Business Driven
Technology
Unit 2
Exploring Business Intelligence
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
Unit Two
O Chapter Six – Valuing Organizational
Information
O Chapter Seven – Storing Organizational
Information – Databases
O Chapter Eight – Accessing Organizational
Information – Data Warehouse
7-2
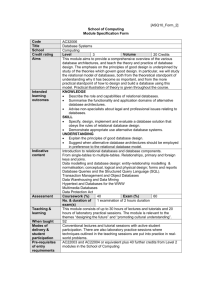
Chapter 7
Storing Organizational
Information—Databases
7-3
LEARNING OUTCOMES
1. Describe a database, a database management
system, and the relational database model
2. Identify the business advantages of a
relational database
3. Explain the business benefits of a data-
driven website
4. Explain why an organization would want to
integrate its database
7-4
STORING INFORMATION IN A
RELATIONAL DATABASE
O Information is everywhere in
an organization
O Information is stored in
databases
O Database – maintains
information about various types
of objects (inventory), events
(transactions), people
(employees), and places
(warehouses)
7-5
STORING INFORMATION IN A
RELATIONAL DATABASE
O Database management systems (DBMS) –Allows users
to create, read, update, and delete data in a relational
database
7-6
STORING INFORMATION IN A
RELATIONAL DATABASE
O Data element – The smallest or basic unit of
information
O Data model – Logical data structures that
detail the relationships among data elements
using graphics or pictures
O Metadata – Provides details about data
O Data dictionary – Compiles all of the
metadata about the data elements in the
data model
7-7
Storing Data Elements in
Entities and Attributes
O Entity – A person, place, thing,
transaction, or event about which
information is stored
O The rows in a table contain entities
O Attribute (field, column) – The data
elements associated with an entity
O The columns in each table contain
the attributes
O Record – A collection of related data
elements
7-8
Creating Relationships
Through Keys
O Primary keys and foreign keys
identify the various entities (tables)
in the database
O Primary key – A field (or group of fields)
that uniquely identifies a given entity in
a table
O Foreign key – A primary key of one table
that appears an attribute in another
table and acts to provide a logical
relationship among the two tables
7-9
Keys and Relationships
7-10
USING A RELATIONAL DATABASE
FOR BUSINESS ADVANTAGES
O Database advantages from a business perspective include
7-11
Increased Flexibility
O A well-designed database should
O Handle changes quickly and easily
O Provide users with different views
O Have only one physical view
O Physical view – Deals with the physical
storage of information on a storage
device
O Have multiple logical views
O Logical view – Focuses on how individual
users logically access information to
meet their own particular business
needs
7-12
Increased Scalability and
Performance
O A database must scale to meet
increased demand, while
maintaining acceptable
performance levels
O Scalability – Refers to how well a
system can adapt to increased
demands
O Performance – Measures how quickly a
system performs a certain process or
transaction
7-13
Reduced Information Redundancy
O Databases reduce information
redundancy
O Information redundancy – The
duplication of data or storing the
same information in multiple
places
O Inconsistency is one of the
primary problems with
redundant information
7-14
Increase Information
Integrity (Quality)
O Information integrity –
measures the quality of
information
O Integrity constraint – rules
that help ensure the quality
of information
O Relational integrity constraint
O Business-critical integrity
constraint
7-15
Increased Information
Security
O Information is an organizational asset and
must be protected
O Databases offer several security features
O Password – Provides authentication of the user
O Access level – Determines who has access to the
different types of information
O Access control – Determines types of user access,
such as read-only access
7-16
DRIVING WEBSITES
WITH DATA
O Data-driven websites – An interactive website kept
O
O
O
O
O
constantly updated and relevant to the needs of its
customers using a database
Content creator
Content editor
Static information
Dynamic information
Dynamic catalog
7-17
DRIVING WEBSITES
WITH DATA
7-18
DRIVING WEBSITES
WITH DATA
O Data-driven website advantages
O Easy to manage content
O Easy to store large amounts of data
O Easy to eliminate human errors
7-19
DRIVING WEBSITES
WITH DATA
7-20
Integrating Information
among Multiple Databases
O Integration – allows separate systems to
communicate directly with each other
O Forward integration – takes information entered
into a given system and sends it automatically to
all downstream systems and processes
O Backward integration – takes information entered
into a given system and sends it automatically to
all upstream systems and processes
7-21
Integrating Information
among Multiple Databases
O Forward integration
7-22
Integrating Information
among Multiple Databases
O Backward integration
7-23
Integrating Information
among Multiple Databases
O Building a central repository specifically for
integrated information
7-24
LEARNING OUTCOME REVIEW
O Now that you have finished the
chapter please review the learning
outcomes in your text
7-25