2.8982 = -2.8982 and So µ+2 = 0 + 2.8982 = 2.8982 so the histogram looks like: Problem 64 0.6 µ-2 µ+2 µ 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 -3 -1 0 1 3 Problem #64(c) Since the probability must be between +/-2.8982, then the probability cannot include the probability of 3 or -3…so the answer is 0.15+0.5+0.15 = 0.8 Problem #65 Both means will be at 3 so that the probabilities will “balance” at that point (equal amounts on both sides of 3). Problem #66 Y since more of the probability is at the mean (less of a standard deviation, or spread in the data).