CHESS_BEARS_2013_Poster - Chess
advertisement
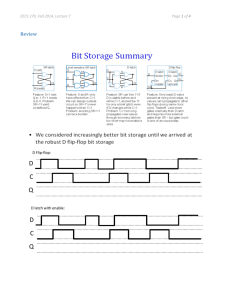
An overview of the CHESS Center Berkeley EECS Annual Research Symposium http://chess.eecs.berkeley.edu/ Cyber-Physical Systems Organization Faculty Edward A. Lee, EECS Alberto Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, EECS Shankar Sastry, EECS Claire J. Tomlin, EECS Karl Hedrick, ME Sanjit Seshia, EECS Masayoshi Tomizuka, ME Hybrid system model of Newton’s Cradle, built using HyVisual. Mission The goal of the Center is to provide an environment for graduate research on the design issues necessary for supporting next-generation embedded software systems. The research focus is on developing modelbased and tool-supported design methodologies for real-time fault-tolerant software on heterogeneous distributed platforms. Staff Christopher Brooks, EECS Charlotte M. Jones, EECS Yulia Golubovskaya, EECS Mary Stewart, EECS Stavros Tripakis, EECS Affiliated faculty Aviral Shrivastava, Arizona State Jonathan Sprinkle, University of Arizona, ECE The Problem: intensive use of embedded software in complex physical systems, such as cars. "A cyber-physical system (CPS) integrates computing and communication capabilities with monitoring and / or control of entities in the physical world dependably, safely, securely, efficiently and in real-time." - S. Shankar Sastry The research laboratory: software frameworks and test systems such as the Toyota test cell for engine control technology. CHESS provides industry with innovative software methods, design methodology and tools while helping industry solve real-world problems. CHESS is defining new areas of curricula in engineering and computer science which will result in solving societal issues surrounding aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics and medical devices. CHESS Software Examples of CHESS software include: • HyVisual, a block-diagram editor and simulator for continuous-time and hybrid systems (shown at the left) The Problem: High speed printing presses require millisecond timing over 100 meters • Metropolis, a design environment for heterogeneous systems • MetroII, enhancements to Metropolis: heterogeneous IP import, orthogonalization of performance from behavior • Precision Timed (PRET) Architecture Simulator. The Problem: intensive use of embedded software in complex physical systems, such as aircraft. • Pt1588, an open source implementation of IEEE1588-2008. • PTARM, a precision timed soft core The research laboratory: software frameworks and test systems such as the STARMAC Quadrotor Aircraft (Prof. Tomlin) Software engineering today is based on principles that abstract away key semantic properties embedded systems, such as time. The result is ad-hoc architectures and brittle systems. Embedded software architecture tomorrow will be built on sound principles that reflect the interaction of the software with the physical world. February 14, 2013 Research The research laboratory: PTIDES: Programming Temporally Integrated Distributed Embedded Systems The PTIDES project focuses on modelbased design principles for eventtriggered real-time distributed systems. • Ptolemy II, a software laboratory for concurrent models of computation • VisualSense, a visual editor and simulator for wireless sensor network systems. • Viptos, a block-diagram editor and simulator for TinyOS Systems. • Design of cyber-physical systems • Hybrid systems theory and practice The Solution: PTIDES is used to • Programming models for embedded control systems generate code for different microcontrollers. • Semantics of modeling languages and methods • Applications in automotive, avionics, sensor networks, and biology • Embedded virtual machines for portable, mobile real-time code • Experimental software platforms (Ptolemy, Metropolis, Giotto, etc.) • Design transformation technology (component specialization, code gen.) • Verification of temporal and safety properties of software • Visual syntaxes for system design Center for Hybrid and Embedded Software Systems This work was supported in part by the Center for Hybrid and Embedded Software Systems (CHESS) at UC Berkeley, which receives support from the National Science Foundation (NSF awards #0720882 (CSR-EHS: PRET), #0931843 (CPS: Large: ActionWebs), and #1035672 (CPS: Medium: Ptides)), the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL #NOOI73-12-1-G015), and the following companies: Bosch, National Instruments, and Toyota.