P A R T
2
Crimes & Torts
Crimes
Intentional Torts
Negligence & Strict Liability
Intellectual Property & Unfair
Competition
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Business Law, 13/e
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
C H A P T E R
6
Intentional Torts
“The good have no need of an advocate.”
Phocion
Learning Objectives
Definition
of Tort
Interference with Personal Rights
Interference with Property Rights
6-4
Definition of a Tort
Tort: civil wrong that is not breach of contract
Four types of wrongfulness are involved:
Intent
Recklessness
Negligence
Strict liability
Standard of proof: preponderance of the
evidence
6-5
Interference with Personal Rights
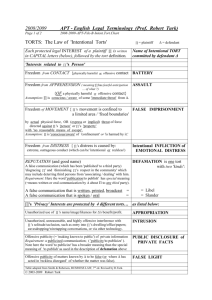
Battery
Intentional and harmful or offensive touching
of another without the person’s consent
Assault
6-6
Intentional attempt or threat to cause harmful
or offensive contact with another person
Attempt must cause reasonable apprehension
of imminent battery in other person’s mind
Interference with Personal Rights
Intentional Infliction of Emotional Distress
A recovery for emotional distress even if no
other tort is proven but wrongdoer’s conduct
must be outrageous before liability imposed
False Imprisonment
6-7
Intentional confinement of another for an
appreciable time without other’s consent
Confinement must be complete, though few
minutes is enough
Interference with Personal Rights
Defamation
Unprivileged publication of false statements
concerning another person
Truth is a complete defense
Invasion of Privacy
6-8
Includes intrusion on solitude (with
reasonable expectation of privacy), public
disclosure of private facts, false light publicity,
commercial appropriation of name or likeness
Defamation & Free Speech
In New York Times Co. v. Sullivan (1964), the
U.S. Supreme Court held that when a public
official brings a defamation case, s/he must
prove the usual elements of defamation and
actual malice (a First Amendment–based fault
requirement)
6-9
Actual malice means knowledge of falsity or
reckless disregard for the truth
Interference with Personal Rights
Misuse of Legal Proceedings
Harm that can result from wrongfully
instituted legal proceedings
Includes malicious prosecution, wrongful use
of civil proceedings, abuse of process
Deceit (Fraud)
6 - 10
Knowing or intentional misrepresentations,
often in connection with a contract
Interference with Property Rights
Trespass to Land
Unauthorized or unprivileged intentional
intrusion upon another’s real property
Requires physical entry onto plaintiff’s land
Private Nuisance
6 - 11
Interference with plaintiff ’s use and
enjoyment of the land
Does not require physical entry onto land
Interference with Property Rights
Conversion
6 - 12
Defendant’s intentional exercise of dominion
or control over plaintiff’s personal property
without plaintiff’s consent through
acquisition, removal, transfer to another,
withholding possession, destruction or
alteration, or use
Test Your Knowledge
True=A, False = B
Battery is the intentional and harmful touching of
another without consent
Assault occurs if the act causes a reasonable
apprehension of imminent battery in another
person’s mind
Courts do not allow recovery for emotional
distress unless the plaintiff was hospitalized
Libel refers to oral defamation and slander refers
to written defamation
6 - 13
Test Your Knowledge
Multiple Choice
The standard of proof a plaintiff must satisfy
in a tort case is the:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
6 - 14
beyond a reasonable doubt standard
more often than not standard
preponderence of the evidence standard
evidentiary standard
Test Your Knowledge
Multiple Choice
If a public official sues for defamation, s/he
must prove the elements of defamation and:
(a) extreme damages
(b) actual malice
The elements of defamation include:
(a) unprivileged publication
(b) false and defamatory statements
(c) without privilege
(d) both (a) and (b), but not (c)
6 - 15
Test Your Knowledge
Multiple Choice
Which of the following torts are not concerned
with interference with property rights?
(a)
(b)
(b)
(c)
6 - 16
invasion of privacy
private nuisance
trespass to land
conversion
Thought Question
For several intentional
torts, such as defamation
or false imprisonment,
there may be rights
belonging to the
defendant, such as free
speech or protection of
property. How should a
court or jury balance these
interests?
7 - 17