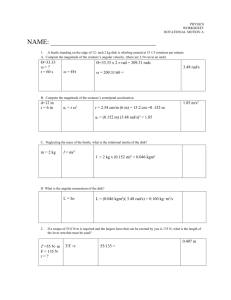
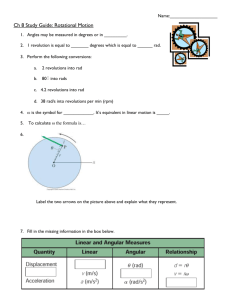
Rotational Motion

When an object spins,
It is said to undergo
Rotational motion.
When measuring rotational
Motion, we will use radians.
A radian is an angle whose
Arc length is equal to its radius,
Which is approximately
Equal to 57.3°
θ = s r
θ = the angle r = the radius s = arc length
360° = 2π rad
We now have a conversion
Between radians and degrees.
θ (deg)
Ben, riding on a carousel,
Travels through an arc length of
11.5 m. If the carousel has a
Radius of 8 m, what is the angular
Displacement? What degree is this?
2.88 rad 165°
Angular speed describes
The rate at which a body
Rotates about an axis, usually
Expressed in rad/s.
ω =
Δθ
Δt
Ben now spins on a stool, if he
Turns clockwise through 10π rad,
During a 10 s interval, what is
The average angular speed
Of his feet?
3.14 rad/s
Angular acceleration is the time
Rate of change of angular speed,
Usually expressed in radians
Per second per second.
Now Ben rotates on the stool
With an initial angular speed of
21.5 rad/s. The stool accelerates,
And after 3.5s, the speed is 28 rad/s. What is the average
Angular acceleration?
1.9 rad/s/s
Angular Kinematics
Rotational
Motion
ω f
= ω i
+ αΔt
Linear
Motion v f
= v i
+ a Δt
Δθ = ω i
Δt + ½α(Δt) 2 Δx = v i
Δt + ½a(Δt) 2
ω f
2 = ω i
2 + 2α(Δθ) v f
2 = v i
2 + 2a Δx
The wheel on an upside-down bike
Rotates with a constant angular
Acceleration of 3.5 rad/s/s. If the
Initial angular speed of the wheel
Is 2 rad/s, through what angular
Displacement does the wheel
Rotate in 2 sec?
11 rad
Torque is a quantity that measures
The ability of a force to rotate
An object around some axis
Torque is a scalar quantity.
Torque has the SI unit of
N*m
τ = Fd(sinθ)
Torque is positive or negative
Depending on the direction
The force tends to rotate
An object.
Torque that is clockwise is
Defined as negative.
Thus torques that produce a
Counterclockwise rotation are
Defined to be positive.
Find the torque produced by a
3 N force applied at an angle
Of 60° to a door 0.25m from
The hinge.
0.65 N m
In order to calculate the moment
Of inertia, you have to use the
Formulas provided in the book
For the many different shapes.
Shape
Thin hoop about symmetry of object
Thin hoop about diameter
Formula for moment of inertia
MR 2
1/2 MR 2
Point of mass about axis MR 2
Disk about axis
Rod about axis through center
Rod about axis through end
Solid sphere about diameter
Thin sphere shell about diameter
1/2 MR 2
1/12 ML 2
1/3 ML 2
2/5 MR
2/3 MR
2
2
A 5m horizontal beam weighing
315N is attached to a wall so
That it rotates. Its far end is
Supported by a cable at an angle
Of 53°, and a 545N is standing
1.5m from the wall. Find the tension
And the force on the beam by the
Wall, R.
Tension = 403 N R = 590N
Newton’s 2 nd Law for
Rotating objects.
τ = Iα
A catapult propels a 0.150 kg
Stone. The length of the
Catapult arm is 0.350m. If the
Stone leaves the catapult with an
Acceleration of 100 m/s 2 , what
Is the torque exerted on the stone.
5.25 Nm
The center of mass of an object
Is the point at which all the
Mass of the body can be
Considered to be concentrated
When analyzing
Translational motion.
Rotational and translational
Motion can be combined.
The moment of inertia is the
Rotational analog of mass.
Equilibrium requires zero net force,
And zero net torque.
A 5.8 kg ladder, 1.8 m long, rests
On 2 saw horses. Sawhorse A is
0.6 m from one end of the ladder
And sawhorse B is 0.15 m from the
Other end of the ladder. What force
Does each sawhorse exert on the
Ladder?
F b
= 16 N F a
= 41 N
The centrifugal force is an
Apparent force.
NOT A REAL FORCE!
It is not a real force because there
Is no physical outward push.
The Coriolis Force is also a
FAKE FORCE!
This is because it is only apparent
To rotating observer.
This is very apparent on Earth
However. It is the reason for
The direction of the winds.