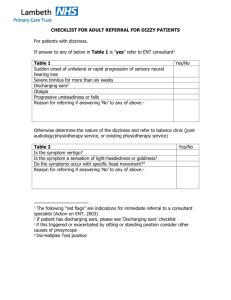
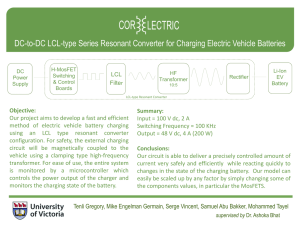
Integration Options into ERCOT systems
advertisement

Integration Options into ERCOT systems Sai Moorty ERCOT Photovoltaic Resource CIM Model (Network Model Management System-NMMS) – Similar to current Generation Resource • Single point of injection into grid • Single Settlement Point • High and low limits – There are other attributes (or lack of) that need more discussions when it comes to modeling: • • • • • • New Resource Type No Synchronous machine with inertia Invertor modeling Reactive capability curve different Short circuit parameters Other? 2 Photovoltaic Resource Energy Management System (EMS) Applications like State Estimation, Power Flow, Contingency Analysis will have no change or minimal change. Currently identified EMS applications that need to be modified or new are: – MODIFICATION: Ancillary Service Capacity Monitor • There may be a need to modify this application to take into account intermittent nature of solar due to cloud cover etc. Note: currently Wind Resources have resorted to not carrying Ancillary Service Responsibilities. – MODIFICATION: Online Transient/Voltage Stability Analysis • There may be a need to change this application if current capabilities cannot model Photovoltaic Resource correctly 3 Photovoltaic Resource Energy Management System (EMS) – NEW: Solar potential forecasting application • Short Term : 5 minute granularity for a rolling window looking out for the next 2 hours • Mid Term : 1 hour granularity for a rolling window looking out for the next 2-7 days. • Input to Solar potential forecasting application (every 30 seconds via telemetry or other process?): – Cloud cover monitor – Solar farm latitude, longitude, alignment of solar panels, and placement angle off horizontal – Air temperature, Back of panel temperature – Wind speed, Wind direction – Global horizontal Irradiance – For concentrated PV installations, in addition to the above, direct normal Irradiance shall be telemetered 4 Photovoltaic Resource Market Management System (MMS) The products that are available are Energy (MWHr) and Ancillary Service Capacity (MW). • Energy (MWHr) is procured in the Day-Ahead Market (DAM) in terms of MW on a hourly granularity • Energy (MWHr) is procured in the Real-Time Maket (SCED) in terms of MW every 5 minutes and is settled on a 15-minute basis • Ancilary Service Capacity (Regulation Up, Regulation Down, Responsive Reserve, Non-Spin) is procured in terms of MW on a hourly granularity in the Day-Ahead Market, Supplementary Ancillary Service Market in the adjustment period and Resources can assume AS responsibility via bilateral trades 5 Photovoltaic Resource Market Management System (MMS) As far as the Day-Ahead Market and Real-Time Markets, our current understanding is that Photovoltaic Resources will not require any modifications to the Market Systems. Expectations is that Photovoltaic Resources will be very similar to Wind Resources as far as the Market Systems (including Reliability Unit Commitment) are concerned. 6 Energy Storage Resource Salient Features of a Energy Storage resource • Do not generate electrical energy like power plants (burning fuel or converting external energy source like wind) – Electrical energy is produced by time-shifting i.e. electrical energy withdrawn from the grid over a particular time period and stored (in some form) and subsequently injected back into the grid at another later period of time • Electrical energy consumed is not like loads – Electrical energy not used for producing products or heating or cooling or lighting. Electrical energy is stored for later release back into the grid. • Bi-directional, i.e. they can produce or consume electrical energy • Electrical energy can be stored for some period of time 7 Energy Storage Resource Salient Features of a Energy Storage resource (continued) • Typically, are fast in responding to control signals – Discharge and charging rates are high. • Typically, Reactive capability in all four quadrants 8 Energy Storage Resource – Modeling parameters Parameter Physical Unit Description Generation Resource Equivalent Max Storage Capacity MWHr Max nameplate energy storage capability n/a Max Storage Level MWHr Max operating energy storage capability n/a Min Storage Capacity MWHr Min nameplate energy storage capability n/a Min Storage Level MWHr Min operating energy storage capability n/a Storing Energy Efficiency % n/a Max MW Discharging Power Min MW Discharging Power MW Once fully charged, the Percentage of energy compared to max storage level, needed to remain charged at max storage level Max operating MW discharging power Min operating MW discharging power MW 9 HSL LSL Energy Storage Resource – Modeling parameters Parameter Physical Unit Description Generation Resource Equivalent Discharging Ramp Rate MW/min Rate for discharging in MW/min Up Ramp Rate Min Duration of discharge min Min time to fully discharge from Max Storage Level n/a Discharging efficiency % Percentage of energy losses during discharge n/a Max operating MW charging power Min operating MW charging power MPC Max MW Charging Power MW Min MW Charging Power MW Charging Ramp Rate MW/min Rate for charging in MW/min Down Ramp Rate Min Duration of charge min Min time to fully charge from Min Storage Level n/a Charging efficiency % Percentage of energy losses during charge n/a 10 LPC Energy Storage Resource – Modeling parameters Parameter Physical Unit Description Generation Resource Equivalent Min Time in Charging Mode Min Time in Discharging Mode Min Time in Offline Mode min Min Up Time Max Number of Off-ToCharging Transitions Max Number of Off-ToDischarging Transitions Time to transition from charging to discharging Time to transition from discharging to charging TBD min min Minimum time to be in charging mode Minimum time to be in discharging mode Minimum time to be in offline mode Maximal number of charging cycles in a day Maximal number of discharging cycles in a day min Min Up Time Min Down Time Max Number of Starts Max Number of Starts n/a min 11 Energy Storage Resource CIM Model (Network Model Management System-NMMS) – Detailed discussions with Resource Entities, QSEs are required to get a common understanding of the modeling requirements – Modeling of Storage Resources can also include aggregation of small storage resources (similar to Aggregated Load Resources) 12 Energy Storage Resource Energy Management System (EMS) Applications like State Estimation, Power Flow, Contingency Analysis will have no change or minimal change. Currently identified EMS applications that need to be modified or new are: – MODIFICATION: Ancillary Service Capacity Monitor • There may be a need to modify this application to take into account the energy storage level. – MODIFICATION: Online Transient/Voltage Stability Analysis – There may be a need to change this application if current capabilities cannot model Energy Storage Resource correctly 13 Energy Storage Resource Energy Management System (EMS) – NEW: Telemetered quantities – for example • Stored Energy Level 14 Energy Storage Resource Market Management System (MMS) The products that are available are Energy (MWHr) and Ancillary Service Capacity (MW). • Energy (MWHr) is procured in the Day-Ahead Market (DAM) in terms of MW on a hourly granularity • Energy (MWHr) is procured in the Real-Time Maket (SCED) in terms of MW every 5 minutes and is settled on a 15-minute basis • Ancilary Service Capacity (Regulation Up, Regulation Down, Responsive Reserve, Non-Spin) is procured in terms of MW on a hourly granularity in the Day-Ahead Market, Supplementary Ancillary Service Market in the adjustment period and Resources can assume AS responsibility via bilateral trades 15 Energy Storage Resource Market Management System (MMS) Due to the limited energy available from Energy Storage Resources, care will have to be taken as to which products are most suitable. There are compliance penalties if Resources do not perform to their obligations Currently there is a pilot project in the works “ Fast Responding Regulation Service” to evaluate the performance of Resources capable of extremely fast regulation service. Storage Resources like Batteries can participate. Introduction of any new technology neutral product will need to be vetted through the stakeholder process 16 Summary ERCOT System Photovoltaic Energy Storage Comment Registration (RARF) Small-Medium Large Dependent on modeling NMMS Medium Large EMS Medium Large MMS Small Large S&B ? ? Schema changes will need to be scalable to anticipated other new types of Resources Additional telemetry and new applications Photovoltaic similar to Wind from MMW perspective Energy Storage will require significant changes Depends on outcome of stakeholder process TBD ? ? 17