HR Diagram
advertisement

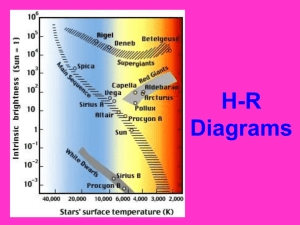
HR Diagram Characteristics of Stars Temperature/Color Mass Luminosity • Absolute Magnitude • Apparent Magnitude The Spectral Sequence O B Hottest 50,000K Bluest A F G K M L Coolest 1300K Reddest Oh Boy, an F grade kills me, Louis! The mass of a star determines the length of its life cycle (how long will it burn). Sun-like Stars Up to 1.5 times the mass of the Sun Huge Star From 1.5 to 3 times the mass of the Sun Giant Star Over 3 times the mass of the Sun Sun/main sequence star Stellar Nebula Red Giant Planetary Nebula Protostar (nursery) Massive Star ( Huge & Giant) Neutron Star Red Supergiant Supernova Black Hole White Dwarf Variables which affect a star’s brightness: Star size Distance from Earth Star temperature Absolute Magnitude vs. • Actual Brightness: How large and hot a star is in relation to other stars. Apparent Magnitude • Apparent Brightness: The amount of light received on Earth from a star. Which star looks like it is giving off more light? •But, which star is actually giving off more light? Luminous/Brighter Stars Dim Stars Hotter Stars Cooler Stars O B A F G K M • Life Cycle of Stars Interactive Investigation http://aspire.cosmic-ray.org/labs/star_life/starlife_main.html • HR Diagram Interacative Lab http://aspire.cosmic-ray.org/labs/star_life/hr_interactive.html • Stellar Evolution/H-R Diagram Simulation http://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/courses/astro101/java/evolve/evolve.htm • Astronomy Place Tutorials http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_bennett_cosmicpers_2/medialib/tutorials/inde x.html