(Physical Chemical Lab Stations and Separation Intro)
advertisement
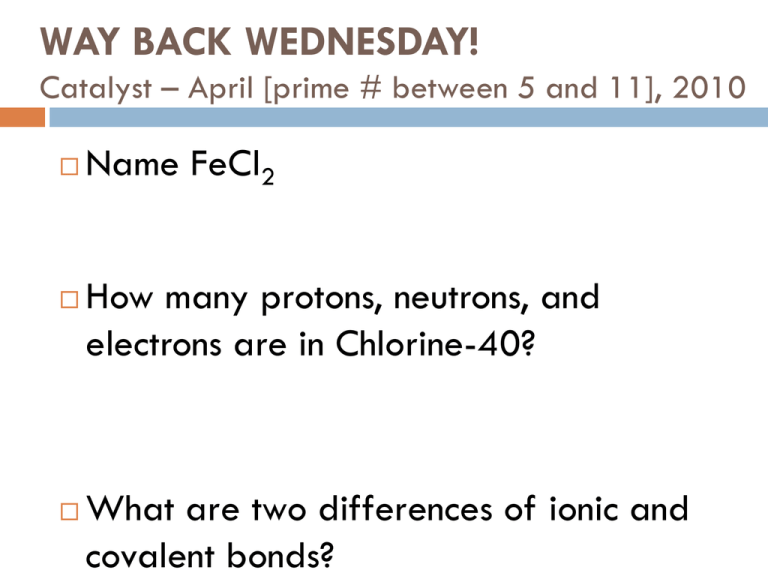
WAY BACK WEDNESDAY! Catalyst – April [prime # between 5 and 11], 2010 Name FeCl2 How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in Chlorine-40? What are two differences of ionic and covalent bonds? Today’s Agenda Catalyst th Go over worksheet (5 only) Physical/Chemical Change Lab Stations (45 minutes) Intro notes on separating mixtures Exit Question Today’s Objectives SWBAT describe matter using physical and chemical properties. SWBAT observe and distinguish between physical and chemical changes. SWBAT begin to learn about separating mixtures. Review Physical or Chemical Change? A physical change is a change, but only physical properties change A chemical change is also a change, but it forms a new substance Evidence of Physical Change Bending, breaking, smashing, freezing, melting, evaporating, crushing, cutting, tearing, sanding, grinding, mixing, separating, dissolving... Evidence of Chemical Change Fizzing, burning or combustion, corrosion, production of odor, heat, cold, light, rust, solids, smoke, decomposition, oxidation, rotting, digestion… Physical and Chemical Change Lab Stations There are EIGHT stations Each group will go to each station for 5 minutes FIVE LAB STATIONS, TWO QUESTION STATIONS, ONE HAIKU STATION During the Haiku stations, you will be required to work on a Chemistry Haiku (5-7-5) You must include the Haiku in order to get credit for the day’s work, so I expect you to be working the entire time More Haikus for extra points! What’s a Haiku? A short 3-line poem with a certain number of syllables on each line First line: 5 syllables Second line: 7 syllables Third line: 5 syllables 5-7-5! Ms. Stroh’s Haiku LY’s class works hard Stroh’s class works even harder To become masters! Alternative Assignment If you weren’t here yesterday or didn’t do your homework… Complete Unit 4 Resume (Homework) Write one Chemistry Haiku Bookwork: Read pages 66-69 and answer questions 15-19 (on page 69) Read pages 70-74 and answer questions 25, 29 (on page 77) Mixtures….of whaaaaat?!?!? Key Point #1: Mixtures are PHYSICALLY combined, so they can be PHYSICALLY separated. A mixture is a combination of two or more substances in which each substance keeps its individual chemical properties. Let’s look at some mixtures… Why is separation of mixtures so important in chemistry? When you perform reactions, you must often isolate certain products… Real-Life Examples of Separating Mixtures Separating components of blood Separating oil from water in an oil spill Getting drinkable water in third world countries How you do that? Key Point #2: Chemists separate mixtures by using differences in physical properties of each part. Physical Properties: Size Density Solubility Magnetism Boiling Point Physical Properties that can be different: Size: Ex. Big Grizzly Bear and little Ida Henry Density : Will it float or sink in water? OR Which is more dense? Ex. Toothpicks and paper clips; Ex. Water and oil Solubility: Will it dissolve in water? Ex. Rocks and sugar Magnetism: Is it magnetic? Ex. Paper and metal clippings Boiling Point : At what temperature does it boil? Ex. Water and oil Density Based off differences in density, you can separate liquids from each other Ex: Oil and Water Magnetism Based on differences is magnetism, you can separate magnetic objects from nonmagnetic objects Ex: Rocks and Coins SEPARATION TECHNIQUES Key Point #3: Filtration separates a solid from a liquid by filtering out the liquid. Ex. sand and water mixture What physical property is being utilized here? Utilizes the solubility and density of the solid Filtration Based on differences in phase state, you can separate solids from liquids using filtration Ex: Sand and water Ex: Spaghetti and water Filtration Crystallization Based on differences in boiling points, you can separate dissolved solids from liquids Ex: Boil salt water to crystallize salt and evaporate water SEPARATION TECHNIQUES Key Point #5: Crystallization separates a solid that has been dissolved in a liquid by boiling off the liquid. Ex. salt water mixture What physical property is being utilized here? Utilizes different boiling points of each substance Distillation Based on differences in boiling points, you can separate two liquids from each other. Liquid A has a boiling point of 100°C Liquid B has a boiling point of 110°C How could I separate these two mixtures? SEPARATION TECHNIQUES Key Point #4: Distillation separates two liquids from each other by boiling off one liquid at a time. Ex. water and alcohol mixture. What physical property is being utilized here? Utilizes the differing boiling points of each substance Individual Whiteboard: Identify the technique (filtration, distillation, or crystallization) you would use to separate the following mixtures: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) Remove rocks from an ocean water sample. A solution of salt water. A mixture of oil and water. Isolate sugar from a sugar-water solution. Salt and ammonium chloride mixture (salt is not soluble in ammonium chloride). A mixture of paperclips and rice. A mixture of water and oil. Separation Challenge Problem: You have a mixture of sand, salt, wood chips, and iron fillings. It is your job to successfully separate all of these components. Possible Materials to use: Magnets Distilled water Funnel Filter paper Hot plate Watch glass Spoon beaker Precipitation Reactions and Filtration BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl( aq) Exit Question Jose found a mixture of pennies dissolved in salt water. Make a procedure for separating each component. *Remember use the differences between the parts!





