Respiratory System
advertisement

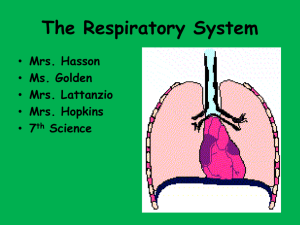
Respiratory System Meggie Devlin, Hannah Dangler, Bryan Kennedy, and Lexi Jones Process of Inhalation • • • Air enters through nose or the mouth o if enters nose, air is moistened, warmed, and filtered by cilia Air passes through pharynx o epiglottis opens to allow air into larynx (voice box) Air enters trachea o branches off into two airways (the bronchi) which lead to the lungs • In lungs, air moves through finer branches of the bronchi, called the bronchioles which end in cup-shaped alveoli What is the diaphragm? • • • Muscular partition between the chest and abdominal cavities o positioned below the lungs Inhalation o diaphragm contracts and flattens o ribs to lift up and out Changing pressure o lungs must also expand with contracting diaphragm allows air to flood into the lungs Main Components of Lungs • • • • • • Primary Bronchus Secondary Bronchus Bronchioles Alveoli Pulmonary Capillaries Bronchi • Primary Bronchus o connects trachea to lungs • Secondary Bronchus o connects primary bronchus to bronchioles • Bronchioles o have alveoli at end that are key to transportation of O2 and CO2 to rest of body • • • Alveoli each lung has about 300 million alveoli tiny air sacs alveoli=covered in capillaries, which connect to a network of arteries and veins that move blood through the body STRUCTURE OF ALVEOLI ● Thin walls for diffusion ○ easy diffusion ● Large surface area in relation to volume ○ more diffusion occurring Gas Exchange in Lungs • Gases move through simple diffusion o always travel from higher partial pressure to lower ● In diffusion, gas travels through two cell-thick walls making up the respiratory membrane ● Partial pressure of oxygen in hemoglobin solution determines how much oxygen can be carried Pressure Gradient in Lungs Gas Partial Pressure in Blood Action Partial Pressure in Alveolar Space Carbon Dioxide 45 mm Hg → 40 mm Hg Oxygen ← 104 mm Hg 40 mm Hg Components of Blood • • • Red Blood cells White Blood cells Platelets • Yellow Liquid Plasma o regulate bleeding and clotting Red Blood Cells • • • • Shape: flat, doubly concave cells Carries oxygen and nutrients associated in hemoglobin Lacks a nucleus Hemoglobin enhances the oxygen carrying capability of blood White Blood Cells • • • • Larger than red blood cells Nucleus, lack hemoglobin Protect against infections Squeeze through capillary pores and fight infectious diseases Platelets • • • • Stop bleeding, help to heal wounds Result as of cell fragmentation Stick and adhere to tears in blood vessels Release clotting factors red blood cell platelet white blood cell Gas Exchange & Transport of Gases • Gas Exchange: process through which different gases are transferred in opposite directions across a specialised respiratory surface o O2 • and CO2 bind to hemoglobin in red blood cells Transport of Gases: transport of oxygen to body cells in the blood o body transports most of the oxygen using the transport protein hemoglobin (red blood cells) How is it connected to the circulatory system? • system begins with inhalation o inhale → diaphragm contract and pulls air into the lungs • • respiratory system brings in oxygen from air outside the body circulatory system moves the oxygen throughout the body using hemoglobin in red blood cells References (1) "Human Physiology - Respiration." Human Physiology - Respiration. N.p., n.d. Web. 06 Nov. 2013. <http://people.eku.edu/ritchisong/301notes6.htm>. (2) Starr, Cecie, and Ralph Taggart. "Chapter 41.4." Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Pub., 1992. N. pag. Print. (3) "Lungs." InnerBody. InnerBody.com, n.d. Web. 06 Nov. 2013. <http://www.innerbody.com/anatomy/respiratory/lungs>. (4) "The Circulatory, Respiratory, and Digestive Systems." The Circulatory, Respiratory, and Digestive Systems. University of Illinois, n.d. Web. 6 Nov. 2013. <http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/lecturesf04am/lect20.htm>. (5) Starr, Cecie, and Ralph Taggart. "Chapter 41.5." Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Pub., 1992. N. pag. Print.