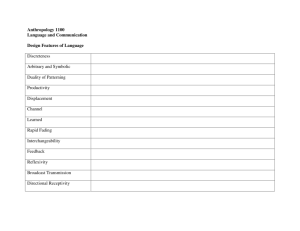
Econ 301: Money and Banking Weekly Detailed Course Outline
advertisement

Welcome to PMBA0608: Economics/Statistics Foundation Fall 2006 Session 4: September 6 Study Chapters 1 through 4 of Mankiw Chapters 1 through 3 of Mendenhall, Beaver and Beaver Send me your questions I will do one or all of the following Answer you privately Publish the answer to your question on line Answer your question in our next class Discuss Assignment 1 1) Problem 5, Page 16 of Mankiw $5 million is sunk cost MC = $1 million MB = $3 million MB>MC should complete the project As long as MB >MC, the answer is the same Discuss Assignment 1 2) Problem 8, Page 17 of Mankiw The new bill will increase the incentive for economic activity. Efficiency may increase for two reasons Resources are not wasted as much as before If tax rates go down current work force will have an incentive to work harder Equity may decline as Current workers’ tax rate may go down Some current welfare recipients may not be able to find jobs the pay a much as welfare. Discuss Assignment 1 3) The discussion on the connection between the article and the economic principle should be well developed. Discuss Assignment 1 4) Question 1.2, Page 10 of Mendenhall, Beaver and Beaver Population of interest is the population of the measurements of the appraisals of the land by all experienced appraisers. Population is large but it does exist, so it is not conceptual. Populations are different Buyers may underestimate. Sellers may over estimate…. More than one appraisal should be used. Discuss Assignment 1 5) Question 1.7, Page 10 of Mendenhall, Beaver and Beaver Population of shopper opinions (in favor or opposed background music) Not possible to examine the entire population as future shoppers are not known. No, sample percentages will not be the same as population percentage but it will serve as an estimate as population percentage. Back to Chapter 2 of Mankiw: Macro/micro economics Macro = big Picture = Forest Focuses on the aggregate markets Micro = small picture = tree Focuses on individual markets Which of the following is a macro/micro topic? The effect of tax policy on the price of gas in Ohio. The effect of tax policy on the general price level in Ohio. The effect of agricultural subsides on the income of farmers. The effect of agricultural subsidies on income tax rates in the U.S. Which of these topics will be covered in a macro/micro economics course? The impact of the 1987 market crash on consumers’ spending. How a higher rate of inflation alters the distribution of wealth and income. The effect of war in Iraq on the price of oil. The effect of the increase in the price of oil on the overall unemployment rate. Normative/Positive Statements Positive Statement is descriptive But not necessarily true can be tested for validity Example Normative statement is an opinion can not be tested for validity Example Note A normative economic statement that is not backed up by positive statement is worthless. Chapter 2 of Mendenhall, Beaver & Beaver (Stat) Which of the following is (are) a Variable? 1. 2. 3. 4. Interest rates My name My weight Price of gasoline 1, 3 and 4. Variable = characteristics that change over time or across different objects. Which of the following is (are) experimental unit (s)? 1. 2. 3. 4. Jackie United States Unemployment rate A PMBA student 1, 2 and 4 Experimental unit = an individual or object on which a variable is measured. Which of the following variables is (are) qualitative? 1. 2. 3. 4. Gender of students in this class Height of students in this class Seasons Cost of production 1 and 3 Qualitative variables can be categorized but not measured. Which of the following variables is continuous? 1. The number of your children over time. 2. Your weight over time. 3. The year 2 Continuous variable can assume all of the infinitely many values corresponding to a line interval. Can a qualitative variable be continuous? No. Gender Male = 1 Female = 2 Budget deficit in billions of dollars. (What kind of graph is this?) 100 0 -100 -200 -300 -400 -500 -600 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Prime rate in the US (What type of graph is this?) Make sure You know how to create a graph using Excel or any other program. Highlight your columns that contain data and click on Chart Wizard. You know what type of graph is more appropriate in different scenarios and why? Histograms are used to show relative frequencies: Example Individual Mark Number of children 1 Jan 0 Mary 0 Jackie 3 Total 4 Histograms are used to show relative frequencies: Example Number of children Relative frequency 0-1 ¾ = 75% 2-3 ¼ = 25% Histograms are used to show relative frequencies: Example Relative frequency 75% 25% 0 1 2 3 Number of kids Do you use a bar graph or a histogram in each of the following situations? 1. You want to compare heights of 10 individuals in this class. Bar 2. You want to compare total revenues of five different companies. Bar 3. You want to compare numbers of companies that make from 0 to $10,000; from $10,000 to $20,000; from $20,000 to $30,000 and so on. Histogram Check out the following interactive site for creating histograms http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/a ctivities/histogram/?jv=1.4.1_02&jb= MSIE The arithmetic mean Helps us describe the sample (xbar)or the population (μ) The sample mean, xbar is xbar = (x1 + x2 + . . . + xn) / n . Mean member of US households = total population /number of households In 2003 =2.57 Mean household income in the US = total income/households In 2003 =$59,067 What is median? 50% of observations fall below median and 50% of observations fall above median In 2003 median income of a household in the US was $43,318 50% of households received less than $43,318. 50% of households made over $43,318. Mean /median Note: Area under the curve is 100% What does this tell you about income equality in the US? Relative frequency 50% of households $43,318 = median 50% of households $59,067 = mean Income household Which nation has more poor households? Mean income is the same Relative frequency Relative frequency $60,000 Nation A income 60,000 Nation B income Need a measure of dispersion in order to describe our data better 1. Range Maximum value – minimum value Makes more sense for small samples Are these two samples the same? Weight sample 1 Four observations: 100, 110, 170, 200 Mean = 145 Median = 140 Range = 100 Weight sample 2 Eight observations: 100, 115, 125, 130, 150, 160, 180,200 Mean = 145 Median = 140 Range= 100 According to mean, median and range, yes. Measures of dispersion: (2) Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) = mean of absolute values of deviation of each observation from mean Weight of individual (wi) in Sample 1 |wi- wbar| 100 45 110 35 170 25 200 55 •MAD = (Σ |wi- wbar|)/n) =(45+35+25+55)/4= 40 What is MAD for Sample 2? Weight sample 2 100, 115, 125, 130, 150, 160, 180,200 Mean = 145 MAD = 27.5 MAD in sample 2 < MAD in sample 1 What does this mean? The distribution of Sample 2 is tighter Measures of dispersion: (3) Variance In population = Σ(wi- wbar)2/n In sample = Σ(wi- wbar)2/n-1 Calculate the variance in Sample 1 and Sample 2 Variance in Sample 1 = 2300 Variance in Sample 2 =1150 Standard deviation is the square root of variance. Empirical Rule If the sample is very large population If the relative frequency distribution is bell shaped Then 68% of observations fall within one standard deviation from the mean 95% of observations fall within two standard deviation from the mean Empirical Rule Suppose standard deviation is 30 Rela. frequency 68% 95% 8 5 1 1 5 145 1 7 5 2 0 5 weight In our example, both samples had the same mean and Sample 1 had a higher standard deviation So, Sample 1 was more variable. But what if two samples have different means? How do we measure which one is more variable? Coefficient of variation = (standard deviating/mean) * 100 The higher the mean, the ______ the CV. The higher the standard deviation, the _____ the CV. Bivariate data Sometimes we want to focus on two variables at the same time Example 1 Are women earning less than men for doing the same job? One of my students wanted to answer this question Collected a sample of area attorneys at different stages of their careers Bivariate data The study of earning gap Earnings Male Female Years after graduation Bivariate data: relationship There is economic theory suggesting that there is a negative relationship (trade off) between inflation and unemployment Collect data on both variables Bivariate data: relationship Plot your points Unemployment rate 1990 1991 1993 1992 1994 •What type of relationship is there between inflation and unemployment? Inflation Is there a measure of correlation between two variables (x and y)? Yes? Correlation coefficient (r) Takes a value between -1 to +1 If r =0 x and y are not correlated If r = -1 x and y are perfectly and indirectly correlated If r = +1 x and y are perfectly and directly correlated How do we calculate r? Formula on Page 66 of stat book Excel calculates it automatically Under fx type =CORREL (A2:A10;B2:B10) Suppose you are told that your salary is at 70th percentile in the distribution of salaries in your organization. What does this mean? 70% of other salaries in your organization are lower than your salary and 30% are higher than your salary. Another measure of relative standing is z-score Measures the number of standard deviations between an observation an the mean of the set. Example If z = 2 Then your salary is lies 2 standard deviations above the mean Formula on page 71 of Stat Book Note: Sections 2.5 and 2.13 of this Chapter are dropped. Assignment 2 Due: On or before September 16 Problem 3, Page 59 of Mankiw Problem 6. Page 60 of Mankiw Application 2.6, Page 24 of Mendenhall, Beaver and Beaver (Use Excel or similar program. Explain why one presentation is more effective.) 4. Application 2.12, Page 33 of Mendenhall, Beaver and Beaver (Use Excel or similar program.) 5. Exercise 2.47, Page 67 of Mendenhall, Beaver and Beaver (Use Excel or similar program.) Notes: 1) Each question has 4 points. 2) Don’t hesitate to contact me. 1. 2. 3.