Down Syndrome (Click to download)
advertisement

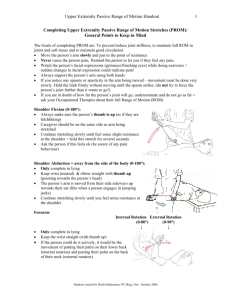
PRESENTATION ON DOWN SYNDROME M. ARUN KUMAR , B.O.T Occupational therapist Down syndrome is a genetic disorder that causes lifelong mental retardation, developmental delays and other problems. , Down syndrome occurs when there is an extra copy of chromosome 21. This form of Down syndrome is called Trisomy 21. The extra chromosome causes problems with the way the body and brain development Common physical signs Decreased muscle tone at birth Excess skin at the nape of the neck Flattened nose Separated joints between the bones of the skull (sutures) Single crease in the palm of the hand Small ears Small mouth Upward slanting eyes Wide, short hands with short fingers White spots on the colored part of the eye (Brushfield spots) Birth defects involving the heart, such as an atrial septal defect or ventricular septal defect Dementia may be seen Eye problems, such as cataracts (most children with Down syndrome need glasses) Early and massive vomiting, which may be a sign of a gastrointestinal blockage, such as esophageal atresia and duodenal atresia Hearing problems, probably caused by regular ear infections Hip problems and risk of dislocation Long-term (chronic) constipation problems Sleep apnea (because the mouth, throat, and airway are narrowed in children with Down syndrome) Teeth that appear later than normal and in a location that may cause problems with chewing Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism ROLE OF OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY FOR CHILDREN WITH DOWN SYNDROME self care skills (feeding, dressing, grooming etc.) fine and gross motor skills skills related to school performance (eg: printing, cutting etc.) Psycho-social adjustment through games and interactive projects, games, plays, and other activities. FINE AND GROSS MOTOR SKILLS REACH : Movement and stabilization of the arm and hand trunk rotation, full elbow extension, slight forearm rotation, and wrist stability, some degree of excess finger extension. GRASP: Attainment of an object with the hand along with reach thumb may be held flexed or abducted to other fingers CARRY: Transporting a hand held object from one place to another Frequently the forearm position and the wrist positionmust be able to be modified during the carry so the object remains in an optimal position. Also shoulder rotation patterns simultaneous with shoulder flexion and abduction. RELEASE: The intentional letting go of a hand –held object To place an object for release, the arm needs to move into position accurately and then stabilize as the fingers and thumb extend. IN-HAND MANIPULATION: The adjustment of an object within the hand after grasp BILATERAL HAND USE: Use of two hands to gather to accomplish an activity Ex- ball throwing skills child must bring the arm into a starting position, Then prepare for projection of the ball into space by moving first the trunk with the scapulohumeral joint then stabilize the shoulder while beginning to extend the elbow Then stabilize the elbow while moving the wrist from extension to a neutral position and simultaneously forcefully extending the fingers and thumb 1. TRUNK AND NECK CONTROL PRONE EXTENSION SUPINE FLEXION TRUNK ROTATION 2. SHOULDER AND ARM STABILITY 3.BIMANUAL COORDINATION 4.FUNCTIONAL GRASP FOREARM SUPINATION WRIST STABILITY ARCH DEVELOPMENT RADIAL-ULNAR DISSOCIATION OPEN WEB SPACE THUMB OPPOSTION IN-HAND MANIPULATION TRUNK AND NECK CONTROL: Strong trunk and neck muscles allow the child to sustain an upright posture and hold up the head and shoulders against gravity. PRONE EXTENSION: The child supports the body on the abdomen(stomach) in a prone position. ACTIVITIES: prone position on a scooter board swing, spinning board coloring, looking at books, playing board games Adaptive positions used SUPINE FLEXION: Supine flexion involves lying on the back in a supine position. ACTIVITIES: Children can reach high with their hands for objects like balls,balloons,bean bags . Can kick, touch, lift objects with their feet Abdominal exercises TRUNK ROTATION: Trunk rotation requires use of trunk extensor and flexor muscles. ACTIVITIES: Sitting /standing on ball and put rings Sitting on balance board do rotation SHOULDER AND ARM STABILITY: Shoulder stability adds to the trunks base of support, which is needed for hand mobility. ACTIVITIES: Attach push pins to a cork board on a wall. Loop colorful rubberbands around the push pins to make patterns Coloring BIMANUAL COORDINATION: Both hands must be used smoothly together for handwriting ACTIVITIES: clay activities, ball thronging FUNCTIONAL GRASP: FOREARM SUPINATION; An efficient pencil grasp the forearm is neither palm down nor palm up. partial suspiration (partial palm –up ) ACTIVITIES: Nut and bolts, clapping hands on the legs palm up and palm down in rhythmic patterns Using a toy screwdriver WRIST STABILITY: An efficient pencil grasp requires stability and 30 degrees of wrist extension ACTIVITIES: Beads ,clay activities ARCH DEVELOPMENT: Transverse (side to side) longitudinal oblique (fingertip to wrist) (diagonal) ACTIVITIES: Manipulating pegs of varying sizes cupping round objects in the palm shake dice,rice,marbles Pulling tiny objects with the thumb and little finger RADIAL-ULNAR DISSOCIATION: Stability on the ulna side (little finger) of the hand supports the skilled movements on the radial side(thumb) of the hand. ACTIVITIES: Using tools ,such as hairbrushes,toothbrushes,play hammers, drum sticks or play screwdrivers Using toy scissors Operating any squeeze or pump spray bottle or squirt gun Pulling ropes, tubing and thick objects OPEN WEB SPACE An open web space(the loose skin between index finger and thumb)in a pencil grasp allows nerves to send accurate sensory-motor information between the tips of thumb, index finger and middle finger, and the brain. ACTIVITIES: Weight bearing on an open hand Gripping or holding wide, hand-sized objects such as a cup, large block THUMB OPPOSITION • In an efficient pencil grasp the thumb rotates toward the little finger resulting in the tip of the thumb moving opposite the tip index finger ACTIVITIES: Using a toy requiring the thumb to push a button opposite the index and middle fingers. Pulling tiny objects out of putty or clay IN-HAND MANIPULATION TRANSLATION -FINGERS TO PALM ACTIVITIES: Getting a coin out of a change purse Crumpling paper Picking up and bringing small piece of food into the palm TRANSLATION-FINGERS TO PALM WITH STABILIZATION Getting two-or more coins out of a change purse, one at a time Picking up pegs or paperclips one at a time to hold two or more in the hand at one time TRANSLATION-PALM TO FINGERS: Moving an object to put it into a container Moving a food item to put it in the mouth TRANSLATION-PALM TO FINGERS WITH STABILIZATION Putting one utensil down where holding several SHIFT Turning pagers in a book Picking up sheets of paper, tissue papers Separating playing cards String beads SIMPLE OR COMPLEX ROTATION Removing or putting on a small jar lid Putting on or removing bolts from nuts Rotation of a crayon or pencil GROSS MOTOR SKILLS Movement of the large muscles in the arms, and legs. Abilities like Rolling Crawling Walking Running Jumping Hopping Skipping Tumble crawl Therapy ball activities vestibular dome Balance beam Walking balance board climbing wall Foam steps Balance bar Barrel activities Rotation board tunnel WHY ARE GROSS MOTOR SKILLS IMPORTANT FOR STUDENTS? Gross Motor skills and mastery of the large muscle groups provide the foundation for movement, coordination and balance. Safety, in the classroom, on the playground, and in the gym. Gross Motor Skills build the foundation for fine motor skills: If a child has difficulty sitting in a chair, writing and coloring will be more of a challenge. ACTIVITIES OF DAILY LIVING: Self – care skills like daily Brushing Toilet tasks Bathing Grooming Dressing Feeding Brushing Step by step method Initially with physical and verbal prompt slowly reduce prompt. 1.Get your toothbrush 2. Put toothpaste on 3. Brush upper surface of lower teeth 4. Brush outer surface of lower teeth 5. Brush inner surface of lower teeth 6. Brush outer surface of upper teeth 7. Brush inner surface of upper teeth 8. Spit 9. Rinse 10. Clean-up Bathing 1.Take water 2. Pouring water over chest 3. Pouring water over left shoulder right shoulder 4. Applying soap over chest left hand left leg right hand right leg back 5. Rubbing all the body part 6. Pouring water 7. Weeping Dressing frames 1. Dressing On/Off On lap method identifying front and back of the shirt or T-Shirt. For T-shirt On/Off lower Garments Eating Grooming Putting shoes VOCATIONAL REHABILITATION PAPER BASED WORK Book binding Paper bags preparation greeting cards making CRAFT AND TAILORING glass painting • • • • • embroidery soft toy making block painting fabric painting DOMESTIC ACTIVITY Tea and snacks preparation Chocolate preparation Chain making gardening AIDS TO DAILY LIVINGS Cross over grip bip gip built-up handle Long handled brushes and combs zip grips