Properties of Stars
advertisement

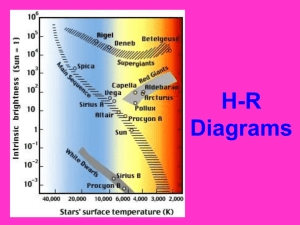
Video Field Trip Stars: Life and Death 1. What happens when stars run out of fuel? 2. What will happen when to the sun when it dies? Properties of Stars Chapter 25, Section 1 Characteristics of Stars • Color is a clue to a star’s temperature • Very hot (30,000 K) stars emit their light in the blue spectrum, red stars are much cooler, stars with temperatures between 5000 and 6000 K appear yellow • Binary Stars – pairs of stars, pulled together by gravity, that orbit each other • Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate – its mass • The mass of a body can be calculated if it is attached by gravity to a partner Star Temperature Binary Stars Concept Check • What is a binary star system? Measuring Distance to Stars • Parallax is determined by taking a picture of a star at one time, and another picture six months later; using the angle between its apparent shift, astronomers can determine how far away it is • The nearest stars have large parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to calculate • Light-Year – unit used to express stellar distance, the distance light travels in one year (~9.5 trillion kilometers) • Our closest star (besides the sun), Proxima Centauri, is about 4.5 light-years away from the sun Parallax Stellar Brightness • Apparent Magnitude – a star’s brightness as it appears to Earth • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, how hot it is, and how far away it is • Absolute Magnitude – how bright a star actually is • To determine absolute brightness, astronomers measure how large the star is, what temperature it is, and what its apparent brightness would be at 32.5 light-years Stellar Brightness Concept Check • What is the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude? Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • A Hertzsprung-Russell diagram shows the relationship between the absolute magnitude and temperature of stars • Main-Sequence Star – This category contains the majority of stars and runs diagonally from the upper left to the lower right on the H-R diagram • Red Giants – a large, cool star of high luminosity • Supergiants – a very large, very bright red giant star • Cepheid Variables – A star whose brightness varies periodically because it expands and contracts, a type of pulsating star • Nova – A star that explosively increases its brightness Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Concept Check • The H-R diagram shows the relationship between what two factors? Interstellar Matter • Nebulae – clouds of dust and gases in space • Emission nebulae consist largely of hydrogen, they absorb ultraviolet radiation emitted by nearby stars • Reflection nebulae merely reflect the light of nearby stars • Astronomers like to study nebulae because stars and planets form from them Dark Nebula – Horsehead Nebula Assignment • Read Chapter 25 Section 1 (pg. 700-706) • Do Section 25.1 Assessment #1-7 (pg. 706)