DNA REPLICATION Web-quest - Lyndhurst School District
advertisement

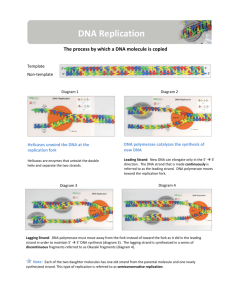
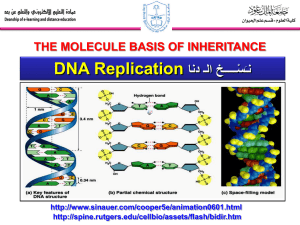
Name: ______________________________ Date: ___________ Block: _____ DNA Replication Quest USE PUFFIN!! If you do not have an iPad, read the hard copies! Use the websites provided in the “DNA Replication Web-quest” in my website, Chapter 9 DNA folder, to answer the questions below about DNA replication. Click on http://www.yourgenome.org/facts/what-is-dna-replication 1. What is DNA replication? _________________________________________________________________ 2. What holds complementary bases (A & T) together? ________________________ 3. What is the first step in DNA replication? _______________________________ 4. The two separated strands will act as ____________________ for making the _________________________________. 5. One of the strands is oriented in the ___________________________ this is the ________________________. The other strand is oriented in the _____________ ________________________ (away from the replication fork), this is the ________________________. As a result of their different orientations, the two strands are replicated differently: 6. Sketch the image of the DNA replication fork pictured below step 4. Click on http://www.wiley.com/college/pratt/0471393878/instructor/animations/dna_replicatio n/index.html USE PUFFIN! If you do not have an iPad, read the hard copy! 7. Why is DNA replication said to be semi-conservative? _____________________ ________________________________________________________________ 8. What enzyme unwinds the DNA strands? ___________________________ 9. What is the function of primase? ______________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 10. What is the function of polymerase? __________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 11. The leading strand is synthesized _________________________, while the lagging strand is synthesized ___________________________. 12. DNA pieces separated by primers in the lagging strand are called _____________________________. 13. List the 4 events that must occur in the lagging strand prior to completing its replication. In other words, how are Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand joined into one continuous strand?