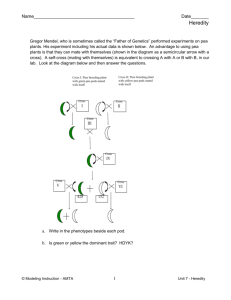
Single cross
advertisement

Hour Finger Hair – yes 1 Tongue Widow’s roll - yes Peak Free Earlobe Hitchhiker Finger Thumb - yes Length Different 11/12 11/12 3/12 11/12 2/12 10/12 3 18/21 17/21 8/21 20/21 11/21 10/21 5 23/25 19/25 15/25 17/25 16/25 14/25 Total: 52/58 47/58 26/58 48/58 29/58 34/58 2 Mendel’s Laws of Heredity Mendel artificially pollinated plants to produce crosses and documented results. All offspring were identical to parents – unexpected finding. Crosses of offspring yielded: 3/4 showed phenotype of dominant gene. 3 Mendel’s Laws of Heredity Law of Dominance: when an organism has 2 different alleles for a given trait, the allele that is expressed is considered dominant. The other allele is recessive. 4 Mendel’s Laws of Heredity Law of Segregation: when gametes are formed by a diploid organism, the alleles that control a trait separate from one another into different gametes, retaining their individuality. 5 Mendel’s Laws of Heredity Law of Independent Assortment: Members of one gene pair separate from each other independently of the members of other gene pairs. 6 Probability vs. Possibility Probability: chance that an event will happen, can be quantified, i.e. mathematical expression. This is not the same as possibility. 7 Single-Factor Crosses Single cross: single trait is followed from one generation to the next. AKA Monohybrid To solve single-factor crosses: 1. Assign a symbol for each allele. 2. Determine genotype of parents and indicate a mating. 3. Determine all possible types of gametes. 4. Determine all possible gene combinations. 5. Determine phenotypes of each gene combination. 8 Single-Factor Crosses Example: Tourette Syndrome autosomal dominant allele, 11q23 if both parents are heterozygous for this allele: do the parents have signs/symptoms of Tourette’s? what is the probability that the offspring will have s/s? 9 Punnett Square Tool to help determine probability of genotypes and phenotypes of progeny of a cross. Example: Tourette’s T t T t 10 Punnett Square Tool to help determine probability of genotypes and phenotypes of progeny of a cross. Example: Tourette’s T T t TT Tt t 11 Punnett Square Tool to help determine probability of genotypes and phenotypes of progeny of a cross. Example: Tourette’s T t T TT Tt t Tt tt 12