Flash Cards Graphing
advertisement

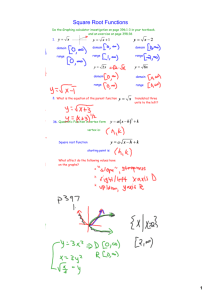
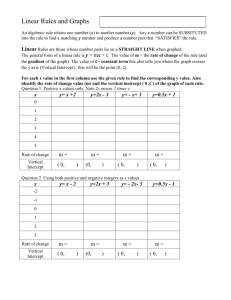
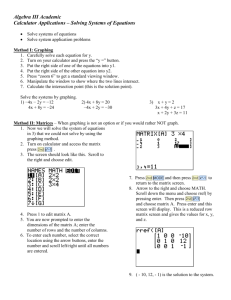
𝟐 𝒚= 𝒙 The Parent Quadratic x intercept: (0,0) y intercept: (0,0) vertex: (0,0) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [0 , ∞) 𝒚 = (𝒙 − 𝟑) 𝟐 Move the vertex of the parent three units RIGHT on X AXIS x intercept: (3,0) y intercept: (0,9) vertex: (3,0) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [3 , ∞) 𝒚 = −(𝒙 − 𝟑) 𝟐 Move the vertex of the parent three units RIGHT on X AXIS and reflect it over the x axis. x intercept: (3,0) y intercept: (0,-9) vertex: (3,0) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , 3] 𝟏 𝟐 𝒚 = (𝒙 + 𝟐) 𝟐 Move the vertex of the parent two units LEFT on X AXIS and the ½ will make it “wider”. x intercept: (-2,0) y intercept: (0,2) vertex: (-2,0) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [ 0, ∞) 𝟐 𝒚 = (𝒙 + 𝟐) - 4 Move the vertex of the parent 3units RIGHT on x axis and 4 units DOWN on the y axis. x intercept: (0,0) (-4,0) y intercept: (0,0) vertex: (-2,-4) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [4, ∞) 𝟐 𝒚= 𝒙 +4 Move the vertex of the parent 4 units up on the y axis. x intercept: none y intercept: (0,4) vertex: (0 ,4) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [4, ∞) 𝒚 = (𝒙 − 𝟑)(𝒙 + 𝟐) Find the x intercepts at 3 and -2. Flips up. x intercept: (3,0) (-2,0) y intercept: (0,-6) vertex: (1/2, -6.25) Add the x intercepts together and divided by 2 to find the x coordinate of the vertex. Substitute ½ into the equation to find y. D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [-6.25 , ∞) 𝒚 = 𝒙(𝒙 − 𝟑)(𝒙 + 𝟐) Find the x intercepts at 0, 3, and -2. Flips up. It’s a CUBIC (note: 3 x’s) x intercept: (3,0) (-2,0) (0,0) y intercept: (0,0) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝒚 = 𝟑(𝒙 − 𝟑)(𝒙 + 𝟐) Find the x intercepts at 3 and -2. Flips up. NOTE: The 3 in front does NOT create an x-intercept! x intercept: (3,0) (-2,0) y intercept: (0,-18) vertex: (1/2, -18.75) Add the x intercepts together and divided by 2 to find the x coordinate of the vertex. Substitute ½ into the equation to find y. D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝒚=𝟒 Did you notice that this is a Horizontal LINE??? x intercept: none y intercept : (0, 4) slope: 0 Note that slope of a vertical line is undefined. D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [4] 𝒚 = 𝟑(𝒙 − 𝟑)(𝒙 + 𝟐) Find the x intercepts at 3 and -2. Flips up. NOTE: The 3 in front does NOT create an x-intercept! x intercept: (3,0) (-2,0) y intercept: (0,-18) vertex: (1/2, -18.75) Add the x intercepts together and divided by 2 to find the x coordinate of the vertex. Substitute ½ into the equation to find y. D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝑦= 𝑥 The Parent Absolute Value x intercept: (0,0) y intercept: (0,0) vertex: (0,0) “V” shaped with “arms” in quadrants 1 and 2 D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [0, ∞) 𝒚 = −(𝒙 − 𝟑)(𝒙 + 𝟐 𝟐) Find the x intercepts at 3 and -2 and -2. Flips into quadrants 2 and 4 because of the -1 in front. It’s a CUBIC. It has a DOUBLE root of -2 OR we could say it has “multiplicity of 2”. Recall that a graph turns at the double root—changes direction! x intercept: (3,0) (-2,0) (-2,0) y intercept: (0,6) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝒚 = (𝒙 − 𝟐) +𝟖 Did you notice that this is a LINE??? y=x+6 x intercept: (−6,0) y intercept : (0,6) slope: 1 Note that it is easy to find the inflection point when the cubic function is in this form. D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝒚 + 𝟏 = −𝟑(𝒙 − 𝟐) Did you notice that this is a LINE??? 5 ( , 3 x intercept: 0) y intercept : (0, 5) slope: -3 Note that it is easy to find the inflection point when the cubic function is in this form. D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝑦 = 𝑥−2 Parent moves 2 units right on x axis. It does NOT move off of 0 on the y axis. x intercept: (2,0) y intercept: (0,0) vertex: (2,0) “V” shaped with “arms” in quadrants 1 and 2 D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [ 2, ∞) 𝑦 =− 𝑥+2 Parent moves 2 units left on x axis. It does NOT move off of 0 on the y axis. It flips! x intercept: (-2,0) y intercept: (0,-2) vertex: (-2,0) “V” shaped with “arms” in quadrants 3 and 4 D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , 2] 𝑦 =− 𝑥+2 +8 Parent moves 2 units left on x axis and 8 units up on the y axis. Flips! x intercept: (-10,0) (6,0) y intercept: (0,6) vertex: (-2,8) “V” shaped with “arms” in quadrants 3 and 4 D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , 8] 𝑦 =3 𝑥+2 +8 Parent moves 2 units left on x axis and 8 units up on the y axis. The three in front makes it “skinnier”. x intercept: none Can’t solve an absolute value that is equal to a negative value! y intercept: (0,14) vertex: (-2,8) “V” shaped with “arms” in quadrants 1 and 2 D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [8 , ∞) 𝑦 = 𝑥+2 −9 Parent moves 2 units leftt on x axis and 9 units down on the y axis. x intercept: (7, 0) (-11,0) Remember: We must split absolute values equations: -9 = x+2 and 9 = x+2 y intercept: (0,-7) vertex: (-2,-9) “V” shaped with “arms” in quadrants 1 and 2 D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: [-9, ∞) 𝟑 𝒚 = (𝒙 + 𝟐) Moves the cubic parent two units to the right. In quadrants 1 and 3. 3 x intercept: ( −2,0) y intercept : (0,8) Inflection point: (-2, 0) Note that it is easy to find the inflection point when the cubic function is in this form. D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝟒 𝒚 = (𝒙 + 𝟐) Moves the quartic parent two units to the right. In quadrants 1 and 2. x intercept: (-2,0) y intercept : (0,16) Inflection point: (-2, 0) Note that a quartic is similar to a parabola but is wider at the “bottom” and closer to the y axis past the points (1,1) and (-1,1). D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝟑 𝒚 = (𝒙 + 𝟐) +𝟖 Moves the cubic parent two units to the left on the x axis and 8 units up on the y axis. In quadrants 1 and 3. x intercept: (−4,0) y intercept : (0,16) Inflection point: (-2, 8) Note that it is easy to find the inflection point when the cubic function is in this form. D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝟓 𝒚 = (𝒙 + 𝟐) +𝟖 Very similar in graph to a cubic but it is “wider” near the inflection point and then nearer the y axis past the points (1,-1) and (1, 1).Moves the parent two units to the right. In quadrants 1 and 3. 5 x intercept: (-2+ −8, 0) y intercept : (0,40) Inflection point: (-2, 8) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝟑 𝒚 = (𝒙 + 𝟐) +𝟖 Moves the parent cubic 2 units left on x axis and 8 units up on y axis x intercept: (-4,0) y intercept: (0,16) inflection point: (-2,8) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝑦= 𝑥 The Parent Square Root x intercept: (0,0) y intercept: (0,0) Starting point: (0,0) D: [0, ∞) R: [0, ∞) 𝑦= 𝑥−4 Move parent 4 units right on x axis x intercept: (4,0) y intercept: none Starting point: (4,0) D: [4, ∞) R: [0, ∞) 𝑦= 𝑥+4 -5 Move the parent 4 units to the left on x axis and 5 units down on the y axis. x intercept: (21,0) y intercept: (0,-3) Starting point: (-4,-5) D: [-4, ∞) R: [-5, ∞) Note how the starting point dictates the “starting point” of the domain and range. 𝑦 =− 𝑥 +2 Move the parent no where on the x axis and 2 units up on the y axis. And flips x intercept: (4,0) y intercept: (0,2) Starting point: (0,2) D: [0, ∞) R: (-∞,2) Note how the starting point dictates the “starting point” of the domain and range. 𝒚 = 𝒙(𝒙 − 𝟑)(𝒙 + 𝟐) Find the x intercepts at 0, 3, and -2. Flips up. It’s a CUBIC (note: 3 x’s) x intercept: (3,0) (-2,0) (0,0) y intercept: (0,0) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞) 𝒚 = 𝒙(𝒙 − 𝟑)(𝒙 + 𝟐) Find the x intercepts at 0, 3, and -2. Flips up. It’s a CUBIC (note: 3 x’s) x intercept: (3,0) (-2,0) (0,0) y intercept: (0,0) D: ( -∞ , ∞) R: ( -∞ , ∞)