Acids and Bases
advertisement

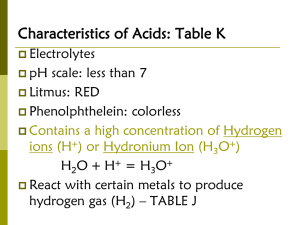
Acids and Bases Chapter 17 A special solution Acids and bases are ALWAYS in a water solution. Your body has water in it so they are always dangerous to living things. Bases are just as dangerous as acids. In low concentrations they are not that dangerous and found all over your house. Acids and Bases •Although they can be dangerous, acids and base do not react with or “eat” everything. •Neither has an effect on glass for example. turn litmus paper have a pH taste react with Aci Re less than 7 sour metals and bases D ase lue more than 7 bitter and feel slippery oils and acids B Common places to find acids and bases Acids Vinegar- acetic acid citrus fruits- citric acid carbonated drinks- carbonic acid Your stomach hydrochloric acid Bases Antacid tablets (calcium hydroxide) Windex- ammonia Oven cleanersodium hydroxide Draino – sodium hydroxide Homework Using the litmus paper provided in class check to see if two common items found in your house are acidic or basic. Report your findings on a piece of paper, and staple the litmus paper with it. You need to report what the items are and if they are acidic or basic. Please exercise caution and common sense. Do NOT test anything dangerous! Definitions Acid- a proton (H+) donor [force feeder] Acids produce H3O+ (hydronium) in water Base- a proton (H+) acceptor [thief] Bases produce OH- (hydroxide) in water Heat of solution Normally dissolving a substance is an exothermic process. You are normally increasing the state of entropy (measure of disorder) Which normally means you will release heat. There are exceptions, dissolving ammonium nitrate is an endothermic process Always do what you oughta … Always add acid to water Dissolving the acid in water releases heat If you have a lot of acid and a little water on top, the water typically boils quickly causing the hot acid to spray out. A lot of water on the bottom typically doesn’t boil if the acid is added slowly enough. Self dissociation of water. Some water will dissociate itself H2O +H2O H3O+ +OHin “pure” water you will find H3O+ has concentration of 1 x 10-7 M OH- has concentration of 1 x 10-7 M The product of the conc. of H3O+ and OHis always 1 x 10-14 [ ]-conc. [H3O+] [OH-] = 1 x 10-14 pH In any solution the H3O+ and OHconcentration is always very small. pH- method of representing the H3O+ concentration in a solution. pH = -log [H3O+] So the pH of water is… pH = - log 1 x10-7 pH = 7 What is a log log stands for logarithm ~we can use them to solve for an exponent. log xy = y log x For example log 1 x10-7 = -7 the log key on your calculator is log10 meaning it will cancel out a 10^. To reverse a log10 raise the whole thing to the 10th power (10^), this is an antilog The reversed pH equation is [H3O+] = 10^(-pH) pH values pH of 7 is neutral- equal [H3O+] and [OH-] below 7 is acidic, higher [H3O+] than [OH-] above 7 is basic or alkaline, higher [OH-] than [H3O+] pOH pOH = -log [OH-] pH + pOH = 14 pOH is the reverse of pH Above 7 is acidic, below 7 is basic pH problems What is the pH of a 2.4 x 10-4 M H3O+? pH = - log 2.4 x 10-4 pH = 3.6 What is the OH- concentration? [H3O+] [OH-] = 1 x 10-14 2.4 x10-4 [OH-] = 1 x 10-14 [OH-] = 4.2 x10-11 M What is the pOH? pOH = - log 4.2x10-11 pOH = 10.4 Backwards problem What is the pOH, [H3O+] and [OH-] of a solution with a pH of 8.7? [H3O+] = 10^(-pH) [H3O+] = 10-8.7 [H3O+] = 2.0 x 10-9 M 1.995…x10-9 [OH-] = 1 x 10-14 [OH-] = 5.0 x 10-6 M pOH + pH = 14 pOH = 5.3



![Acids and Bases Homework 3O+]? 1000x lower in [H ]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008705019_1-bcba3d05374bbb16a4904187ff3180b5-300x300.png)