Star Classification Lab: H-R Diagram Worksheet
advertisement

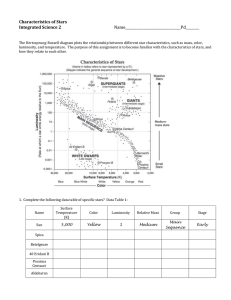
Name: __________________________________ Period: _______ Date:_____________ LAB # ___________ All labs must be completed in pencil CLASSIFICATION of STARS Introduction: In the beginning of the 20th century, two astronomers, Hertzsprung and Russell developed a system of classifying stars based on their color, temperature, spectral class, and size. This graph is called the H-R diagram. The H-R diagram plots a star’s luminosity; the energy released by a star as compared to the Sun’s energy released; against its spectral class which is determined by temperature. Different temperature ranges appear in different sections of the visible spectrum. Hotter stars appear blue, while cooler stars appear red. Stars get their energy and ability to “shine” by a processes called nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion is when elements in stars combine to make a heavier element. Hydrogen atoms fuse together to form Helium and this releases a lot of energy. Stars are categorized into spectral classes named “giants,” “super giants,” “main sequence,” and “white dwarfs.” These names help to determine the age of stars based on their temperature and luminosity. Most stars (about 90%) including our Sun are main sequence stars. Objective: Using the data tables and the graph provided, you will chart actual stars based on their temperature and luminosity to determine their spectral class. Procedure: Read the directions carefully and check them off as they are completed. 1. Plot the stars found in tables 1 – 4 on the blank H-R diagram provided (one per group) a. Note Y-axis of the H-R diagram is logarithmic. This means every bold line on the Y-axis increases the scale by a power of ten! (ex: 10; 100; 1,000; 10,000 ….) 2. Plot the main sequence stars from Table 1 in pencil 3. Plot the red giant stars from Table 2 in red 4. Plot the blue giant stars from Table 3 in blue 5. Plot the dwarf stars from Table 4 in black a. Split this task up within the members of your lab group b. Use your best estimation skills to plot the data that has been given 6. Refer to Table 5 and very lightly shade in the chart to reflect the temperature of each type of star cluster 7. Using page 15 of your ESRT label each area on your graph with the appropriate star class 8. Plot the following stars from your ESRT onto your graph in pencil and label them a. Barnard’s star b. Polaris 9. Answer the questions that follow TABLE 1 – Main sequence stars STAR NAME Regulus TEMPERATURE K (kelvin) 12000 LUMINOSITY 85 Beta Tauri 12000 700 Vega 9700 250 Castor 9200 300 Sirius A 9200 50 Altair 7750 30 Procyon A 6500 65 Alpha Centauri A 5900 2 The Sun 5900 1 Tau Ceti 4900 0.7 Epsilon Eridani 4600 0.5 Cygni A 3800 0.08 Alpha Centauri B 4000 0.7 Kapteyn’s Star 3300 0.005 Lacaille 8760 3400 0.04 Lacaille 21185 3200 0.007 TABLE 2 – Red giant stars STAR NAME Capella TEMPERATURE K (kelvin) 6000 LUMINOSITY 350 Pollux 3800 60 Arcturus 4600 120 Aldebaran 4000 110 Antares 3400 7500 Betelgeuse 3200 15000 TEMPERATURE K (kelvin) 18000 LUMINOSITY 300 Spica 19500 700 Achernar 17500 1100 Beta Crucis 21000 10000 Alpha Crucis 19500 5000 Rigel 11500 30000 Beta Centauri 21000 1100 TEMPERATURE K (kelvin) 8200 LUMINOSITY 0.005 6500 0.02 TABLE 3 – Blue giant stars STAR NAME Bellatrix TABLE 4 – Dwarf stars STAR NAME Sirius B Procyon B TABLE 5 STAR TEMPERATURE 2000 – 5000 COLOR RED 5000 – 7500 YELLOW 7500 – 11000 WHITE 11000 – 30000 BLUE Name: __________________________________ Period: _______ Date:_____________ LAB # ___________ All labs must be completed in pencil CLASSIFICATION of STARS Discussion Questions: Answer the following questions in FULL AND COMPLETE sentences. The lab will not be graded unless it follows the proper format. 1. Describe the process in which stars get their energy. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What are the four characteristics in which stars are classified on the H-R diagram (re-read the intro for help). ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Observe the X-axis. What do you notice is unusual about the X-axis of the H-R diagram? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Describe the relationship between the following using a one sentence statement: Use words such as: increase; decrease; greater than; less than Ex: As rain increases, plant growth increases a. Star size (see your ESRT for this info.) and luminosity ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 5. How are Polaris and the Sun similar? How are they different? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Our Sun is halfway through its lifecycle. Explain which stages it will evolve into during the last half of its life (use the reading and diagram on page 1 to help you). ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Name: __________________________________ Period: _______ Date:_____________ LAB # ___________ All labs must be completed in pencil CLASSIFICATION of STARS Discussion Questions: KEY 1. Describe the process in which stars get their energy. Stars get their energy by nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion is when hydrogen atoms combine to make heavier atoms such as helium. 2. What are the four characteristics in which stars are classified on the H-R diagram (re-read the intro for help). The 4 characteristics in which stars are classified are color, temperature, spectral class, and size. 3. Observe the X-axis. What do you notice is unusual about the X-axis of the H-R diagram? The x-axis of the H-R Diagram is unusual because the numbers are decreasing. The x-axis is also unusually spaced. 4. Describe the relationship between the following using a one sentence statement: Use words such as: increase; decrease; greater than; less than Ex: As rain increases, plant growth increases a. Star size (see your ESRT for this info.) and luminosity As star size increases, luminosity increases. 5. How are Polaris and the Sun similar? How are they different? Polaris and the Sun have similar temperatures, but different luminosities and sizes. 6. Our Sun is halfway through its lifecycle. Explain which stages it will evolve into during the last half of its life (use the reading and diagram on page 1 to help you). The Sun is currently a main sequence star which is approximately an “adult.” The Sun will age into a giant, perhaps a super giant, and eventually a dwarf.