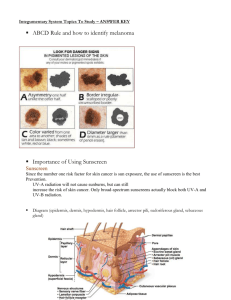
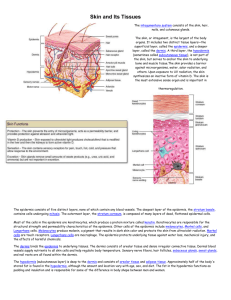
Integumentary System Notes
advertisement
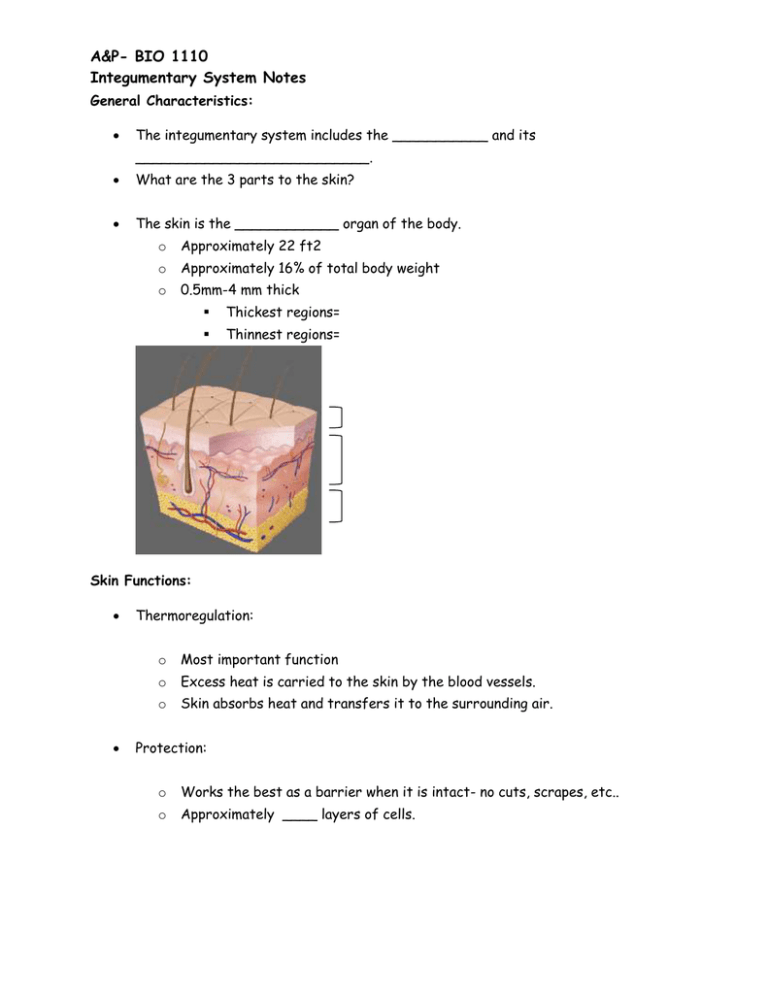
A&P- BIO 1110 Integumentary System Notes General Characteristics: The integumentary system includes the ___________ and its ___________________________. What are the 3 parts to the skin? The skin is the ____________ organ of the body. o Approximately 22 ft2 o Approximately 16% of total body weight o 0.5mm-4 mm thick Thickest regions= Thinnest regions= Skin Functions: Thermoregulation: o Most important function o Excess heat is carried to the skin by the blood vessels. o Skin absorbs heat and transfers it to the surrounding air. Protection: o Works the best as a barrier when it is intact- no cuts, scrapes, etc.. o Approximately ____ layers of cells. A&P- BIO 1110 Integumentary System Notes Sense organ: o Sensations of touch, vibration and pain o Collects information from the outside world and sends it to the brain o What parts of the body are the most sensitive? Secretion and absorption: o o Secretion: Secretes ____________ and _____________ through glands. What wastes can the skin remove? Absorption: Taking materials into the body through the skin. Most absorbed- ____________________ vitamins (A, D, E, K) Some toxins are absorbed- rubbing alcohol, acetone, chlorine Vitamin D production: o When exposed to sunlight, the precursor becomes vitamin D because the light energy transforms its shapes. o It takes hours of sun exposure to produce the amount of vitamin D in a glass of milk. Is it worth it? Epidermis: Outer Layer of Skin What is the function of the epidermis? Cells of the epidermis: o Keratinocytes These cells make up _____ % of the epidermis What is keratin? A&P- BIO 1110 Integumentary System Notes Most keratinocytes are _______ They don’t really become flattened until they reach the top layers due to pressures from above and below as the cells move up the epidermis. o What is keratinization? Happens as cells move up through the epidermis This is what eventually kills the keratinocytes Melanocytes What is the function of melanocytes? Produce melanin- It is produced by _______________ feedback. The more exposurethe more melanin produced- which means the more the skin can be exposed to the sun. We all have the same # of melanocytes per square inch of the skin. Our melanocytes just produce a varying amount of melanin. o o Langerhans cells What is the function of Langerhans cells? These are ________________________- engulf and destroy Merkel cells Function to gather information (touch, temperature, vibration, and pain) and send it to the brain to be interpreted. o Melanocytes, Langerhans cells and Merkel cells account for the remaining _____% of the epidermis. Layers of the epidermis: o Stratum Basale A&P- BIO 1110 Integumentary System Notes Lies above the dermis and blood vessels in the dermis supply this layer with blood (by diffusion) Here is where _________________________takes place, producing new skin cells and pushing older cells toward the surface. o Stratum Spinosum- superficial to the _______________________. Cells have small projections “spiny” that help lock the cells together like velcro. o Stratum Granulosum- superficial to the _________________________. Cells are starting to look more squamous because of pressure from the cells above and below. Layer where _______________________ starts and cells produce keratin in large quantities. Can see granules of keratin in the cells. The transition layer between __________________ and __________ cells. o Stratum Lucidum- superficial to the ____________________________. o Only found on the ____________________________________. Shock absorbers Stratum Corneum- the most superficial layer of the epidermis Spines start to break off which causes the cells to fall off Waterproofs the skin Takes ___________________ for cells to reach this layer from the stratum basale.