Catalyst - haganchemistry
advertisement

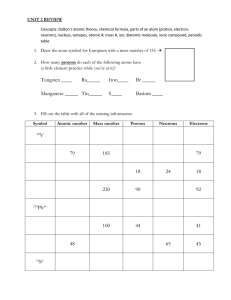
CATALYST 1. What is the difference between a substance and a mixture? Give one example of each. 2. What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change? Give one example of each. 3. Magnesium reacts with oxygen to produce magnesium oxide. If 2.4g of magnesium reacts to make 2.9g of magnesium oxide, how many grams of oxygen react? ANNOUNCEMENTS • Unit 1 exam on Friday 9/21 • Study guide and practice problems posted online at haganchemistry.wikispaces.com • Grades are up, if you have missing work this needs to be turned in by Thursday • khagan@dadeschools.net • Office hours this week • Thursday 2:30 – 3:30 • Friday 2:30 – 3:30 UNIT 1 REVIEW AND ATOMIC STRUCTURE UNIT 2, DAY 1 OBJECTIVES • Start Unit 2 (45 min) • SWBAT define atomic number and mass number, and and explain the role of atomic number in determining the identity of an atom. SWBAT determine its number of protons, neutrons, and electrons given the identity of an atom SWBAT Describe the structure of atoms in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons, and differentiate among these particles • Unit 1 Exam Review (40 min) • SWBAT review key objectives from Unit 1. AGENDA • Start Unit 2 (45 min total) • I Do: Notes on Atomic Structure • We Do: Whiteboard Problems • You Do: Complete Worksheet, Answer Independent Questions • Unit 1 Exam Review (40 min total) • I Do: Recap Key Points • We Do: Whiteboard Test Problems • You Do: Independent Review Problems • Closing: Answer EQ ATOMIC STRUCTURE • 3 Subatomic Particles: • Protons: Large and Positive (+1), in the Nucleus • Neutrons: Large and Neutral (0), in the Nucleus • Electrons: Small and Negative (-1), outside the Nucleus Atomic number = (Number of protons) 3 Lithium Number of neutrons = Mass number – atomic number Li 7 Mass number = Number of protons + neutrons Lithium Electrons Protons 3 Neutrons 4 Lithium Number of protons This is because the atom is neutral. The charges balance out! = Number of electrons Electrons 3 -3 charge Protons 3 +3 charge Neutrons 4 No charge Lithium WE DO: WHITEBOARD EXAMPLE TABLE Substance Symbol Atomic Number Lithium Li 3 Carbon C 6 Fe Mass Number 7 Number of Protons Number of Neutrons 6 26 30 *round the mass number to the nearest whole number Number of Electrons YOU DO: INDEPENDENT WORK • Complete the remainder of the table independently. If you finish early, continue on to the following problems. • P. 119 #23, 28, 29, 30 • P. 122 #47, 48, 49 UNIT 1 KEY TOPICS 1. Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes 2. States of Matter: 1. Energy and Definite/Indefinite 3. Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures 1. Differentiate between them 2. Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous 4. Separation Techniques 1. Filtration, Chromatography, Crystallization, Distillation 5. Law of Conservation of Mass 1. Definition 2. Calculating change in mass and giving reasons for change. WE DO: WHITEBOARDS 1 • Review the sample data for the reaction of Baking Soda and Vinegar below. • Calculate ∆m . • Give one possible reason for the change in mass. Mass of system before change (g) 3. 89 g Mass of system after change (g) 3.84 g ∆m (g) WE DO: WHITEBOARDS 2 • Where would one expect the motion of the particles to be the highest? What state of matter is found at that point? • Identify the points where the matter has a definite/indefinite shape and a definite/indefinite volume. WE DO: WHITEBOARDS 3 • Classify the following as a physical or chemical property. • • • • Flammability Reactivity Color Mass • Classify the following as a physical or chemical change. • Melting Ice • Mixing Paint • Rust Forming • List 2 pieces of evidence that a chemical change has taken place. WE DO: WHITEBOARDS 4 • Draw molecular diagrams of an element, compound and a mixture WE DO: WHITEBOARDS 4 • Classify the following as an element, compound, heterogeneous mixture or homogeneous mixture 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. O2 (Oxygen) Sugar (C12H22O11) Powerade Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Steel (Fe, C, Cr) Fruit Salad WHITEBOARDS 5: • True or False. If it is false, correct it. • Filtration is commonly used to separate solids from liquids or gases e.g. in air conditioning and in wastewater treatment. • Distillation separates mixtures based on how fast they move through a liquid • Chromatography uses crystals to separate different substances. • Crystallization separates liquids based on the differences in their boiling points YOU DO: INDEPENDENT REVIEW PROBLEMS • Start with the set you struggle most with. 1. P/C Prop and Change: p. 55 #39-41, p. 56 #60-61, p. 57 # 77 2. States of Matter: p. 55 # 45, Rank the states of matter of chlorine in terms of increasing kinetic energy. 3. Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures: p. 55 # 53 (justify by drawing a particle diagram), #48, 50 4. Separation Techniques: p. 41 #17, 19, Is the crystal that forms during crystallization “pure”? Why or why not? 5. Law of Conservation of Mass: p. 57 # 80, 86, p. 59 #11 CLOSING • How can I best review for the Unit 1 Exam? • Homework: Review for the exam. The remaining review problems are posted on the website along with an answer key.