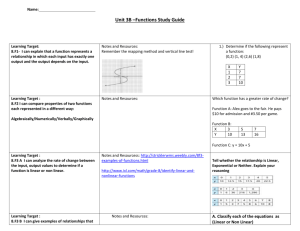
Strat Mgmt Slides

Strategic Management
GM 105
Dr. Lindle Hatton
CANOE THEORY
Think of your organization as a long canoe
The canoe has a destination
Everyone in the canoe has a seat and paddle
Everyone is expected to paddle
Those who won’t paddle have to get out of the canoe
Those who prevent others from paddling have to readjust or get out of the canoe
There are no passengers in the canoe
There is a Coxswain
No other crewmember has a title
Crewmembers are multi-talented
The canoe theory understands crisis
The canoe theory says you have the right to be happy
CANOE THEORY
BUILT TO LAST
Preserve the Core
Stimulate Progress
Stimulate Progress
Best Practices
Strategic Leadership
BUILT TO LAST
(Collins, 1994)
BIG HAIRY AUDACIOUS GOALS
(BHAGs)
CULT-LIKE CULTURE
TRY A LOT OF STUFF AND KEEP
WHAT WORKS
HOME-GROWN MANAGEMENT
GOOD ENOUGH NEVER IS
GOOD TO GREAT
(Collins, 2001)
Level 5 Leadership
First Who…Then What
Confront the Brutal Facts
The Hedgehog Concept
A Culture of Discipline
Technology Accelerators
The Flywheel and The Doom Loop
Core Ingredients of
Learning Organizations
Mental Models – everyone sets aside old ways of thinking.
Personal Mastery - everyone becomes self-aware and open to others.
Systems Thinking – everyone learns how the whole organization works.
Shared Vision – everyone understands and agrees to a plan of action.
Team Learning – everyone works together to accomplish the plan.
The Bananas
Bananas in the
Organization
Exercise
We tried that and it didn’t work.
We don’t do it that way here.
Mary is the only one who can do that so…..
Strategic Leadership
Ability to anticipate, envision, maintain flexibility, and empower others to create strategic changes as necessary
Leadership is the process of transforming an organization from what it is to what the leader would it become
Three interdependent activities
Setting a direction
Designing the organization
Nurturing a culture dedicated to Excellence
Top Management Team (TMT)
Charge
Private versus Public
Organizations
Purpose
Goals
Financing
Decision-Making
Key Stakeholders
Strategic Management
Versus
Strategic Planning
Features of Successful
Strategic Management
Has support of organization’s executive officer.
Is user friendly.
Is participatory, not left to planners.
Is flexible.
Leads to resources decisions.
Engages and motivates all staff.
Is fresh and continuous, not static and stale.
Features (Continued)
Is Proactive
Not a Quick Fix
Part of Quality Management
Payoffs Increase over Time
Lessons Learned About
Strategic Planning
Plans must be tailored to organization.
No one size ‘fits’ all.
Time to complete takes longer – expect
50% more than planned.
Process needs a shepherd.
Visionaries needed at beginning and detail types thereafter.
Why Managers Don’t Plan
Time Consuming
High Demands
Not Rewarded
Executives Don’t Support It
Too Risky
Strategic Management Model
Scanning
Where are we now?
Strategy Formulation
Where do we want to be?
Strategy Implementation
How do we get there?
Measurement/Performance
How do we measure our progress?
Strategic Management Model
Strategy Formulation
Where do we want to be?
Vision
Mission
Values
Goals
Objectives
VISION
Vision without Action is a Daydream
Action without Vision is a Nightmare
Not Optional
Stretch – 30+ Years
8-10 Words in length
Future State
Brief and Memorable
VISION (Continued)
Inspiring and Challenging
Descriptive of the Ideal
Vision Examples
“Light the Fire Within”
“A Safer Future for All Communities”
“See the Mountains – Breathe Freely”
To Be the Happiest Place on Earth
To Be the World’s Best Quick Service
Restaurant
Vision Levels of People
Some people never see it. (Wanderers)
Some people see it but never pursue it on their own. (Followers)
Some people see it and pursue it. (Achievers)
Some people see it and pursue it and help others see it. (Leaders)
John Maxwell, Developing The Leader
Within You, 1993.
VISION EXERCISE
Mission Statement
In the absence of a clearly defined direction one is forced to concentrate on confusion that will ultimately consume you.
MISSION
What is our purpose?
Describes current state
Timeline is 3-5 Years
Builds on our distinctive competencies
Tends to focus on Core Business
30-35 Words in length
Mission Examples
“To Lead All Communities in Disaster
Preparedness, Mitigation, and Recovery by
Maximizing Assistance and Support.”
“Caltrans Improves Mobility Across
California.”
To produce superior financial returns for our shareholders as we serve our customers with the highest quality transportation, logistics, and e-commerce.
MISSION EXERCISE
Corporate Governance
What is it?
Codes of Governance
Role of the Board of Directors
Role of Top Management Team
Executive Compensation
Corporate Governance
System by which a firm’s owners control its affairs.
Does it work?
Codes of Governance
The Cadbury Code: 1992
Sarbanes-Oxley Act: 2002
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board
“Triple bottom line”
Four major issues:
Ownership structure and influence
Fianacial Stakeholder rights and relations
Financial transparency and information disclosure
Board structure and processes (audit)
Role of the Board of Directors
Monitor
Evaluate and influence
Initiate and determine
Organization of Board
Insiders versus outsiders
CEO/chair position
Committees’ Effectiveness
Role of Top Management Team
Who is the TMT?
Executive Leadership and Strategic Vision
Articulates strategic vision for corporation
Sets the model for others to identify and follow
Communicates high performance standards and builds confidence in followers’ abilities to meet standards
Managing strategic planning process
Executive Compensation
Incentive alignment
Executive Ownership
Incentive compensation
Salary
Bonus
Stock Options
LT Bonus
VALUES
Guiding Principles
Help establish Culture
Part of Preserving the Core
Core Ideology
Value Examples
CHP PRIDE
HP WAY
J & J Credo
“Build the Spirit of the Place”
Ethical Awareness Model
Organizational Ethics
Individual Ethics
Personal Values
VALUES EXERCISE
Strategic Management Model
Scanning:
Where are we now?
Macro Analysis (STEP, PESTEL, ETC.)
Industry Analysis – Competitive
Intelligence
SWOT Analysis
Internal versus
External Elements
Why Scan?
To know your position in the environment
To respond effectively to constant change
To see the organization as a whole
To avoid surprises
To survive
To lay the foundation for strategic issues
SCANNING:
Key Environmental Variables
Macro Environment: STEP, PESTEL
Task Environment: Industry
Internal Environment: Focal
Organization
Socio-Cultural Variables
Lifestyle Changes
Career Expectations
Regional Shifts in Population
Life Expectancies
More women in workforce
Greater concern for fitness
Postponement of family formation
Increase in temporary workers
Technological Variables
Total Federal Spending for R&D
Total Industry Spending for R&D
Focus of Technological Efforts
Patent Protection
Wireless Communications
Nanotechnology
Productivity Improvements
Genetic engineering
Economic Variables
GDP Trends
Interest Rates
Money Supply
Inflation Rates
Unemployment Levels
Wage/Price Controls
Energy Availability & Cost
Disposable & Discretionary Income
Political-Legal Variables
Antitrust Regulations
Tort Reform
Environmental Protection Laws
Taxation at local, state, federal levels
Hiring and Promotion Laws
Americans Disabilities Act of 1990
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
Demographic Variables
Aging Population
Rising affluence
Changes in Ethnic Composition
Geographic distribution of population
Disparities in income levels
Global Variables
Increasing Global Trade
Currency Exchange Rates
Emergence of Indian and Chinese
Economies
Trade agreements (NAFTA, EU, ASEAN)
Creation WTO
STEP EXERCISE
Socio-Cultural
Technological
Economic
Politico-Legal
Industry Analysis
6 Forces Analysis
Industry Competitors
Suppliers/Vendors
Customers/Clients
Potential New Entrants
Substitutes
Other Stakeholders
Role of Complementors
New Entrants and Entry Barriers
Absolute cost advantages
Access to inputs
Government policy
Economies of scale
Capital requirements
Brand identity
Switching costs
Access to distribution
Proprietary products
Buyer Power (Channel and End
Consumer)
Buyer volume and information
Brand identity
Price sensitivity
Threat of backward integration
Product differentiation
Substitutes
Supplier Power
Supplier concentration
Differentiation of inputs
Switching costs
Threat of forward integration
Cost relative to total purchases in industry
Substitutes
Switching costs
Buyer inclination to substitute
Variety of substitutes
Price-performance tradeoff of substitutes
Necessity for product or service
Degree of Rivalry
Exit barriers
Industry concentration
Fixed costs
Industry growth
Intermittent overcapacity
Switching costs
Brand identity
Diversity of rivals
Corporate stakes
Other Stakeholders
Employees
Unions
Government
Trade and Professional Associations
Other Direct Influencers
Role of Complementors
Number of complements
Relative value added
Difficulty of engaging complements
Buyer perception of complements
Complement exclusivity
Tend to increase profits by increasing demand for an industry’s products
6 FORCES EXERCISE
Competitive Profile Analysis
Identify Key Competitive Factors
Identify key Competitors
COMPETITIVE PROFILE
EXERCISE
Industry Foresight
Customer
Needs
Unarticulated
Articulated
Customer
Served Unserved Types
Internal Environment
Internal Profile Analysis
SWOT Analysis
Internal Profile Analysis
Identify Key Core Functions
Identify Key Measures for Core
Functions
Build Matrix
SWOT Analysis
Internal Environment
Strengths
Weaknesses
External Environment
Opportunities
Threats
SWOT EXERCISE
Strategic Management Model
Strategy Formulation
Where do we want to be?
Vision
Mission
Values
Goals
Objectives
GOAL
Supports the Mission
Deals with One Issue or Item of Focus
Reflects a primary activity or strategic direction
Describes the “To Be” State
“BHAG”
Encompasses a long period, i.e. at least
3 years
Goal Examples
Achieve excellence in the delivery of disaster recovery and mitigation programs.
Professionally develop our employees as a reflection of DAD’s key attributes and values.
Increase the supply of housing, especially affordable housing.
Become a model for customer service.
To provide benefits in correct amounts and issued in a timely manner.
Goal Statements Litmus Test
Goal Exercise
OBJECTIVES
Add specificity beyond Goals
Answer the questions
What is to be accomplished?
When?
Should contain the SMART Elements
OBJECTIVES: SMART Model
Specific
Measurable
Aggressive but Attainable
Results-Oriented
Timeframe
Strategic Objective Examples
By June 30, 2005 achieve 75% rating on the
DAD service index from all stakeholders.
Increase sales growth 6-8% in the next 5 years. (P&G)
Cut corporate overhead costs by $30 million per year. (Fortune Brands)
Operate 6,000 stores by 2010 – up from
3,000 in the year 2000. (Walgreen’s)
Reduce greenhouse gases by 10 percent
(from a 1990 bast) by 2010. (BP Amoco)
Objectives Litmus Test
Strategic Objective Exercise
Strategic Management Model
Strategy Implementation
Everyone is Responsible
Few Guidelines
No Easy 10-Step Checklist to Follow
Strategic Management Model
Strategy Implementation
Most open-ended part of Strategic Mgmt
People implement strategies not
Organizations
Strategic Management Model
Strategy Implementation
How do we get there?
Work Action Plans
GOOMs
Strategy Implementation
Considerations
7-S Framework – Strategic Fit
Human Resources
Patience
7-S Framework
Shared Values
Strategy
Structure
Systems
Skills
Style
Staff
Human Resource Rule
Hire Smart
Train Hard
Manage Effectively
Parable of the Bamboo
It takes patience and discipline to develop and empower people; in fact, it’s like growing bamboo. Once the seed is planted, you must water it daily for four years before the tree breaks ground – then it grows 60 feet in 90 days! Executives who nurture people can get similar results…How, you ask, can such rapid growth be possible? It results from the miles of roots that develop in those first four years.
Preparing people to perform is the task of leadership.
Implementation Strategies
GOOMs
Implementation Conference
CEO involvement
Other Strategies?
GOOMs
Goals
Outcomes
Objectives
Measures
Definitions
Goal: Broad, General BHAG
Outcome: Desired end result and report performance
Objective: What and When
Measure: A quantified unit that assesses progress or achievement
GOOM Example
Goal 1: Achieve excellence in the delivery of disaster recovery and mitigation.
Outcome: Increased Customer Satisfaction
Objective 1.1: By June 30, 2005, achieve
75% rating on the DAD Service Index from all stakeholders.
Measure: DAD Service Index (DSI)
GOOM Exercise
Sponsor:
Organization: n.n Goal
Outcome n.n Objective
Measure
Work Action Plan Template
Completion Date
Task Description Team Lead Staff Hours Completion
Date
Strategic Management Model
Measurement / Performance
Why do we measure our progress?
Why Measure?
Reactive Reasons
Government Intervention
Fewer Resources and Smaller Budgets
Increased Demand for Accountability
Mandated
Why Measure?
Proactive Reasons
Makes us more responsive to public needs
Provides feedback on mission accomplishment
Creates blueprint for linking budget to outcomes
Good management and good public policy
Measurement / Performance
How do we measure our progress?
5 Types of Measures
Input
Output
Outcome
Quality
Efficiency
INPUT Measure
Amount of resources needed to provide a particular product or service.
Examples:
Number of FTEs or PYs
Number of eligible clients
Number of customers requesting service
Number of applications received
Number of sales orders received
OUTPUT Measure
Amount of products or services provided
Examples:
Percent of highways resurfaced
Number of police reports filed
Number of vaccinations given to school-age children per year
Number of shafts produced in a single operating shift
OUTCOME Measure
Reflect the actual results achieved and/or their impact or benefit.
Examples:
Reduction in incidence of disease
Percentage of discharged patients living independently
Percent of increase in tourists
Percent of monthly programmed sales orders filled on time
QUALITY Measure
Reflect the effectiveness in meeting the expectations of customers and stakeholders
Examples:
Number of defect reports compared to number of reports produced
Number of course ratings in highest category related to total number of course ratings
EFFICIENCY Measure
Also known as productivity measures.
Reflect the cost of providing products or services.
Examples:
Output/Input
Output/Time
Output/Cost
Outcome/Cost
Keeping Plans Off The Shelf
All Staff Meeting
Announce Phases
Review and Assess Plans at Quarterly
Sessions
Sponsors and Team Leads for Strategic
Goals and Strategic Objectives
Deming Philosophy – PDCA
Developing Bench Strength
“Drill Down” Application
Sponsors, Team Leads, and Team
Members
Work Action Plan
“Project” Champion
Leadership Training
Leadership Conference Presentations
Establishing Organizational
Permanence
Training Emphasis
Certification
Awards & Recognitions
“Caught-Ya”
Celebrations
Walk the Walk
NEXT STEP