Genetics
advertisement

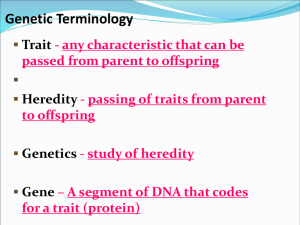
Genetics • Heredity: is the passing of traits from parent to offspring. – Every organism is a collection of traits, all from its parents • Trait: are physical or genetic characteristics of an individual organism • Genes control the traits by producing proteins. – A Gene is a small section of DNA that codes for certain proteins. • An alternative form of genes are called alleles – Organisms have at least two genes for every trait. – They receive at least one from each parent. • The study of how traits are inherited through action of genes is the science of GENETICS. Gregor Mendel • Gregor Mendel is often referred to as the “father of genetics”. – He was a monk that was born in Austria in 1822. – He was experimenting in garden with peas. Through his experiments he discovered that some genes were either dominant or recessive. • Dominant because it dominated or is always shows itself (D, a capital letter) • Recessive because it was hidden when the dominant gene was present (d, lowercase) Freckles No Freckles Dimples No dimples Tongue roller Non-roller From Mom From Dad Genotype: Genotype is the actual genes for a particular trait expressed with letters Homozygous dominant (Purebred) – TT - two capital letters Heterozygous (hybrid) – Tt - one of each letter (big and small) Homozygous recessive (Purebred) – tt - two lower case letters Phenotype: Phenotype is physical expression of the genotype Genotype Phenotype TT tall plant Tt tall plant* tt short plant** * dominant allele always is expressed over the recessive allele ** recessive trait is expressed only if there is no dominant gene If R = red, and r = white What is the genotype of homozygous dominant? – RR What is the heterozygous genotype? – Rr What is the homozygous recessive genotype? – rr If R=red and r =white What is the phenotype of of RR? – Red What is the phenotype of Rr? – Red What is the phenotype of rr? – White Mendel’s Experiments led him to 3 Laws of Inheritance The Law of Dominance The Law of Segregation The Law of Independent Assortment Law of Segregation – Segregation is the separation of alleles during gamete formation. – Since only one egg or one sperm will contribute to the new offspring, only one allele for a trait is passed on – The chance that any allele will be passed on is 50% - Mendel’s Work Segregation Law of Independent Assortment the inheritance of alleles for one trait doesn’t affect the inheritance of alleles for another trait – accounts for the many genetic variation observed in plants, animals and other organism. Predicting Traits • A tool used to predict and compare the genetic variations that will result from a cross is a Punnett Square. If two parents are crossed (TT X tt), what are the resulting offspring? You can determine phenotypes using a Punnet square. t t T T Tt Tt Tt parent Tt parent Genotypes: 4 Tt Phenotypes: 4 Tall This is the first or parent generation Now try on your paper a cross of two of the offspring from the parent generation. This is called the first generation or the F1. T t T t TT Tt Tt tt Genotypes: 1TT: 2Tt : 1tt Phenotypes: 3 Tall: 1 Short. Dihybrid Crosses A two-factor cross follows two different genes as they pass from one generation to the next. – Explains the Law of Independent Assortment Let’s Solve Together In guinea pigs, the allele for short hair (S) is dominant to long hair (s), and the allele for black hair (B) is dominant over the allele for brown hair (b). What is the probable offspring phenotype ratio for a cross involving two parents that are heterozygotes for both traits? Example 1: Dihybrid Short hair = dominant = SS or Ss Long Hair = recessive = ss Black coat = dominant = BB or Bb Brown coat = recessive = bb SsBb x SsBb (gametes done by the FOIL method) – SB, Sb, sB, sb and SB, Sb, sB, sb Example 1: Punnett Square Parents: SsBb x SsBb SB Sb sB sb SB SSBB SSBb SsBB SsBb Sb SSBb SSbb SsBb Ssbb sB SsBB SsBb ssBB ssBb sb SsBb Ssbb ssBb ssbb Example 1: Answer the Question What is the probable offspring phenotype ratio for a cross involving two parents that are heterozygotes for both traits? – 9/16 Black, short coats – 3/16 Black, long coats – 3/16 Brown, short coats – 1/16 Brown, long coats Incomplete Dominance – in which one allele is not completely dominant over another; a blending in the heterozygous = red Incomplete Dominance RR RW = pink WW = white RR x WW R W W R RW RW RW RW What are the phenotypes of the offspring? All the offspring will be Pink Codominance – can see both alleles at the same time. Codominance Feathers in chickens FWFW – White Feather FBFB – Black Feather FWFB – Half Black Half White FWFW xWFBFB F FB FB FW FWFB FWFB FWFB FWFB What are the phenotypes of the offspring? All of the offspring will be half black and half white Sex-linked traits Are traits that are controlled by the X or Y chromosomes. Sex-linked disorders, which are disorders caused by abnormal sex chromosomes. – Occurs more often in men than women. • Most are recessive – Two common disorders • Colorblindness and hemophilia Colorblindness Test Hemophilia A person’s blood clots very slowly or not at all. Danger from small bumps and cuts A recessive gene on the X-chromosome – Occurs more in males than females Multiple Alleles – three or more alleles of the same gene. Blood Types in Humans – Single gene, but four phenotypes • • • • Type A can be IAIA or IAi Type B can be IBIB or IBi Type AB only IAIB (codominant pattern here) Type O only ii (both recessive) – All 3 blood types are dominant to O Practice Problem Cross a person with AB blood with a person with B blood. (2 crosses). What are the possible blood types of the children? Blood tranfusions Universal Donor Universal Acceptor Polygenic Traits Traits controlled by two or more genes Examples – Eye color – Skin color – Hair color - Human Genetic Disorders A Pedigree • A pedigree is a chart or “family tree” that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait. Pedigree analysis • Pedigree analysis reveals Mendelian patterns in human inheritance; tracks certain traits through a family – data mapped on a family tree = male = female = male w/ trait = female w/ trait Simple pedigree analysis 1 3 3 4 2 1 4 5 2 5 6 6 Genetic counseling • Pedigree can help us understand the past & predict the future The importance of the environment An individual phenotype depends on environment as well as on genes. – Temperature – Nutrition The product of a genotype is generally not single, rigidly defined phenotype but a range of possibility influenced by the environment. Human Genetic Diseases 1 2 2006-2007 Human Genetics Disorders • Genetic Disorder: is an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosome. – Caused by mutations in the DNA of genes, or the overall structure and number of chromosomes Recessive disorders • Your genotype is homozygous recessive (aa) – Heterozygotes (Aa) have a normal phenotype because one “normal” allele produces enough of the required protein – A carrier is a person who doesn’t have the disease but carry the gene for the disease Heterozygote crosses • Heterozygotes as carriers of recessive alleles Aa x Aa A female / eggs male / sperm A a A a AA AA Aa Aa Aa a carrier Aa Aa aa carrier disease A Aa a Cystic Fibrosis • The body produces abnormally thick mucus in the lungs and intestines. • This mucus makes it hard to breathe – Caused by a removal of 3 bases from DNA Tay-Sachs • Primarily Jews of eastern European (Ashkenazi) descent & Cajuns (Louisiana) – non-functional enzyme fails to breakdown lipids in brain cells • fats collect in cells destroying their function • symptoms begin few months after birth • seizures, blindness & degeneration of muscle & mental performance • child usually dies before 5yo Sickle-Cell Disease • Affects hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen • Cells have an unusual sickle-shape • They clog blood vessels, make it difficult for blood flow Huntington’s disease • Dominant inheritance – repeated mutation on end of chromosome 4 – build up of “huntingtin” protein in brain Testing… Would you causing cell death want to know? • • • • memory loss muscle tremors, jerky movements starts at age 30-50 early death – 10-20 years after start 1872