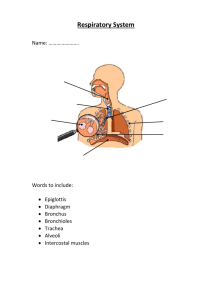
The Structures of the Lungs that Deliver Oxygen to the
advertisement
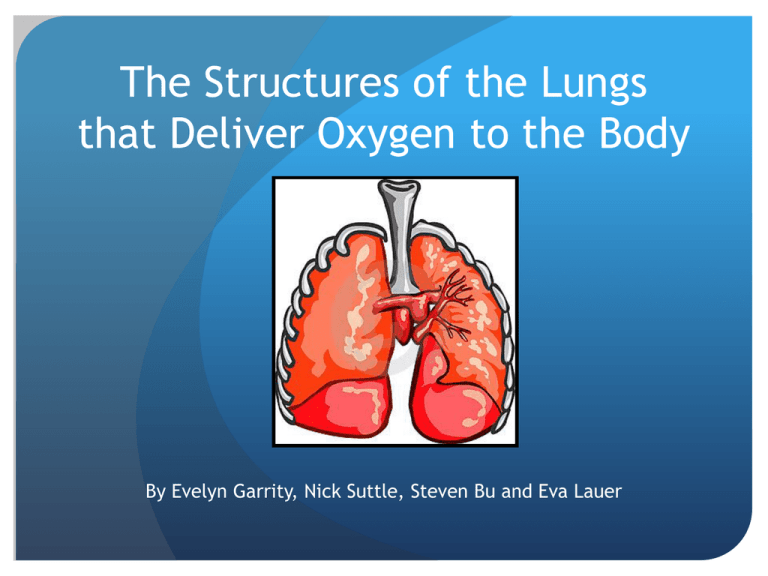
The Structures of the Lungs that Deliver Oxygen to the Body By Evelyn Garrity, Nick Suttle, Steven Bu and Eva Lauer Overall Function Bring oxygen from atmosphere into bloodstream and to bring carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the air Pathway for Air nasal cavities (or oral cavity) -> pharynx -> trachea -> primary bronchi (right & left) -> secondary bronchi -> tertiary bronchi -> bronchioles -> alveoli (site of gas exchange) Main Structures Primary bronchi Secondary bronchi Tertiary bronchi Bronchioles Alveolar sacs Alveoli Pulmonary Capillaries Cilia Photograph of Lungs Without Connective Tissue Alveoli Location Function Structure Alveoli (continued) Structural Component Functional Benefit Alveoli are arranged in grapelike clusters Greatly increases surface area for gas exchange Thin walls- one cell thick Increases rate of diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between alveoli and blood Densely covered with blood capillaries Large contact area between alveoli and blood supply Inner walls are lined with pulmonary surfactant Lowers the surface tension within the alveoli and prevents them from collapsing Walls of alveoli are moist Aids rate of diffusion of gases Alveoli contain stretch receptors Prevents alveoli from over-filling with air and causing damage to the thin walls Delivery Analogy Sources Used "Alveoli." Structure and Function. Cool School, Web. 7 Nov 2009. <http://www.coolschool.ca/lor/BI12/unit11/U11L03.htm>. No Author, . "Human Physiology." Respiration. Bio 301, Web. 6 Nov 2009. <http://people.eku.edu/ritchisong/RITCHISO//301notes6.ht m>. Starr, Cecie , and Ralph Taggart. Biology the Unity and Diversity of Life. Ninth. 1. United States: Brooks/Cole, 2001. Print. "Exchanging Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide ." Merck Manuals: Online Medical Library . Home Edition. NJ, USA: Merck and Co, Inc, 2009. Print.