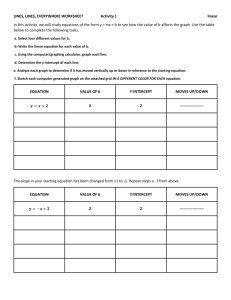
File - Mrs. Hille's FunZone
advertisement
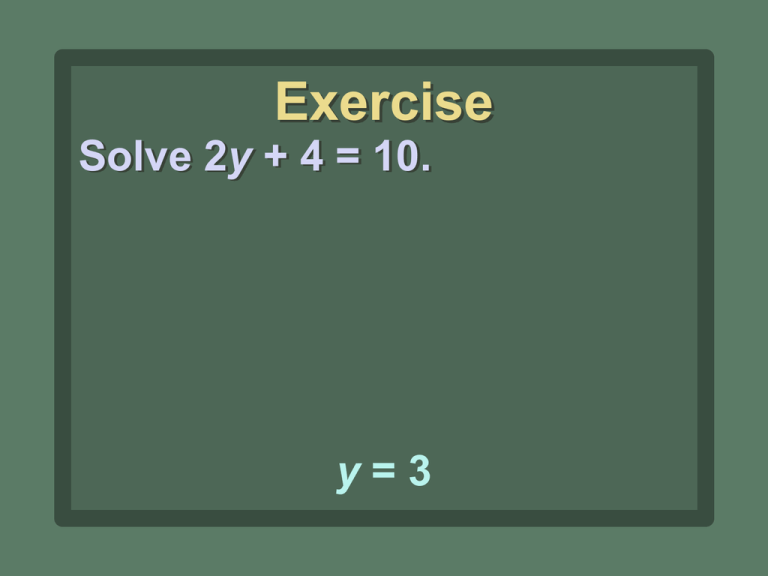
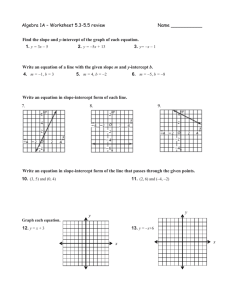
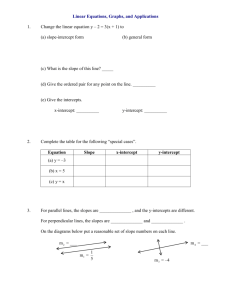
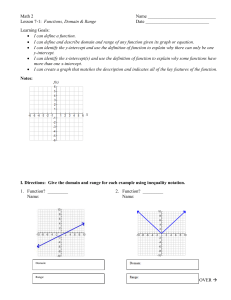
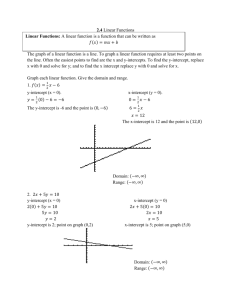
Exercise Solve 2y + 4 = 10. y=3 Exercise Solve y − x = 5. y=x+5 Exercise Solve x + y = 5. y = −x + 5 Exercise Solve −6x + y = 12. y = 6x + 12 Exercise Solve −6x + 2y = 12. y = 3x + 6 Y-intercept The y-intercept is the point where a line crosses the y-axis. X-intercept The x-intercept is the point where a line crosses the x-axis. Example 1 Find the x- and y-intercepts of the line 2x + 3y = 6 and use them to graph the line. 2(0) + 3y = 6 2x + 3(0) = 6 3y = 6 2x = 6 2 2 3 3 y=2 x=3 y x Slope-intercept form The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is y = mx + b. The slope of the line is m, and the y-intercept is at (0, b). Example 2 Find the slope and y-intercept of y = 3x − 2. The equation is in slopeintercept form, y = mx + b. The slope is m = 3. Since b = −2, the y-intercept is (0, −2). Example 3 Change 2x − y = 10 to slopeintercept form. 2x − y = 10 − 2x − 2x −y = −2x + 10 −1 −1 −1 y = 2x − 10 Graphing an Equation Using the Slope-Intercept Form 1. Solve the equation for y to put it in slopeintercept form. 2. Plot the y-intercept at (0, b). Graphing an Equation Using the Slope-Intercept Form 3. Express the slope (m) as a ratio to find the rise and run. Graphing an Equation Using the Slope-Intercept Form 4. From the y-intercept, use the rise and run to graph two other points. 5. Draw a line through the points. y x Example 4 Use the slope-intercept form to graph the line y = 3x − 2. 1. Identify the y-intercept as (0, −2) and plot it on the graph. 2. Express the slope as a ratio to find rise and run: 3 rise m = 3 = 1 = run . Example 4 Use the slope-intercept form to graph the line y = 3x − 2. 3. From (0, −2),move up three and right one to plot a second point on the line, (1, 1). 4. Draw a line through the two points. Example 4 Use the slope-intercept form to graph the line y = 3x − 2. 3 rise 5. Use m = 3 = 1 = run to check your graph. From (0, −2) move down three and left one to plot a third point. y x Example 5 Graph the line 2x + 3y = 3. 2x + 3y = 3 − 2x − 2x 3y = −2x + 3 3 3 3 −2x y= 3 +1 y x Example Find the x- and y-intercepts of the line 3x + 2y = 12. (4, 0) and (0, 6) Example What are the x- and y-intercepts of y = 5? Note that y = 5 no matter what x is, so the y-intercept is (0, 5). If y = 0, then the equation becomes 0 = 5, which is not true. There is no x-intercept. Example What are the x- and y-intercepts of x = 5? Note that x = 5 no matter what y is, so the x-intercept is (5, 0). If x = 0, then the equation becomes 0 = 5, which is not true. There is no y-intercept. Example Determine the slope and y-intercept of 6x + 4y = 3 by converting to slope-intercept form. 3 3 y=− x+ 2 4 3 3 (0, ) m=− 2 4 Example Graph the line y = −3x. y x Example Graph the line y = 3x − 2. y x Exercise Write an equation for a line with the these characteristics: slope of 4 and y-intercept (0, 12). y = 4x + 12 Exercise Write an equation for a line with the these characteristics: slope of 0 and y-intercept (0, −9). y = −9 Exercise Write an equation for a line with the these characteristics: undefined slope and x-intercept (5, 0). x=5 Exercise Write an equation for a line with the these characteristics: x-intercept (3, 0) and y-intercept (0, 6). y = −2x + 6