ol - Amazon S3

REVISION
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
HYDROCARBON
Organic compounds that consist of hydrogen and carbon only
HOMOLOGOUS SERIES
A series of organic compounds that can be described by the same general formula
FUNCTIONAL GROUP
A bond or an atom or a group of atoms that determine(s) the physical and chemical properties of a group of organic compounds
C H n 2 n
2 alkanes
C H n 2 n
1
X haloalkanes
C H n 2 n alkenes
C H n 2 n
2 alkynes
C H n 2 n
1
OH alcohols aldehydes ketones esters
R CO
R '
R COO
R '
Carboxylic acids
Single bonds
Double bonds halides
Carbonyl with hydrogen Carbonyl
Carbonyl with oxygen
Carbonyl with hydroxyl hydroxyl
Tripple bonds
IUPAC NAMES
IUPAC NAMES
IUPAC NAMES
2-methylbut-1-ene
1-bromo-2-chlorocyclopentane
2-methylprop-1-ol
4,4-dimethylpent-2-yne
3-methylbutanal
IUPAC NAMES
pent-2-one
Propanoic acid
Methyl butanoate
IUPAC NAMES
When naming halo alkanes, the halogen atoms do not get preference over alkyl groups – numbering should start from the end nearest to the first substituent , either the alkyl group or the halogen.
In halo alkanes, where e.g. a Br and a Cℓ have the same number when numbered from different ends of chain, Br gets alphabetical preference
When writing IUPAC names, substituents appear as prefixes written alphabetically (bromo, chloro, ethyl, methyl), ignoring the prefixes di- and tri.
SATURATED COMPOUNDS
Compounds in which there are no multiple bonds between C atoms in their hydrocarbon chains. .
UNSATURATED COMPOUNDS
Compounds with one or more multiple bonds between
C atoms in their hydrocarbon chains.
You have two test tubes with compound X an Y, respectively.
Both have a molecular formula of C H , but you suspect that X might be saturated.
5 10
You want to set up an experiment to test your hypothesis a
Wr ite an investigative question b c d
f e
Write a list of chemicals and apparatus that you will use.
What safety precautions will you follow
Write down the procedure for your experiment
How will you use your obs ervations to justify your hypothesis
Write down the IUPAC name of compound Y.
MOLECULAR FORMULA
A chemical formula that indicates the type of atoms and the correct number of each in a molecule
STRUCTURAL FORMULA
A structural formula of a compound shows which atoms are attached to which within the molecule. Atoms are represented by their chemical symbols and lines are used to represent ALL the bonds that hold the atoms together.
CONDENSED STRUCTURAL
FORMULA:
This notation shows the way in which atoms are bonded together in the molecule, but DOES NOT SHOW ALL bond lines.
ISOMERS
STRUCTURAL
Organic molecules with the same molecular formula, but different structural formulae.
CHAIN
Same molecular formula, but different types of chains
POSITIONAL
Same molecular formula, but different positions of the side chain, substituents or functional groups on the parent chain,
ISOMERS
C H
6 14
Hexane
2-methylpentane
2,2-dimethylbutane
QUESTIONS ABOUT REACTIONS when you have the REACTANTS… propene Compound X
In the follwong reaction, give the name of compound X.
A
B
C
D
Propyne
Propane
Propan 2 ol
QUESTIONS ABOUT REACTIONS when you have the REACTANTS… propene
In the follwong reaction, give the name of compound X.
A
B
C
D
Propyne
Propane
Propan 2 ol
Compound X
QUESTIONS ABOUT REACTIONS when you have the REACTANTS & PRODUCTS
Some organic reactions are shown in the flow diagram below a
Name the type of reactions illustrated by A, B, C and D . b
Use condensed structural formulae and write a balanced equation for reaction C.
c
W rite down the structural formula for compound X
In order to obtain product Y, C H Br is heated with a concentrated solution of KOH
3 7 under reflux. d
Use condensed structural formulae to write a bal anced equation for the reaction
A group of learners decided to heat C H Br with dilute sodium hydroxide, instead of the
3 7 concentrated potassium hydroxide, under reflux e
Write down the IUPAC name of the or ganic compound that they will obtain.
a
A
addition
B
substutution
C
substutution
D
elimination b
CH CH CH Br
3 2 2
KOH
CH CH CH OH
3 2 2
KBr c
propene (see below) d
CH CH CH Br
3 2 2
KOH
CH CH
3
CH
2
KBr
H O
2 e
propan ol
PHYSICAL ATTRIBUTES
BOILING POINTS
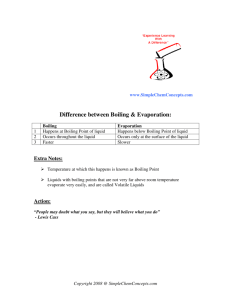
Stronger forces = highest boiling points, because more energy is neede to break the bonds
Increases with size
Because van der Waals forces increases with size, therefore longer chains have stronger forces and need more energy to break the bonds
Decreases with brancing, because branched chains cannot fit tightly together, therefore they are further apart and the van dier Waals forces weaker. Less energy is neede tot break the bonds
VAPOUR PRESSURE
(how easily it evapourates)
Decrease with size, because van der Waals force increase with size
Long chaings have stonger forces, therefore more energy is needed to break the bonds and so longer chains take longer to evapourate
MELTING POINTS
Stronger forces = highest boiling points, because more energy is neede to break the bonds
Increases with size
Because van der Waals forces increases with size, therefore longer chains have stronger forces and need more energy to break the bonds
Increases with simmetry (of spherical shapes), because symmetrical molecules have a small surface area, meaning they can be packed close together and intermolecular forces are stronger…more energy is needed to to break the molecules from the solid network structure
SOLUBILITY
“Like dissolves like”
THEREFORE
If the intermolecular forces between the solvent and solute are the same, it will dissolve
It the forces are different, it will not dissolve
VISCOSITY
Resistance to flow (how sticky it is)
Increases with size, because van der Waals forces increase with size
Long chains have stronger forces and will therefore have a high viscosity
Die teenstand teen vloei ( of hoe taai dit is)
QUESTIONS ABOUT BOILING POINTS,
SOLUBILITY, VISCOSITY etc.
Which one of the following compounds will have the highes boiling points?
QUESTIONS ABOUT BOILING POINTS,
SOLUBILITY, VISCOSITY etc.
Which one of the following compounds will have the highes boiling points?
QUESTIONS ABOUT BOILING POINTS,
SOLUBILITY, VISCOSITY etc.
The boiling points of branched alkanes are lower than their corresponding straight chain isomers, because branched alkane chains have...
A Greater molecular
B Shorter chain lenghts
C More electrons
D Smalle r surface areas masses
QUESTIONS ABOUT BOILING POINTS,
SOLUBILITY, VISCOSITY etc.
a
Which chemical properties of alkanes and alcohols make them suitable to be used as fuels
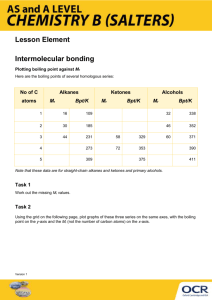
The table shows the boiling points of the first six alkanes an d the first six alcohols c b
What trend in boiling po int can be observed from the graph?
Provide a reason for the trend mentioned in b
by referring to the type of intermolecular forces e
Explain, referring to the type of intermolecular forces, why th e boi ling points of alcohols are higher than the boiling points of alkanes.
QUESTIONS ABOUT BOILING POINTS,
SOLUBILITY, VISCOSITY etc.
a
Alkanes & alcohols have low boiling points & combust easily b
Boiling points increase with chain lenght c
Van der Waals forces increase with molar mass e
Alcohols forms hydrogen bonds that are stronger than van der
Waals forces of alkanes. More energy is needed to break the bonds between alcohols, therefore their boiling points are higher
QUESTIONS ABOUT BOILING POINTS,
SOLUBILITY, VISCOSITY etc.
There exists two structural isomers for the organic compound with molecular formula C H O
2 4 2 a
Define th e t erm structural isomer b
W rite down the structural formula of these two is ome rs and next to each it s IUPAC name.
State with reason which ONE of these isomers c d
e
Has the higher boiling point
Has the higher vapour pressure
Will the vapour pressure of carboxylic acids increase or decrease if the numb er of carbon atoms in the chain increases? Give a reason for your answer
QUESTIONS ABOUT BOILING POINTS,
SOLUBILITY, VISCOSITY etc.
a
theory b
.methyl methanoate etanoic acid c
Boiling points of carboxylic acids are higher that esters' because hydrogen bonds are stronger that van der Waals forces and needs more energy to be broken d
The vapour pressure of esters are higher than carboxylic acids, because van der Waals forces are weaker than hydrogen bonds and needs less energy to be broken. Therefore esters will evapourate faster than car boxylic acid s e
decrea se vapour pressure decreases with size, because van der Waals forces increases with size
Long chains have stronger forces and needs mo re energ y to be br oken