AOS 2 Pop Ballad
advertisement

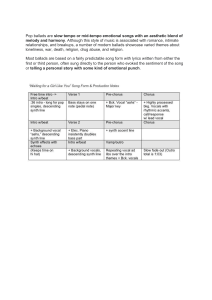
AOS 2 Pop Ballad * Ballads - songs that tell an emotional story. * Ballads have been around since at least the 15th century, when they would have been sung by wandering minstrels (troubadours). * Modern ballads (pop/rock) still tell stories - they are often slow and sad. * Ballad lyrics are usually about love. * Pop ballads follow a verse/chorus structure. Some songs also include a pre-chorus, middle 8/bridge, intro and outro/coda. * Each verse has the same rhythm and tune but with different lyrics. * The vocal part is very important, the accompaniment is usually quite simple and of lesser importance. * The main tune is called the melody, the backing is called the accompaniment. * Pop ballads are homophonic in texture (melody and accompaniment following a chord pattern). * Accompaniment - chord progressions are usually played on a guitar or piano. Other instruments may also be included such as strings or drum kit. A typical chord progression is G D Em C or I, V, VI, IV in any key. * 'Pop' is a shortened version of the word popular. * The tempo of a pop ballad can be moderato (moderato), andante (at a walking pace), adagio (leisurely) or lento (slow). Generally ballads are quite slow to emphasise the emotional meaning of the words. * The melody is sung legato (smoothly). * The melody line is usually sung by a solo singer however there are ballads sung by duos such as The Everly Brothers (1960s) or Paul Simon and Art Garfunkel (1970s). Duos would sing in close harmony. * Pop ballads are usually in 4/4 time, however there are ballads in other time signatures such as 3/4. * Voice types should be known for this area of study. Male: tenor (medium-high), baritone (medium-low), bass (low) and female: soprano (medium-high), Mezzo-soprano (medium), alto (medium-low). Alto is short for contralto. * Backing singers or even a whole choir can be used to help emphasise the lyrics. They are most often used in the choruses or towards the end of the song to heighten the drama. * Chords in the accompaniment are also usually legato in style with either soft repeating block chords, broken chords or arpeggios. * Key changes are quite common in ballads. The final chorus is often 'lifted' to enhance the emotion towards the end of the song. Changing key is called modulation. The key change will sound a little higher than the previous chorus. * Early ballads (15th century) would mostly be in strophic in form, this would sound like: verse 1, verse 2, verse 3 etc...other sections would not be included. Listening examples: Your Song by Elton John The man who can't be moved by The Script Someone like you by Adele Dream by The Everly Brothers Where do you go to my lovely (example in 3/4 time)