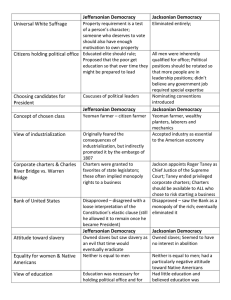
“The Jacksonian Democrats of the 1830s had virtually the same
advertisement

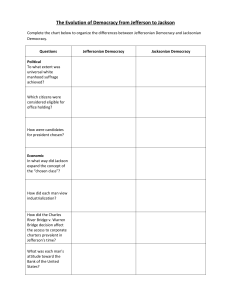
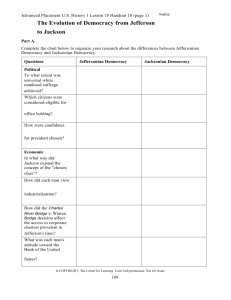
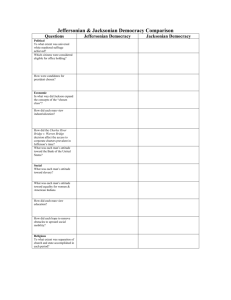
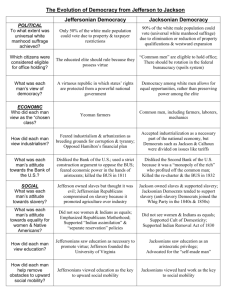
“The Jacksonian Democrats of the 1830s had virtually the same political views as the Jeffersonian Democrats of an earlier era.” Assess the validity of this statement. Sam DeWolfe, James Francis, and Graham Tyson Jeffersonian and Jacksonian Democracy are the same in just about every regard. Their views and goals as presidents were the same. Both are in favor of the common man and feel that it is the common people who should have the biggest influence on government, not the wealthy aristocrats. They also support states rights and feel that the federal government should not get involved with the states affairs. Both Jefferson and Jackson shared almost identical views on minorities. The Jeffersonian and Jacksonian Democracies contrasted and compared to each other in the area of politics and economics. First, the conditions in which a citizen was considered eligible for office holding was similar. In the Jeffersonian Democracy, an eligible citizen was one that was average rather than rich and well born. Likewise, Jackson declared all ordinary and intelligent (white) citizens equally qualified to serve. However, he eventually started what is known as the "spoils system" in which longterm officeholders were removed for rotation. Next, how the candidates for President were chosen was done differently. For example, in Jefferson's time the two highest voted candidates became the President and the Vice-President of the United States. On the contrary, in the age of Jackson, a candidate was chosen by a nominating convention and the President and Vice-President ran for their offices separately. Last, each man's attitude toward the Bank of the United States was comparable. Jefferson encouraged State banks and was originally opposed to the national bank. Similarly, Jackson and his followers strongly opposed the Second Bank of America. He won the "Bank War" by having federal income deposited in state banks, while he continued to draw money out of the national bank. In summary, the political and economic conditions of the Jeffersonian and Jacksonian Democracies were equally related and different. Conclusion In conclusion, it is quite clear to see how sharp and distinct the similarities and differences were between the Jeffersonian and Jacksonian Democracies. More specifically, they are shown in the areas of politics, economics, social life, and religion. Indeed, their viewpoints, opinions, and ideas all helped establish the strong democracy that America has today.