Retailing
advertisement

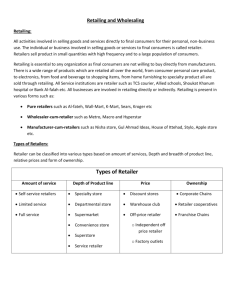
Retailing What is Retailing? • Retailing includes all the activities involved in selling products or services directly to final consumers for their personal, nonbusiness use. 11-2 Types of Retailers Retailers are classified based on: Amount of Service They Offer Breadth & Depth of Product Lines Relative Prices Charged How They Are Organized 11-3 Amount of Service • Self-Service Retailers: – Serve customers who are willing to perform their own “locate-compare-select” process to save money. • Limited-Service Retailers: – Provide more sales assistance because they carry more shopping goods about which customers need information. • Full-Service Retailers: – Usually carry more specialty goods for which customers like to be “waited on.” 11-4 Product Line Classification Specialty Stores: Carry narrow product lines with deep assortments within those lines, e.g jewelry, Books stores ,sports goods Single line-shopper stop Limited line- raymonds Super speciality-all brands Department Stores: Carry a wide variety of product lines—typically clothing, home furnishings, and household goods. Each line is operated as a separate department managed by specialist buyers or merchandisers. E.g- akbarally’s 11-5 Product Line Classification Supermarket: Large, low-cost, low-margin, high-volume, self-service store that carries a wide variety of food, laundry, and household products.e.g- foodland & garware Convenience Stores: Small stores located near residential areas that are open long hours 7 days a week and carry a limited line of high-turnover convenience goods. 11-6 Web-Based Supermarket In the battle for “share of stomachs,” Safeway and many large supermarkets have added Web-based sales. 11-7 Product Line Classification Superstores: Much larger than regular supermarkets and offer a large assortment of routinely purchased food products, nonfood items, and services. Offer dry cleaning, shoe repair Category Killers: Giant specialty stores that carry a very deep assortment of a particular line and is staffed by knowledgeable employees. e.g toys R U, home depot 11-8 Discussion Question • What type of impact did the emergence of category killers have on department stores? 11-9 Relative Prices Classification Discount Store: A retail institution that sells standard merchandise at lower prices by accepting lower margins and selling at higher volume. e.g walmart, big bazaar •Sells goods at discounted price •Carries national brands •Operational costs r min. as self service & no frills •Location in low rent areas, it draws customers from distant areas 11-10 Off-Price Retailer: Retailer that buys at less-than-regular wholesale prices and sells at less than retail. Examples are factory outlets, independents, and warehouse clubs. Factory Outlet: Off-price retailing operation that is owned and operated by a manufacturer and that normally carries the manufacturer’s surplus, discontinued, or irregular goods. Independent Off-Price Retailer: Off-price retailer that is either owned and run by entrepreneurs or is a division of a larger retail operation. 11-11 Factory Outlets Factory outlet malls and value-retail centers have blossomed in recent years, making them one of retailing’s hottest growth areas. 11-12 Relative Prices Classification Warehouse Club: Off-price retailer that sells a limited selection of brand-name grocery items, appliances, clothing, at deep discounts to members who pay annual membership fees. 11-13 Organizational Classification Chain Stores: Two or more outlets that are owned and controlled, have central buying and merchandising, and sell similar lines of merchandise. Voluntary Chain: A wholesaler-sponsored group of independent retailers that engages in bulk buying and common merchandising. 11-14 Organizational Classification Retailer Cooperative: A group of independent retailers that bands together to set up a jointly owned, central wholesale operation and conducts joint merchandising and promotion efforts. Franchise: A contractual association between a manufacturer, wholesaler, or service organization (a franchiser) and independent businesspeople (franchisees) who buy the right to own and operate one or more units in the franchise system. 11-15 Franchising Franchisees now command 35% of all retail sales in the U.S. Subway is one of the fastest growing franchises, with nearly 20,000 shops in 74 countries. 11-16 Retailer Marketing Decisions 11-17 Price, Promotion, & Place Decisions Price policy must fit its target market and positioning, product and service assortment, and competition Can use any or all of the promotion tools—advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, public relations, and direct marketing—to reach consumers Location-road infrastructure,power and public transport Visibility-ability to see the store,parking lo 11-18 Mall of America • The Mall of America “megamall” contains: – Over 520 specialty stores – 49 restaurants – 7-acre indoor theme park – Underwater World featuring hundreds of marine specimens – A two-story miniature golf course. 11-19 Business model • Low margin-high turnover – High operational efficiency – Economic drivers- high inventory turnover, low operating cost – Operating drivers- merchandise ,cost, sales productivity mgmt. 11-20 Trends in retailing • New retails forms& • • • • • • • combinations-gas stations include food stores Shorter life span Electronic age-non store retailing via mail, tv, phones Intertype competition-discount store vs deptt. Store Deptt. Stores gave way to malls Technology-Pcs for forecast, control inventory costs, scanning systems. Unique formats & strong brand positioning. Mc, gap Establishments provide people to congregate e.g tea shops, café coffee day, book stores, pubs 11-21 Wholesaling • Wholesaling includes all activities involved in selling goods and services to those buying for resale or business use. • Difference b/w wholesalers & retailers – Less attention to promos, atmosphere, location then retailers – Transactions are larger ,cover large trade area – Govt. dealing will be different 11-22 Functions Provided by Wholesalers Management Services & Advice Selling & Promoting Buying & Assortment Building Market Information Bulk-Breaking Risk Bearing Warehousing Financing Transportation 11-23 Types of Wholesalers • Merchant Wholesalers- independently owned business take title to merchandise they handle – Largest group of wholesalers – Account for 50% of wholesaling – Two broad categories: • Full-service wholesalers • Limited-service wholesalers – Cash n carry ,truck wholesalers, drop shippers, rack jobbers ,producers cooperatives, mail order wholesalers 11-24 Types of Wholesalers • Brokers – Do not take title to goods, Perform fewer functions – Brokers bring buyers and sellers together – Paid by party who hired them – Do not carry inventory, no finance, risk – E.g food brokers, real estate, insurance • Agents – Agents represent buyers or sellers on more permanent basis – Manufacturers’ agents – written agreement on • Pricing • territories • delivery, order procedure – Apparel, furniture, electrical goods 11-25 Types of Wholesalers • Manufacturers’ Sales Branches and Offices – Wholesaling by sellers or buyers themselves rather than through independent wholesalers. 11-26 Wholesaling In Action Grainger is by far the world’s leading wholesaler of maintenance, repair, and operating supplies. 200,000 products,520 branches Satellite network Online ordering 11-27 Wholesaler Marketing Decisions 11-28 11-29 Trends in Wholesaling Must Constantly Improve Services and Reduce Costs Distinction Between Large Retailers & Wholesalers is Blurry Will Continue to Increase the Services Provided to Retailers Wholesalers Are Now Going Global 11-30