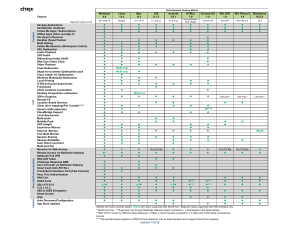
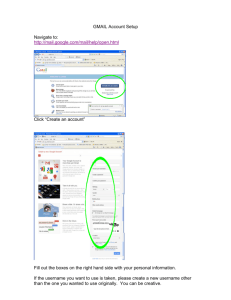
Services
Synergy 609
What’s new in NetScaler 10.1?
Hands-on lab exercise guide
May 2013 – Version 1.0
Services
Table of Contents
Table of Contents .............................................................................................................................................. 2
Overview............................................................................................................................................................. 3
Lab Topology Diagram .................................................................................................................................... 5
Exercise 1: New UI Layout.............................................................................................................................. 7
Exercise 2: StoreFront built-in monitoring ................................................................................................. 17
Exercise 3: Configuring NetScaler Gateway SAML Two-factor Authentication .................................. 25
Exercise 4: NetScaler Gateway Plug-in support for Windows 8 .............................................................. 52
Exercise 5: Networking and Traffic management enhancements............................................................ 64
Exercise 6: SPDY gateway ............................................................................................................................. 95
Exercise 7: Clustering spotted VIP support .............................................................................................. 108
Challenge Exercise 8: XenMobile and NetScaler Integration................................................................. 131
Challenge Exercise 9: DataStream Kerberos Authentication using Microsoft SQL ........................... 184
Optional Exercise 10: NetScaler 10.1 Quiz ............................................................................................... 212
Page 2
Services
Overview
Hands-on Training Module
This training module has the following details:
Objective
Provide hands on experience on the new features included in the next
release of NetScaler: 10.1.
Audience
Primary: Citrix Customers and Partners
Lab Environment Details
This section is used to describe the lab environment and the virtual machines that are used.
Machine
XenServer
Site1-AD.training.lab
Site1-Exchange
Site1-NetScaler1
Site1-NetScaler2
Site1-SharePoint
Site1-SQLServer1
Site1-Win8Client
Site1-XenMobile
Site2-AD.training2.lab
Site2-CentOS
Site2-Insight
Site2-NetScaler1
Site2-NetScaler2
Site2-PVS1
Site2-PVS2
Site2-SQLServer2
Site2-Win8Client
Site2-XenApp
Site2-XenDesktop
Details
Hosts virtual machines
Active Directory Domain Controller for Site1
Exchange Server for Site1
NetScaler 1 in Site1
NetScaler 2 in Site1
SharePoint server in Site1
SQL Server in Site1
Windows 8 Client in Site1
XenMobile Device Manager
Active Directory Domain Controller for Site2
SimpleSAML PHP Identity Provider
NetScaler Insight Center Server in Site2
NetScaler 1 in Site2
NetScaler 2 in Site2
Provisioning Services Server 1 in Site1
Provisioning Services Server 2 in Site1
SQL Server in Site2
Windows 8 Client in Site2
XenApp Server 1 in Site2
XenDesktop Server 2 in Site2
Required Lab Credentials
Below are the login credentials required to connect to the workshop system and complete the lab
exercises.
Page 3
Services
Machine
XenServer
Site1-AD.training.lab
Site1-Exchange
Site1-NetScaler1
Site1-NetScaler2
Site1-SharePoint
Site1-SQLServer1
Site1-Win8Client
Site1-XenMobile
Site2-AD.training2.lab
Site2-CentOS
Site2-Insight
Site2-NetScaler1
Site2-NetScaler2
Site2-PVS1
Site2-PVS2
Site2-SQLServer2
Site2-Win8Client
Site2-XenApp
Site2-XenDesktop
Username
root
TRAINING\Administrator
TRAINING\Administrator
nsroot
nsroot
TRAINING\Administrator
TRAINING\Administrator
TRAINING\Administrator
TRAINING\Administrator
TRAINING\Administrator
root
nsroot
nsroot
nsroot
TRAINING2\Administrator
TRAINING2\Administrator
TRAINING2\Administrator
TRAINING2\Administrator
TRAINING2\Administrator
TRAINING2\Administrator
Password
Citrix123
Citrix123
nsroot
nsroot
Citrix123
Citrix123
Citrix123
Citrix123
Citrix123
Citrix123
nsroot
nsroot
nsroot
Citrix123
Citrix123
Citrix123
Citrix123
Citrix123
Citrix123
Page 4
Services
Lab Topology Diagram
Dual Site Setup – Multiple Subnets
Public Bond
eth4
RemoteSite Uplink
MainSite Uplink
PublicIP #0
PublicIP #1
PublicIP #2
SQL1
eth3
eth1
eth0
PublicIP #3
PublicIP #4
WAN emulator
Site-to-Site link
192.168.30.0/24
MainSite - Site 1
192.168.10.0/24
AD
eth2
Router1
Router2
SharePoint
@
AD
RemoteSite - Site 2
192.168.20.0/24
CentOS - SAML
PVS1
PVS2
Exchange
Apache1
Apache2
SQL2
XenMobile
Win7Target
NetScaler1
Win7VDA
NetScaler1
XAStudent
Win8Client
NetScaler2
Win8Client
XenApp XenDesktop
PrivateSubnet
192.168.15.0/25
Apache3
Page 5
Services
External Access
Lab Features:
Public Network
5 Public IP address
Pre-configured NAT rules for external access
Common services fully configured
WAN emulation for all links (Site-to-Site, Public)
External
Client
SoftLayer DNS (Authoritative for: mycitrixtraining.net)
Example A record:
1-2-3-4.mycitrixtraining.net -> 1.2.3.4
Public Bond
eth4
RemoteSite Uplink
MainSite Uplink
PublicIP #0
PublicIP #1
PublicIP #2
eth2
eth3
eth1
eth0
PublicIP #3
PublicIP #4
WAN emulator
Site-to-Site link
192.168.30.0/24
Router1
Router2
Link Configuration
Public Bond
eth4
RemoteSite Uplink
MainSite Uplink
PublicIP #0
PublicIP #1
PublicIP #2
eth2
eth3
eth1
eth0
WAN emulator
PublicIP #3
PublicIP #4
Site-to-Site link
192.168.30.0/24
Router1
Router2
Page 6
Services
Exercise 1: New UI Layout
Overview
In this exercise
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: 5 minutes.
Step Action
1.
Once logged in at the self-paced portal, click the Start lab button to launch a connection to
published XenCenter.
2.
When XenCenter loads, right-click the XenCenter node and select Add…
3.
On the Add New Server screen enter the XenServer IP address provided on the portal
and in the Password field enter the password provided on the portal. The user name will
always be root.
Page 7
Services
Step
4.
Action
In XenCenter, click on the Site2-Win8Client VM and choose the Console tab. Login with
the following Credentials:
Username: TRAINING2\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
NOTE: For better performance, switch to a Remote Desktop connection.
5.
Click on the Desktop tile.
Page 8
Services
Step
6.
Action
Open Internet Explorer and navigate to the NetScaler Administration UI using the default
credentials:
http://192.168.20.50
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Page 9
Services
Step
7.
Action
First, create the Subnet IP for the NetScaler to contact backend resources. In the First
Time wizard, enter the following parameters:
IP Address: 192.168.20.50
Subnet IP: 192.168.20.51
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
DNS (IP address): 192.168.20.11
Time Zone: GMT-07:00-PDT-America/Los_Angeles
Click Continue.
8.
9.
10.
NOTE: Please make sure you click on Add when configuring the DNS server IP address
In the Manage Licenses, click Continue.
Review the information and click on Done to complete the wizard.
Save your configuration by clicking on the Save icon.
Page 10
Services
Step
11.
12.
Action
In the Configuration section, note the new six new nodes in the GUI.
Expand System and note the new layout:
Note that Web Interface has been moved here. CloudBridge Connector is the new
branding for CloudBridge as previous available in NetScaler 10.0.
Page 11
Services
Step
13.
Action
Expand AppExpert
AppExpert retains its own node as per NetScaler 10.0; however, it now houses some new
guests! Rewrite, Responder are now included in this node. Some new features are AppQoE
(Application Quality of Experience) and Spillover.
14. EExpand Traffic Management:
x
p
a
n
d
Note this is new home for Load Balancing, Content Switching, DNS, SSL/Offload,
and GSLB.
Page 12
Services
Step Action
15. TClick on Load Balancing > Virtual Servers. Now the action buttons have been moved to
hthe top:
e
The Action drop-down box is the equivalent of right-clicking on an object.
There are now clickable “breadcrumbs” to let you know where you are and allow you to
jump to a previous level easily:
16.
Highlight the Load Balancing node. Note in the bottom right-hand corner is the new
home for the status bar:
Continue to the next step.
17. CClick on Monitors. Select tcp-default and expand:
l
i
c
k
Now the details of an object are expandable for extra detail.
At the bottom of the page on the right-hand side is the pagination options:
Page 13
Services
Step
18.
19.
Action
Click SSL. Note that the SSL options have been converted to HTML/JavaScript. Select
Server Certificate Wizard. The new wizard is dynamic:
Click Done.
Navigate to SSL > Certificates > Install. The new pop-up does not use Java anymore so
loads faster:
Click Close.
Page 14
Services
Step
20.
Action
Click SSL > Policies > Add. See the new Policy Manager, which has been revamped to
make building and evaluating policy expressions easier:
21. TFor all the following exercises, we need to enable the following basic features: SSL
Offloading, Load Balancing, NetScaler Gateway and Content Switching
Navigate to Configuration -> System -> Settings -> Configure Basic Features. Check the
options listed above and click OK.
Page 15
Services
Step
22.
Action
We will also need to enable some advanced features for the exercises. Navigate to
Configuration -> Settings -> Configure Advanced Features and ensure the following
options are enabled: Responder.
Click OK.
END OF EXERCISE
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
New and improved layout included in the NetScaler 10.1 UI.
The end-user experience has been improved to make the usage of the UI
easier and more intuitive.
Page 16
Services
Exercise 2: StoreFront built-in monitoring
Overview
In this exercise, we will leverage the new monitors included in NetScaler 10.1 to monitor StoreFront
servers when used in load balanced environments.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: 10 minutes.
Step Action
1. Continue on using Site2-NetScaler1 from Site1-Win8Client.
2. In the NetScaler Administration console, navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management > Load Balancing -> Servers -> Add.
Create a server object for Site2-XenApp and Site2-XenDesktop VMs using the following
information:
Server Name: XenApp
IP Address: 192.168.20.14
Server Name: XenDesktop
IP Address: 192.168.20.15
Click Create for each server.
NOTE: When any object is created, there will be a notification in the NetScaler UI in the
bottom right-hand corner of the web page:
Now click Close.
Page 17
Services
Step Action
3. In NetScaler 10.1, a new built-in monitor was introduced for checking the health of
StoreFront servers. For this we need to use the CLI as early firmware builds prevented these
new monitors from being created from the GUI.
Open PuTTY and connect via SSH to 192.168.20.50 using nsroot/nsroot credentials.
NOTE: If you receive a PuTTY Security Alert for this or any subsequent exercises please
select Yes to continue:
At the CLI prompt, enter the following command to create a new monitor for StoreFront
Server # 1 (Site2-XenApp):
> add lb monitor sf1-https STOREFRONT -hostName sf1.training2.lab
-interval 20 -resptimeout 10 -storefrontacctservice YES
4.
Create an additional monitor for the second StoreFront server (Site2-XenDesktop) server.
From the same PuTTY session, enter the following command:
> add lb monitor sf2-https STOREFRONT -hostName sf2.training2.lab
-interval 20 -resptimeout 10 -storefrontacctservice YES
Page 18
Services
Step Action
5. Return to the NetScaler Configuration utility. Create the services for both StoreFront servers.
Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Services -> Add.
Add a service for each StoreFront server using the following parameters:
Service Name: SF1-XenApp
Protocol: SSL
Server: XenApp
Port: 443
Monitor: sf1-https
Service Name: SF2-XenDesktop
Protocol: SSL
Server: XenDesktop
Port: 443
Monitor: sf2-https
Click Create for each service and the Close.
Page 19
Services
Step Action
6. Before we create the virtual server, we need to import the certificate issue to the internal
FQDN for internal connections.
Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> SSL -> Certificates -> Install. Add a
new certificate using the following parameters:
Certificate-Key Pair Name: wildcard.training2.lab
Certificate File Name: /nsconfig/ssl/wildcard.training2.lab.cer
Certificate Key File Name: /nsconfig/ssl/wildcard.training2.lab.key
Select the drop-down arrow beside Browse and select Appliance.
Click Create and then Close.
GUI Display Issue:
Internet Explorer 10 prevents from uploading a certificate to the appliance. If you experience
an issue with this step, please switch to Google Chrome and complete the certificate upload
process.
Page 20
Services
Step Action
7. Next, create the virtual server used for internal connections. Navigate to Configuration ->
Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Virtual Server -> Add.
Use the following parameters:
Name: SF_vserver
IP Address: 192.168.20.110
Protocol: SSL
Port: 443
Bind the two StoreFront services created in the previous step. Do not click Create yet!
Page 21
Services
Step Action
8. Next we will configure the required persistence settings for all receiver types to connect
successfully. Persistence is required so that client connections are directed to the same
backend Storefront server during the session.
Click on the Method and Persistence tab and configure SOURCEIP persistence using the
following parameters:
Persistence: SOURCEIP
Timeout: 2mins
IPv4 Netmask: 255.255.255.255
9.
We are not quite finished with this section. Do not click on Create yet!
Since this is a SSL virtual server, we need to bind an SSL certificate. Click on the SSL
Settings tab. Select the wildcard.training2.lab certificate in the Available pane and click
Add to bind it to the virtual server.
Click Create and then Close.
Page 22
Services
Step Action
10. We are ready to test the load balancing configuration. Open a new tab in Internet Explorer
and navigate to the following URL:
11.
https://sflb.training2.lab/Citrix/StoreWeb/
An ActiveX control will try to run in the browser in order to detect the local installation of
Citrix Receiver. As we have this installed already we will allow this control to run.
Click Allow.
12. Login to the StoreFront virtual server with these credentials:
Username: TRAINING2\user1
Password: Citrix123
13. Once the applications and desktops are listed, launch a desktop and/or an application to
verify that the delivery infrastructure is working optimally. Close the applications and logoff
from the desktop launched. Continue to the next step when finished.
Page 23
Services
Step Action
14. Save you configuration by returning to the NetScaler Configuration Utility and clicking on the
Save Icon on the upper right corner. Click Yes at the prompt to save the running
configuration.
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
StoreFront built-in monitors are included in NetScaler 10.1. These monitors
check the health of the IIS application pools required in a StoreFront
deployment.
These monitors are USER scripts leveraged by the monitoring daemon to
send properly formatted HTTP request to StoreFront in order to verify the
health of the service.
Page 24
Services
Exercise 3: Configuring NetScaler Gateway
SAML Two-factor Authentication
Overview
In this exercise, we will go through the configuration of SAML two-factor authentication in order to
access resources. This new enhancement is part of NetScaler Gateway and now IT administrators can
enforce SAML authentication with an external identity provider (IdP). In addition to SAML, the
administrator can request credentials from LDAP and/or RADIUS authentication sources for added
security.
In this lab exercise, we will leverage the open source SAML idP called SimpleSAMLPHP and Windows
Server 2008 R2 Network Policy Server (NPS) for RADIUS authentication.
Estimated time to complete this lab: 20 minutes.
Step
Action
1.
In XenCenter, select the Site2-CentOS VM. Click on the Console tab and login with the
following credentials:
Login: root
Password: Citrix123
2.
Verify that the web services are running by typing the following command in bold (see
example below):
[root@idp-cc ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd status
httpd (pid 1172) is running...
Log off from the VM by typing exit in the console. We will come back to this VM in order
to configure it so it can communicate with NetScaler Gateway.
3.
In XenCenter, select the Site2-Win8Client VM. Return to the NetScaler Configuration
utility. Provide the following credentials, if necessary:
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Page 25
Services
Step
4.
Action
Next, we need to create a NetScaler Gateway virtual server to login using SAML
authentication.
Click on the NetScaler Gateway feature and on the right-pane, select Create/Monitor
NetScaler Gateway under Getting Started
5.
In the NetScaler Gateway welcome page, click on Get Started
Page 26
Services
Step
6.
Action
Under NetScaler Gateway Settings, enter the following parameters:
Name: agsaml.training2.lab
IP address: 192.168.20.111
Port: 443
Click Continue.
7.
Next, under Certificate, select Choose Certificate. From the drop-down menu, select the
wildcard.training2.lab server certificate.
Click Continue.
Page 27
Services
Step
8.
Action
Next, under Primary Authentication, we’re going to configure a new LDAP policy and
profile. Select Configure New and enter the following parameters:
IP Address: 192.168.20.11
Port: 389
Time out (seconds): 3
Base DN: dc=training2,dc=lab
Admin Base DN: administrator@training2.lab
Server Logon Name Attribute: sAMAccountName
Password: Citrix123
Confirm Password: Citrix123
NOTE: Leave Secondary Authentication set to None for now. We will come back and
configure RADIUS authentication later in this lab.
Click Continue.
Page 28
Services
Step
9.
Action
Next, we need to configure the Enterprise Store Settings.
Select CloudGateway and set the following parameters:
Deployment Type: Windows StoreFront
StoreFront FQDN: sflb.training2.lab
Use HTTPS: checked
Receiver for Web Path: /Citrix/StoreWeb
PNAgent Path: /Citrix/Store/PNAgent/config.xml
Single Sign-on Domain: TRAINING2
STA URL: http://xenapp.training2.lab:8080
Click Done.
Page 29
Services
Step
10.
Action
Verify that you have a NetScaler Gateway appliance created on the upper-right hand side
(see screenshot below):
11.
Continue to the next step.
Now, we need to configure StoreFront for external access. In XenCenter, select the Site2XenApp VM and click on the console tab. Login with Domain Administrator credentials:
12.
Username: TRAINING2\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Open the Citrix StoreFront console. A shortcut is on the desktop. Wait until the
StoreFront console loads completely. This might take around 15-20 seconds. Select the
Authentication node located on the left pane.
13. aIn the Authentication options, select Add/Remove Methods in the right column.
g
s
a
m
l
Click OK.
Page 30
Services
Step
14.
Action
Next, go the Gateways node. We’re going to create a new Gateway Server to allow
incoming communication from the new agsaml.training2.lab NetScaler Gateway virtual
server.
Select Gateways > click on Add Gateway Server and enter the following parameters:
Display name: AG-SAML
Gateway URL: https://agsaml.training2.lab
Deployment mode: Appliance
Set server as Access Gateway Enterprise Edition: checked
Subnet IP address: 1.1.1.1 (see note below for additional explanation).
Logon type: Domain only
Click Next.
TIP: Select and copy the Gateway URL as you will need it in the next screen.
NOTE: Since we are using the same appliance for StoreFront load balancing as well as NetScaler
Gateway for external access, we are selecting using IP 1.1.1.1 for the subnet IP to prevent internal
XenApp/XenDesktop sessions to be given the parameters for launching the application through
the gateway.
When selecting an IP that is not used by any appliance, StoreFront relies on the X-Citrix-Gateway
header to identify connections originated through the gateway.
Continue with the next step.
Page 31
Services
Step
15.
Action
Under Enable Silent Authentication window, enter the following callback URL:
Callback URL: https://agsaml.training2.lab
16.
Click Next.
Under the Secure Ticket Authority (STA) window, enter the XenApp server as an STA
server.
Click Add and enter for STA URL: http://XenApp.training2.lab:8080
Click Create.
Page 32
Services
Step
17.
18.
Action
Review the information and click Finish on this window.
Next, we need to go to the Store and enable remote access.
Navigate to Stores node and click on Enable Remote Access.
Page 33
Services
Step
19.
20.
Action
Select No VPN tunnel and select the Gateway (AG-SAML) we recently added.
Click OK.
Next, we need to propagate the changes made on StoreFront1 (Site2-XenApp VM) to
StoreFront2 (Site2-XenDesktop VM).
In the StoreFront console (from XenApp VM), go to Server Group node and click on
Propagate Changes and then OK.
Page 34
Services
Step
21.
22.
Action
Once Propagation is complete, verify that it was successful.
Click OK.
Before we jump into the SAML configuration on the NetScaler Gateway, let’s test if the
virtual server is properly configured to work with Receiver for Web.
From the Site2-Win8Client, open Internet Explorer and enter the following URL:
https://agsaml.training2.lab
Login to the NetScaler Gateway virtual server.
Username: user1
Password: Citrix123
Page 35
Services
Step
23.
24.
Action
Verify that you can login to the NetScaler Gateway virtual server and launch applications
from the Receiver for Web site.
Click Log Off.
Now, we need to configure a SAML policy for NetScaler Gateway. This way users will not
authenticate at the NetScaler Gateway virtual server but instead on the SAML idP server.
Return to the NetScaler Configuration Utility and navigate to Configuration -> NetScaler
Gateway -> Policies -> Authentication -> SAML
Page 36
Services
Step
25.
26.
Action
Click Add. Under Create Authentication Policy, name the policy as SAML-NG-Pol and
click on New to create a profile.
Under Create Authentication Server window, enter the following parameters:
Name: SAML-NG-Prof
IDP Certificate Name: wildcard.training2.lab
Redirect URL: https://idpcc.training2.lab/simplesamlphp/www/saml2/idp/SSOService.php
User Field: blank
Signing Certificate Name: wildcard.training2.lab
SAML Issuer Name: agsaml.training2.lab
Default Authentication Group: blank
Two Factor: OFF
Reject Unsigned Assertion: uncheck
Note: We’re leaving Two Factor authentication turned OFF for now. Once we verify that
SAML authentication is working correctly on the NetScaler Gateway virtual server, we
will come back and turn it ON.
Click Create.
Page 37
Services
Step
27.
Action
Back in the Create Authentication Policy window, we need to define an expression to
allow users login using SAML authentication.
Click on the drop-down menu and select True value.
28.
Select Add Expression
Click Create and then Close.
Page 38
Services
Step
29.
30.
Action
Verify the SAML policy exists with the corresponding profile.
Continue to the next step.
Next, we need to bind the SAML authentication policy to the NetScaler Gateway virtual
server. To do this, we will connect via PuTTY to the NetScaler and bind the policy.
From the Windows 8 client, go to the desktop and open PuTTY
Let’s connect to the NetScaler using the NSIP: 192.168.20.50
31.
Click Open.
Login with the following credentials:
Login as: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Page 39
Services
Step
32.
Action
First, we need to unbind the LDAP policy from the agsaml.training2.lab virtual server in
order to test SAML authentication.
In PuTTY, type the following command:
33.
34.
35.
> unbind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -policy
192.168.20.11_LDAP_pol
Next, we need to bind the SAML policy to the agsaml.training2.lab virtual server. Type the
following command:
> bind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -policy SAML-NG-Pol
-priority 100
Click on the Save icon to save the current configuration.
In the Site2-Win8Client VM, close any running instances of Internet Explorer. Re-open
Internet Explorer and navigate to the following URL: https://agsaml.training2.lab
In this test, you should get redirected to the idP login site instead of the NetScaler
Gateway login page.
Page 40
Services
Step
36.
Action
Enter the following credentials:
Username: user1
Password: Citrix123
37.
Click Login.
Once you login through the idP, you will notice that your request is redirected to the
NetScaler Gateway virtual server; however, the following error appears:
Why do we get this error?
This error appears because NetScaler Gateway redirected the user authentication request
to the SAML idP portal in order to be validated. Once the idP entity validates user
credentials, it generates a SAML token acknowledging the user has provided valid
credentials and this authentication token is returned back to the NetScaler Gateway.
Since SAML assertions do not include any credentials in the response, there is no domain
account information available in order for the NetScaler Gateway to perform single signon into StoreFront. As a result, the StoreFront server generates the following error
“Cannot complete your request”.
In order to allow domain users to login successfully to StoreFront, we need to enable two
factor authentication with SAML. This way, we can pass LDAP credentials to StoreFront
and successfully complete the Single sign-on process.
Continue to the next step.
Page 41
Services
Step
38.
Action
To enable two-factor authentication on SAML, go back to PuTTY and ensure that you are
still connected to the NetScaler SSH session. If not, re-connect to the NetScaler NSIP:
192.168.20.50.
Login: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Type the following command:
> set authentication samlAction SAML-NG-Prof -samlTwoFactor ON
39.
Next, we need to bind the LDAP policy to the NetScaler Gateway virtual server to prompt
now users for domain credentials.
In the PuTTY session, type the following command:
> bind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -policy
192.168.20.11_LDAP_pol -priority 110
40.
Let’s verify that both policies are bound to the agsaml.training2.lab virtual server.
Type the following command:
> sh run | grep agsaml
add vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab SSL 192.168.20.111 443
add authentication samlAction SAML-NG-Prof -samlIdPCertName
wildcard.training2.lab.cerwildc -samlSigningCertName wildcard.training2.lab.cerwildc samlRedirectUrl "https://idp-cc.training2.lab/simplesamlphp/www/saml2/idp/SSOService.php"
-samlRejectUnsignedAssertion OFF -samlIssuerName agsaml.training2.lab -samlTwoFactor ON
bind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -staServer "http://xenapp.training2.lab:8080"
bind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -policy SAML-NG-Pol -priority 100
bind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -policy 192.168.20.11_LDAP_pol -priority 110
bind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -policy PL_OS_192.168.20.111 -priority 100
bind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -policy PL_WB_192.168.20.111 -priority 100
bind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -policy PL_AG_PLG_192.168.20.111 -priority 100
bind vpn vserver agsaml.training2.lab -policy PL_PNA_192.168.20.111 -priority 100
You can see that both SAML-NG-Pol and 192.168.20.11_LDAP_pol are bound to the
VPN vserver agsaml.training2.lab.
41.
Continue to the next step.
Let’s save the NetScaler configuration by typing the following command:
> save config
NOTE: SAML policies can only be bound to the primary authentication source and not the
secondary.
Page 42
Services
Step
42.
Action
Next, let’s test the authentication process once more. From the Site2-Win8Client VM,
close Internet Explorer and open a new window. Navigate the following URL:
https://agsaml.training2.lab.
You should get redirected to the idP portal automatically.
43.
Continue to the next step.
Login using the following credentials:
Username: user1
Password: Citrix123
Click Login.
Page 43
Services
Step
44.
Action
After successful authentication at the idP portal, your request will be redirected back to the
NetScaler Gateway login page.
At this point, NetScaler Gateway is prompting users to provide domain credentials to login
to virtual server. Please enter the following credentials:
45.
Username: user1
Password: Citrix123
Once you login, you should get redirected to the StoreFront Receiver for Web site and
single sign-on will work without issue since we have provided LDAP credentials to
StoreFront instead of the SAML token.
Page 44
Services
Step
Action
NOTE: At this this point, we have two-factor SAML authentication enabled. As the second
authentication source, we are using LDAP.
What if you would like to increase security by enabling a third authentication source, such as
RADIUS?
The authentication flow is as follows:
1- Users will first authenticate at the SAML idP authentication service
2- Users will then provide LDAP and RADIUS credentials at the NetScaler Gateway login page
Let’s try this out!
46. From the Site2-Win8Client VM, open a new Internet Explorer tab and login to the
NetScaler Configuration Utility http://192.168.20.50
47.
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Click on NetScaler Gateway > expand Policies > expand Authentication > and click on
RADIUS. Click on Add to create a new RADIUS policy. Enter the name of RADIUS-Pol.
Click on New.
Page 45
Services
Step
48.
Action
In the Create Authentication Server window, enter the following information:
Name: RADIUS-Prof
IP Address: 192.168.20.11
Port: 1812
Secret Key: Citrix123
Confirm Secret Key: Citrix123
Password Encoding: mschapv2
Click Create.
Page 46
Services
Step
49.
50.
51.
Action
Next, set the expression to ns_true by selecting True Value and click on Add Expression.
Click Create and then Close.
Verify the RADIUS policy has been created successfully.
Continue to the next step.
Next, we need to bind the RADIUS policy as part of the Secondary authentication in the
NetScaler Gateway virtual server.
Under the NetScaler Gateway node > select Virtual Servers and open the
agsaml.training2.lab.
Page 47
Services
Step
52.
Action
Go to Authentication tab, select Secondary under Authentication Policies and click on
Insert Policies to add the RADIUS-Pol policy.
Click OK.
Page 48
Services
Step
53.
54.
Action
Save the changes by clicking on the Save button
Let’s test our configuration!
From the Site2-Win8Client VM, close and re-open Internet Explorer and navigate to the
following URL: https://agsaml.training2.lab.
You should get redirected to the SAML idP portal. Login with credentials:
Username: user1
Password: Citrix123
Click Login.
Page 49
Services
Step
55.
Action
Once logged in successfully to the SAML idP portal, you should get redirected to the
NetScaler Gateway virtual server login page prompting for two-factor authentication. Enter
the following credentials for domain and RADIUS:
Username: user1
Password 1: Citrix123
Password 2: Citrix123
Note: Since we’re using RADIUS authentication from Windows, the same domain
password is used as RADIUS password.
56.
Click Log On.
If credentials are correctly entered, you should get logged in to the NetScaler Gateway
virtual server and perform single sign-on with StoreFront to access published resources.
Congratulations! You have configured external access to StoreFront using NetScaler Gateway with
triple factor authentication for added security.
END OF EXERCISE
Page 50
Services
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
NetScaler Gateway virtual server now supports a new authentication method
- SAML
IT Admins can now enable 3-factor authentication if desired to increase the
level of security to their resources
SAML authentication at the NetScaler Gateway virtual server is only
supported for browser-based connections and not for Citrix Receiver client
connections to a PNAgent or Store.
Page 51
Services
Exercise 4: NetScaler Gateway Plug-in
support for Windows 8
Overview
In this exercise, we will go through the installation and logging configuration of NetScaler Gateway Plug-in
for Windows 8 workstations. We will learn the new look and feel of the NetScaler Gateway Plug-in and
it’s interoperability with Citrix Receiver 3.4.
In this exercise, we will leverage the same NetScaler Gateway virtual server used in the Exercise #1 –
agsaml.training2.lab that has 3-factor authentication enabled.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: 20 minutes.
Step
1.
2.
Action
Open Internet Explorer and login to the Site2-NetScaler1 management IP
http://192.168.20.50
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Expand the NetScaler Gateway > click on Virtual Servers > open agsaml.training2.lab.
In order to test VPN connectivity, change the virtual server settings to SmartAccess
Mode.
Page 52
Services
Step
3.
Action
Next, let’s unbind any session policies that were set by the NetScaler Gateway wizard. Click
on the Policies tab, select each policy and click on the Unbind Policy button.
Please make sure there are no policies bound to the virtual server:
Page 53
Services
Step
4.
Action
Next, we need to create a new Session Policy to allow VPN connections through the
NetScaler Gateway.
Click on Insert Policy > select New Policy…
5.
Under Create NetScaler Gateway Session Policy, enter the name of VPN-Pol and click on
New for the profile.
Page 54
Services
Step
6.
Action
Under Create NetScaler Gateway Session Profile, enter the following parameters under
Client Experience:
Name: VPN-Prof
Home Page: https://xenapp.training2.lab/Citrix/StoreWeb
Clientless Access: OFF
Plug-in Type: Windows/Mac OS X
Single Sign-on to Web Applications: checked
Click Create.
Page 55
Services
Step
7.
8.
9.
Action
Set the expression to ns_true by selection the option True Value in the drop-down menu
and selecting Add Expression.
Click Create.
Click OK under the Configure NetScaler Gateway Virtual Server window.
Save the changes by clicking on the Save button.
Page 56
Services
Step
10.
Action
From the Site2-Win8Client VM, close Internet Explorer and then reopen it.
Navigate to the following URL: https://agsaml.training2.lab.
You should get redirected to the SAML idP portal to login. Enter the following credentials:
Username: user1
Password: Citrix123
11.
If authentication is successful, you should get redirected to the NetScaler Gateway virtual
server login page. Enter the following credentials:
Username: user1
Password 1: Citrix123
Password 2: Citrix123
Click Log On
Page 57
Services
Step
12.
Action
Once logged in, you should get prompted to install the Citrix Access Gateway Plug-in for
Windows. Click on Download and click on Run.
13.
Click Install on the Citrix Access Gateway Plug-in Setup.
14.
Wait until the installation completes and then click Finish.
Page 58
Services
Step
15.
Action
Once the VPN connection is successful, you should get redirected to the StoreFront
Receiver for Web site. To login, enter the following credentials:
Username: TRAINING2\user1
Password: Citrix123
Click Log On.
16.
NOTE: You will lose the remote desktop connection to the VM. Switch to a console
connection to continue with the rest of the exercise.
OPTIONAL: Once logged in, launch any application (like Calculator) to ensure
connectivity.
Page 59
Services
Step
17.
18.
Action
Logoff from the VPN session. Right-click on the Receiver icon and click About.
To complete the logoff, expand Advanced and Click on Access Gateway Settings ->
Logoff
Click Yes at the prompt.
Page 60
Services
Step
Action
INFO: What about if I want to run the NetScaler Gateway Plug-in without Citrix Receiver?
You can execute the Plug-in directly by clicking on the Citrix Access Gateway icon in the Start
Menu on Windows 8:
NOTE: If you want to run the NetScaler Gateway Plug-in independently, make sure to exit Citrix
Receiver first from the taskbar and then, click on Citrix Access Gateway icon.
Page 61
Services
Step
19.
Action
OPTIONAL: Is there any other logging that can be enabled on Citrix Receiver along with
NetScaler Gateway Plug-in?
Yes. There is Receiver and VPN logging that can enabled and it is available at
http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX134101
Once the registry keys are set, you can find logs that pertain to the overall functionality of
the VPN client along with Citrix Receiver. The logs are the following:
-
Location: %localappdata%\Citrix\AGEE\nssslvpn.txt
o Written by nsload.exe
o Contains username, VPN logon URL, CAG type identification (EE or 5.x),
version, etc.
-
Location: C:\ProgramData\Citrix\AGEE\nscltapi.txt
o Contains information about the type of VPN connection that is being
established
o We can see if it’s a full VPN, ICA Proxy etc.
10:55:19.845 vpnCookie size : "65", URL :
"https://agsaml.training2.lab/" and clientType :
"2,cvpn,agent"
END OF EXERCISE
Page 62
Services
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
NetScaler Gateway 10.1 now supports Windows 8 operating system to run
the NetScaler Gateway Plug-in
Please note that the Citrix NetScaler Gateway Plug-in 10.1 version does not
support Windows 8 RT releases (ARM-based devices such as Microsoft
Surface). The plug-in is only supported on Intel-based Windows 8 devices
(32-bit or 64-bit.)
Page 63
Services
Exercise 5: Networking and Traffic
management enhancements
Overview
In this exercise, we will explore some of the new networking and traffic management features available in
NetScaler 10.1, including TFTP load balancing, NAT46 translations - when transitioning from an IPv4 to
an IPv6 infrastructure, and Traffic Domains - for configuration and traffic isolation.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: 15 minutes.
Step Action
In our lab, we have two PVS servers (Site2-PVS1, Site2-PVS2) and a single PVS target (Site2Win7Target). The target is set to boot from the network, get an IP address from DHCP and use the
DHCP options to find the bootstrap image to “stream” the OS.
1.
Start the PVS target. Right-click on the Site2-Win7Target and click on start.
Page 64
Services
Step
2.
Action
The machine will boot and receive an IP from DHCP; however, it will not find the required
options in the DHCP offer packet in order to load the bootstrap image.
Click on the Site2-Win7Target console tab and inspect the output.
3.
For a successful boot, we need to configure DHCP to include the correct options. In
XenCenter, click on the Site2-AD.training.lab VM, click the Console tab and login with
the credentials provided:
Username: TRAINING2\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Page 65
Services
Step
4.
5.
Action
Open the DHCP console. Expand the IPv4 scope and right-click on the Scope Options
node to configure the necessary options:
In the Scope Options, include the following parameters:
Option 66: 192.168.20.16 (This is the address of one of the PVS servers)
Option 67: ARDBP32.BIN (This is the bootstrap image)
Click OK.
Page 66
Services
Step Action
NOTE: The challenge with this configuration is the limitation of only being able to include a single
IP in the Boot Server Hostname Option. Even though, we could use DNS round robin and include
a hostname with multiple IP addresses as part of the response, there is no mechanism to monitor the
correct functionality of the TFTP service.
This is where NetScaler adds value as it has native support for Load Balance TFTP servers and
monitor for a known payload.
Later in this lab, we will configure the NetScaler appliance to fully load balance TFTP. For now, we
will concentrate on the boot process.
Continue to the next step.
6.
Next, let’s reboot the Target machine. In XenCenter, right click on the Site2-Win7Target
and start the VM. Switch to the console tab and observe the output.
Does it receive the bootstrap file and prompts to boot the OS?
TIP: In certain occasions, the console output window does not refresh automatically. Hit
ENTER once to force the display of the latest output.
Page 67
Services
Step
7.
8.
Action
From the boot menu, select 1 and wait for the OS to boot. At this point the PVS target will
login to the PVS cluster and retrieve the vDisk image on demand in order to boot the
necessary OS components.
NOTE: This process will take between 2-3mins to complete.
OPTIONAL: Login to the Site2-Win7Target VM to make sure that it works as expected.
Use the local administrator account using the following credentials:
Username: WIN7-PROD\Administrator
Password: citrix
In the next section, we will create the TFTP load balancing configuration and then proceed to test
the solution.
9.
From XenCenter, right click on the Site2-Win7Target VM and select shutdown.
Page 68
Services
Step
10.
Action
Return to the Site2-Win8Client VM. If credentials are requested, use the following:
Username: TRAINING2\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
TIP: Windows 8 has a new behavior when reconnecting using Remote Desktop to an
existing session as prevents you from typing a password. If this occurs, click on the arrow to
go back to the account selection and select Other. This will allow you to enter a password.
11.
Open Internet Explorer and navigate to the NetScaler Administration utility
http://192.168.20.50
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Page 69
Services
Step
12.
Action
Create the server objects for our load balancing configuration. Navigate to Configuration ->
Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Servers -> Add.
Create two objects, one for each PVS server using the following information:
Server Name: PVS1
IP Address: 192.168.20.16
Server Name: PVS2
IP Address: 192.168.20.17
Click Create each time for each server and then Close to return to the console.
13.
Create the services for the TFTP servers. Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management
-> Load Balancing -> Monitors -> Add.
Under the Standard Parameters tab, enter the following:
Name: tftp-mon
Type: USER
Interval: 5secs
Response Time-out: 2
Page 70
Services
Step
14.
Action
Click on the Special Parameters tab. Use the following information:
Script Name: nstftp.pl
TIP: Since this is a script on the appliance, click on Browse button and select the correct
file.
Click Create and then Close to continue.
Page 71
Services
Step
15.
Action
Create the services for the TFTP servers. Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management
-> Load Balancing -> Services -> Add.
Use the following parameters:
For PVS1
Service Name: TFTP1_svc
Protocol: TFTP
Server: PVS1 (192.168.20.16)
Port: 69
Monitors Configured: tftp-mon
For PVS2
Service Name: TFTP2_svc
Protocol: TFTP
Server: PVS2 (192.168.20.17)
Port 69
Monitors Configured: tftp-mon
Click Create each time to complete the configuration for each service, then Close to
continue.
Example:
Page 72
Services
Step
16.
Action
Next create the virtual server and bind the TFTP services to it. Navigate to Configuration > Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Virtual Servers -> Add.
Use the following parameters:
Name: TFTP_vserver
Protocol: TFTP
IP Address: 192.168.20.110
Port: 69
Click Create and then Close to continue.
NOTE: No persistence configuration is necessary as the TFTP transaction will stick to the same
server until completion. The next TFTP transaction will be load balanced according to the load
balancing method configured, by default, LEASTCONNECTIONS.
17. Verify the status of the virtual server. It should show UP with two services bound.
Continue with the next step.
Next, we will make the necessary changes to the DHCP scope to redirect TFTP requests to the
NetScaler TFTP virtual server.
18. Select the Site2-AD.training2.lab VM and login using the following credentials, if required:
Username: TRAINING\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Page 73
Services
Step
19.
Action
Return to the DHCP administration console and modify the scope to include the VIP as
part of the configuration.
Click OK.
Page 74
Services
Step
20.
Action
Now, it is time to test the setup. In XenCenter, power ON the Site2-Win7Target VM.
Inspect the boot log and make sure the TFTP VIP is included in the DHCP reply.
21.
In the Site2-Win7Target console, select option 1 to boot the OS to make sure it works as
expected.
22.
Let’s simulate a PVS node failure. In XenCenter, shutdown Site2-PVS1.
Page 75
Services
Step
23.
Action
Go back to Site2-Win8Client. In the NetScaler configuration utility, navigate to
Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Services.
Is the TFTP service for PVS1 down?
Click on the Refresh icon to retrieve the latest status.
24.
Continue to the next step.
In XenCenter, reboot Site2-Win7Target. Inspect the console log.
Does it still get the bootstrap file?
Page 76
Services
Step
25.
26.
Action
Now, let’s simulate a PVS1 recovery and PVS2 failure. In XenCenter, start Site2-PVS1 and
shutdown Site2-PVS2. Wait until both VMs fully boot.
Go back to Site2-Win8Client, on the NetScaler console, inspect the services status.
Refresh the list using the Refresh icon on the top right.
TFTP1_svc should be UP and TFTP1_svc should be DOWN.
Page 77
Services
Step
27.
Action
Reboot the Site2-Win7Target VM. The target VM should be able to boot as there is no
service interruption unless all the PVS servers part of the load balancing configuration are
DOWN.
28.
In order to release some resources, shutdown Site2-PVS1, Site2-PVS2, and Site2Win7Target VMs.
Congratulations! You have configured TFTP load balancing for a Citrix Provisioning
Services deployment. Next, we will explore additional networking enhancements included
in NetScaler 10.1.
29.
NAT46 Enhancements
Page 78
Services
Step
30.
Action
In this exercise we will explore the new stateless NAT46-NAT64 translation feature
included in NetScaler 10.1. For this, we will use a NetScaler appliance setup in two-arm
mode and two hosts on each attached network. See diagram:
Please make sure all three VMs are running.
Site1-NetScaler2
Site1-Apache3
Site1-Win8Client
31.
Go back to the Site1-Win8Client VM. Login using the following credentials, if required:
32.
Username: TRAINING\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Open Internet Explorer and navigate to the Site2-NetScaler2 Configuration Utility at
http://192.168.10.55. Login with username nsroot and password nsroot.
In the First Time Configuration wizard, enter a the following parameters:
33.
NetScaler IP Address: 192.168.10.55
Subnet IP Address: 192.168.10.56
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
DNS (IP address): 192.168.10.11
Time Zone: GMT-07:00-PDT-America/Los_Angeles
34.
35.
36.
Click Continue.
In the Manage Licenses, click Continue. We already have the necessary licenses installed on
the system.
Review the information on the next section. Click Done to submit the changes.
To prevent the appliance initializing the First Time User wizard in the event of a reboot,
save your configuration. Click on the Save icon on the top right.
Page 79
Services
Step
37.
38.
Action
Next, let’s enable the necessary features. Navigate to Configuration -> System -> Settings > Configure Advanced Features. Enable the IPv6 Protocol Translation feature.
Click OK.
In this exercise, we will use the Site1-Apache3 VM which is behind the NetScaler
appliance. Let’s set the IPv6 address. For this, we will have to reinitialize the interface in
order for the IPv6 configuration to take effect. Login to the VM and execute the following
command:
Username: root
Password: Citrix123
# /etc/init.d/net.eth0 restart
Page 80
Services
Step
39.
Action
Verify the server’s IPv6 address. Login and execute the following credentials:
# ifconfig
You should see the global IPv6 address assigned to the eth0 interface:
9900::2/96
40.
In order to get IPv6 connectivity, let’s assign an IPv6 address to the NetScaler. Go back to
the NetScaler configuration utility and navigate to Configuration -> Network -> IPs ->
IPv6s -> Add.
Enter the following parameters:
IPv6 Address: 9900::1/96
Type: SNIP
Leave the other settings with default values.
41.
Click Create and then Close.
On Site1-Win8Client, open an SSH connection to the NetScaler using PuTTY. Login to
Site1-NetScaler2 using the provided information:
IP address: 192.168.10.55
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Page 81
Services
Step
42.
Action
From the CLI, ping the IPv6 address of the server sourcing the traffic from the IPv6 SNIP.
Execute the following command:
> ping6 -c 4 -S 9900::1 9900::2
NOTE: the ‘-S’ above is in capitals!
Do you have connectivity?
In order to map IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses in a stateless manner, a new parameter was
introduced in the INAT configuration. This INAT parameters are composed of a pre-defined prefix
that will be used when mapping IPv4 to IPv6 addresses and vice versa. Only 96-bit prefixes can be
configured as the prefix is appended to the 32 bit IPv4 address for 128 bits that make up an IPv6
address.
43. For this configuration, we are using the IPv6 prefix 9900::/96.
Navigate to Configuration -> System -> Network -> Configure INAT parameters. Use the
following prefix:
Prefix: 9900::/96
Click OK.
Page 82
Services
Step
44.
Action
Next, we need to configure the corresponding INAT rule to map an IPv4 address to an
IPv6 address. Navigate to Configuration -> System -> Network -> Routes -> INAT ->
Add.
Enter the following parameters:
Name: inat-test
Public IP Address: 192.168.10.105 IPv6: Unckecked.
Private IP Address: 9900::2 IPv6: Checked
Mode: Stateless
Click Create and then Close.
45.
Inspect that the IP addresses were added correctly. From the NetScaler configuration utility,
navigate to Configuration -> System -> Network -> IPs -> IPv4.
Was a new VIP added?
Page 83
Services
Step
46.
Action
From the Site1-Win8Client VM, open another open a command prompt and send a PING
to the “external” IPv4 address defined in our INAT configuration.
C:\ ping 192.168.10.105
47.
Was the ping successful?
Inspect that the translation is working properly. Go back to the Site1-Apache3 console.
Perform a TCPDUMP for IPv6 traffic to show the incoming packets:
48.
# tcpdump ip6
Open a new tab in Internet Explorer and navigate to a web application hosted by the Site1Apache3 VM. Login with the credentials provided.
http://192.168.10.105/phpmyadmin/
49.
50.
Username: root
Password: Citrix123
Return back to the PuTTY session to Site1-Apache3. Click on a few links and inspect the
TCPDUMP output.
Do you see any IPv6 traffic to port 80?
Note the source IPv6 address. (Highlighted in the box). You will use this information in the
next step.
NOTE: The source IP might be different in your lab. Since the Site1-Win8Client VM is
configured for DHCP, it is possible that it is assigned a different source address.
Page 84
Services
Step
51.
Action
The 32-bit IPv4 address is prepended the prefix configured before. Let’s decode the
address. Take the source IPv6 address noted in the previous step. Return back to Internet
Explorer in Site1-Win8Client and open a new tab. Navigate to the following URL:
http://192.168.10.105/php/ipv6.php
Enter the prefix and appended address as shown below:
Click Submit.
52.
NOTE: The encoded source IP address might be different in your lab.
The results page should show you the IPv4 address where the request come from:
Congratulations! You are now serving content from an IPv6 enabled server over an IPv4 network.
Next we will explore the configuration required to configure traffic domains.
TRAFFIC DOMAINS
In this exercise, we will leverage the mew traffic domains feature to allow IP reuse in order to create
server and services objects with the same configuration. This allows an administrator to provide a
simple level of multi-tenancy by using the same IP ranges in the same appliance.
53. In Site1-Win8Client. Open IE and navigate to the configuration utility for Site1NetScaler2.
http://192.168.10.55/
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Page 85
Services
Step
54.
55.
Action
Enable the Load Balancing feature. Navigate to Configuration -> System -> Configure
Basic Features. Check the Load Balancing options and then OK.
In order to reach IPv4 resources on the Private Subnet, add a Subnet IP in the following
range: 192.168.15.0/24
Navigate to Configuration -> System -> IPs -> Add
IP Address: 192.168.15.1
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Type: Subnet IP
Click Create and then Close.
Page 86
Services
Step
56.
Action
Let’s create a server object on the default traffic domain: 0
In the NetScaler Administration console, navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management
-> Load Balancing -> Servers -> Add.
Server Name: Apache3
IP Address: 192.168.15.2
Page 87
Services
Step
57.
Action
Create the corresponding service. Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management ->
Load Balancing -> Services -> Add
Service Name: Apache3_svc
Server: Apache3
Protocol: HTTP
Port: 80
Traffic Domain: Blank (Default)
Configured Monitors: tcp
58.
NOTE: This indicates Traffic Domain 0
Click Create and then Close.
Inspect the state of the service. It should be UP as monitor probes are send and received
correctly from the Subnet IP configured previously.
Verify the service status. Continue to the next step.
Page 88
Services
Step
59.
Action
Next, we’ll create a port-based VLAN to use it in our Traffic Domains configuration
Navigate to Configuration > System > Network > VLANs. Click Add.
VLAN ID: 100
Alias Name: TD100
Interface Bindings: (Check) 1/2
Click Create and Close.
INFO: A port-based VLAN is locally configured on the NetScaler and involves no 802.1q tagging.
This setting defines a new broadcast domain and segregates traffic to VLAN members.
60. Next, we will configure a new Traffic Domain. Go to Configuration > System > Network
> Traffic Domains. Click Add.
Use the following parameters:
Traffic Domain: 100
Alias Name: TD100
Do not click create just yet. We will add a VLAN binding next.
Page 89
Services
Step
61.
62.
Action
In the VLAN Bindings section, click on +Add
Select VLAN 100 and click the + sign next to it so that it appears on the configured
column:
Click Create and then Close.
Page 90
Services
Step
63.
Action
Let’s check the status of the service previously configured. Navigate to Configuration ->
Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Services
What is the state of the Apache3_svc? Why is it DOWN?
Since the interface is now bound to Traffic Domain 100 and all other objects (service, server, and
Subnet IP) are still part of Traffic Domain 0, the monitor probes will not be successful. Next, we will
override the configuration to configure new objects on Traffic Domain 100 with the same settings.
64. Let’s start with a new Subnet IP on Traffic Domain 100. Navigate to Configuration ->
System -> Network -> IPs -> Add.
Use the following parameters:
IP Address: 192.168.15.1
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Traffic Domain ID: 100
Type: Subnet IP
Click Create and then Close.
Page 91
Services
Step
65.
66.
Action
Notice duplicate entry. The only difference is the Traffic Domain ID which allows the
appliance to differentiate between entries with the same configuration and tie them to a
particular traffic domain.
Continue to the next step.
Next, create a new server object in Traffic Domain 100. Navigate to Configuration ->
Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Servers -> Add.
Click Create and then Close.
Page 92
Services
Step
67.
Action
Do the same for the service. Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load
Balancing -> Services -> Add.
Note that when you change Traffic Domain drop-down list to 100, the Server option
disappears.
68.
69.
Click Create and Close.
Inspect the service state. It should be UP indicating that TCP probes are being received.
Congratulations! You have re-used the same IP addresses for existing services by leveraging
the new Traffic Domains feature available in NetScaler 10.1. This allows you to provide a
basic degree of multi-tenancy by overloading the configuration and segregating traffic to a
particular interface or broadcast domain.
END OF EXERCISE
Page 93
Services
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
Citrix Provisioning Services use TFTP to transfer a bootstrap file in order to
stream the vDisk containing the OS image.
The PVS target contains no VHD and it completely boots off the network.
The NetScaler appliance monitors each TFTP server part of the PVS pool,
retrieves and inspects the bootstrap image file “ARDBP32.bin” for
consistency.
If any TFTP server goes down, it no longer affects the provisioning process
as the NetScaler re-routes a new TFTP request to an available server.
The new NAT46 feature allows enterprise to have a mixed environment. By
leveraging the NetScaler appliance as an IPv6 gateway, we can allow IPv4
resources to contact IPv6 hosts seamlessly.
NAT46 stateless translations do not allocate any resources on the appliance
to track the state of connections by employing a simple algorithm that allows
us to map IPv4 addresses into an IPv6 space.
Traffic domains allows simple multi-tenancy and IP re-use.
When using Traffic Domain, you can process traffic for multiple traffic
domains using the same interface by leveraging 802.1Q tagging. Also, it is
possible to restrict a Traffic Domain by binding a port-based VLAN to a
particular interface.
Page 94
Services
Exercise 6: SPDY gateway
Overview
In this exercise, we will take a practical approach to seeing the SPDY protocol in action using Mozilla
Firefox and Google chrome browsers with various utilities in order to dive deeper. We will use the
existing SF_vserver virtual server for StoreFront created in exercise 4. We will enable SPDY on the
virtual server to allow us to experience some of the SPDY enhancements included in NetScaler 10.1.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: 20 minutes.
Step Action
1.
Logon to the Site2-Win8Client VM. If required, use the following credentials to login:
2.
3.
4.
Username: TRAINING2\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Navigate to the Desktop and run Mozilla Firefox
For this exercise we will familiarize ourselves with Firebug. Firebug is a Web Developer
add-on for Firefox that includes many tools that help with the analysis of web traffic. This
will be useful for the analysis of the benefits of using the SPDY protocol.
Click on the Firebug icon:
In Firebug, enable the Net panel. Select the Net tab and click on Enable.
Page 95
Services
Step
5.
6.
7.
Action
Make sure All is selected
In Firefox open up URL https://sflb.training2.lab/Citrix/StoreWeb
This is the Load Balanced virtual server in front of the StoreFront servers.
Firstly we want to see some results in Firebug with SPDY disabled. Firebug will display the
output of requests, responses and will include timings, headers, cookies etc.
The key to interpret this data is on the
right. The Gray bars represents requests
that are blocking subsequent requests.
In the Firebug display above, we see that
each request for an object on the HTML
page has to be fulfilled first before
moving onto the next request.
We will see SPDY mitigates this by
multiplexing numerous GET requests
simultaneously in the next steps.
Hover over one of the requests and examine the output, then continue to the next step.
Page 96
Services
Step
8.
Action
Let’s see SPDY in action! Close the Firefox browser. Open Internet Explorer and login to
the Site2-NetScaler1 management IP http://192.168.20.50
9.
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Virtual Servers.
Highlight the SF_vserver and select Open.
Select the Profiles tab.
10.
In the HTTP Profile option, click New.
Page 97
Services
Step
11.
Action
In Create HTTP Profile dialog box enter the following parameters: :
Name: SPDY
SPDY: Checked
Leave the rest of the parameters with the default values. Click Create. In the Virtual Server
Properties, click OK to commit the changes.
Page 98
Services
Step
12.
Action
Open up Firefox again, enable Firebug and navigate to the same URL:
https://sflb.training2.lab/Citrix/StoreWeb
In Firebug, you should see a display something like in the screenshot below:
TIP: Hit CTRL+F5 to force Firefox to refresh all objects on the page.
This shows off SPDY at work! After the initial load of /Citrix/StoreWeb we see multiple
simultaneous requests for elements in the page being requested. There is no blocking of the
GET requests which should result in faster page load times!
NOTE: Do not be alarmed if you see any elements in red that display a 404 Not Found
error.
Page 99
Services
Step Action
INFO: SPDY is enabled on the NetScaler virtual server; however, all communication with the
backend web servers is over HTTP. How does the NetScaler keep track of the various streams
when it sends multiple GET requests simultaneously?
ANSWER: The NetScaler adds a header to the GET requests to the web servers. This header is
called X-NS-SPDY-STREAM and is given a value for the stream. Here is an example screenshot
from a packet trace taken on the NetScaler and visualized in Wireshark.
13.
To view whether we can see a SPDY connection, we will leverage the built-in debugging
utilities in Google Chrome.
Open up the Chrome browser from the desktop on Site2-Win8Client. Enter the following
URL:
https://sflb.training2.lab/Citrix/StoreWeb/
Page 100
Services
Step
14.
Action
In Chrome, open up a new tab and enter in this URL chrome://net-internals
From the list select SPDY. You should see a SPDY status page like this:
15.
This confirms that SPDY is working and fully configured in the virtual server.
Switch back to Mozilla Firefox. Let’s see what support it has for SPDY.
Open a new tab, and enter about:config in the URL field. This will expose the advanced
settings for Firefox.
Click I’ll be careful, I promise!
Page 101
Services
Step
16.
Action
In the search bar, enter spdy
This shows us that the version of Firefox we are running has support for SPDY protocols
version 2 and 3.
17.
Continue to the next step.
OPTIONAL: Viewing SPDY related HTTP Headers in Firefox.
While we have Firebug open, expand one of the requests from the client. A good example is
‘GET /Citrix/StoreWeb’. In the Header tab you should see a header set by Firefox – ‘XFirefox-SPDY’.
Page 102
Services
Step Action
INFO: The rest of this exercise is optional. It involves taking a packet capture using Wireshark to
observe the SPDY related information. If you are interested in learning a bit more about the inner
working of SPDY, continue with this exercise.
18. Download and install Wireshark:
http://www.wireshark.org/download.html
Version 1.10.0rc1 is needed for Windows 8.
19. View SPDY working in a client side Wireshark packet trace:
On the Site2-Win8Client navigate to Start -> Wireshark.
Navigate to Capture menu and select Interfaces
20.
21.
Make sure the checkbox beside Citrix interface is checked.
Select Options.
Page 103
Services
Step
22.
Action
In the Capture Options dialog box, double-click the interface
Page 104
Services
Step
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
Action
In the Capture Options dialog box, double-click the interface
Click Start
Switch to the Firefox browser, open up the URL https://splb.training2.lab/
Switching back to Wireshark, there should be some packets visible in the capture. In the
Filter bar, enter the following Display Filter: ssl.handshake.extensions_npn
Select Apply
Select a Server Hello packet, such as the example below:
Page 105
Services
Step
28.
Action
In the middle window, select and expand Secure Sockets Layer
Expand TLSv1 Record Layer: Handshake Protocol: Server Hello
Expand Handshake Protocol: Server Hello
Expand Extension: next_protocol_negotiation
Expand Next Protocol Negotiation
Page 106
Services
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
NetScaler support for SPDY is only available for SSL virtual servers.
SPDY uses TLS Next Protocol Negotiation to negotiate the version of
SPDY used during the SSL handshake
Client browser support for SPDY is built-in to Google Chrome and
Mozilla Firefox.
Page 107
Services
Exercise 7: Clustering spotted VIP support
Overview
In this exercise we will setup a 2-node cluster using the improved NetScaler UI included in NetScaler
10.1. Then we will configure a Spotted VIP configuration to “stick” traffic for a particular virtual server
to a specific node in the cluster. This is one of the new enhancements in NetScaler 10.1: spotted entity
support.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: XYZ minutes.
Step Action
A NetScaler Cluster uses a dedicated network segment to “steer” traffic between nodes. This is
called the backplane. Our first step is to create a new network in XenServer and bind this to the
NetScaler appliances as a secondary interface.
1.
In this exercise, we will use the NetScaler appliances located in Site1. First, let’s make sure
that both of the NetScaler appliances are powered ON. In XenCenter, make sure that
Site1-NetScaler1 and Site1-NetScaler2 are UP and running
2.
In XenCenter, highlight the XenServer host and select the Networking tab. Click on Add
Network. Select Single-Server Private Network and Click Next.
3.
4.
5.
Label this Network: NetScalerBackplane. Click Next.
Leave the Automatically add this Network to new Virtual machines unchecked and
click Finish.
Now let’s add virtual interfaces to the NetScaler appliances used in this exercise. In
XenCenter, highlight the Site1-NetScaler1 VM and click on the Networking tab.
Page 108
Services
Step
6.
7.
Action
Click Add Interface. Select NetScalerBackplane in the Network drop-down menu. Click
Add.
Do the same for Site1-NetScaler2.
NOTE: Site1-NetScaler2 has already another virtual interface configured:
InternalPrivateSubnet. This network will be used in a different exercise. Add the
additional interface as a third interface.
8.
Reboot both VMs in order for the NetScaler appliances to recognize the new interfaces.
Wait until both NetScaler appliances come back online.
Page 109
Services
Step
9.
Action
In this exercise, we will use the Site1-Win8Client to configure the cluster. Login with the
following credentials if required:
10.
Username: TRAINING\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Click on the Desktop tile.
11.
Open Internet Explorer and login to the Site1-NetScaler1 management IP.
http://192.168.10.50
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Since these appliances are not fully configured, you are greeted with the First-Time Configuration
Wizard. Continue to the next step.
12. On the System section, add a SNIP: 192.168.10.51. Use the following parameters:
NSIP: 192.168.10.50
SNIP: 192.168.10.51
Hostname: Blank
DNS: 192.168.10.11 (Click Add).
Time Zone: GMT-07:00 PDT-America/Los_Angeles
13.
14.
Click Continue.
On the Manage Licenses section, click Continue as a valid license for clustering is already
installed.
Review the information and click Done.
Page 110
Services
Step
15.
Action
Save your configuration by clicking on the Save icon and click Yes at the prompt.
NOTE: This is important as the appliance will display the Initial Configuration Wizard if it
does not find a valid Subnet IP defined.
16.
Navigate to Configuration -> System -> Cluster -> Manage Cluster. On the Cluster
Configuration, use the following parameters:
Cluster instance id: 1
Cluster IP address: 192.168.10.60
Backplane interface: 1/2
17.
Click Create.
Click Yes on the confirmation for warm reboot. The appliance will save its configuration
and proceed to reinitialize.
Page 111
Services
Step
18.
Action
Close the browser and open a new instance. Wait about 30-60secs for the NetScaler
appliance to warm reboot. Since this appliance is now part of a cluster (a 1-node cluster at
this point), connect to the Cluster IP to continue configuring the 2-node cluster.
http://192.168.10.60
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
19.
TIP: If you get redirected to a search engine results page, this means that the appliance is
still initializing the cluster components before it can accept connections to the cluster IP.
Wait a few moments and try again.
When setting up a cluster, the existing configuration is cleared for any node that joins the
cluster, including the initial node. You will get greeted once more by the configuration
wizard. Add the same subnet IP and DNS server.
SNIP: 192.168.10.51
DNS(IP Address): 192.168.10.11
20.
Click Continue twice and then Done.
It is time to add the second NetScaler appliance to the cluster. Navigate to Configuration ->
System -> Cluster -> Manage Cluster.
Click on Add.
Page 112
Services
Step
21.
Action
On the Create Cluster Node window, enter the following parameters:
Node id: 1
NetScaler IP address: 192.168.10.55
Backplane Interface: 1/1/3 (See note below for additional explanation)
State: ACTIVE
Cluster node credentials: nsroot / nsroot
Configuration Coordinator credentials: nsroot / nsroot
NOTE: Due to presence of Network ‘InternalPrivateSubnet’ this forces the
‘NetScalerBackplane’ interface to 1/1/3
22.
Click Create.
Click OK on the warning stating that the node will be rebooted. Then click Close to finish.
Page 113
Services
Step
23.
Action
At this point, the cluster has been fully configured and both nodes should report the
Admin and Operational State as ACTIVE.
On the cluster configuration utility, navigate to Configuration -> System -> Cluster ->
Nodes.
Check that both nodes are reporting the correct state. Click the Refresh to get the latest
status.
24.
The cluster architecture requires that one of the appliances assume the configuration
coordinator role, which is the node responsible for replicating the configuration to all nodes
in the cluster. Usually, the first appliance that joins the cluster assumes this role. In the same
window, scroll to the right to visualize the Configuration Coordinator column.
Which node is the CCO?
Click OK on the Configure Cluster Instance window and then continue to the next step.
Page 114
Services
Step
25.
Action
As a final step, we need to define the way traffic enters the cluster. For this exercise, we will
use a LinkSet. Navigate to Configuration -> System -> Network -> LinkSets -> Add.
Use the following parameters:
LinkSet: LS/1
Interfaces: 0/1/1 and 1/1/1
Click Create and then Close.
NOTE: Why are we selecting these interfaces? The LinkSet configuration determines the
uplink where the cluster will receive incoming traffic. In clustering, interfaces are renamed
to a 3-tuple to include the cluster node owner. The format for cluster interfaces is as
follows:
nodeID/controller/interface number
26.
e.g.: Interface 0/1/1 is interface 1/1 on node with ID 0.
Save your configuration by clicking on the save icon.
Page 115
Services
Step Action
Congratulations, your cluster is fully operational!
Next, we will configure an additional virtual server entity and assign a particular node to handle
traffic for the application. We will explore the difference between enabling and disabling strict mode.
27. Let’s enable the correct modes. In the cluster configuration utility, navigate to Configuration
-> System -> Settings -> Configure Modes.
Enable Use Subnet IP and Layer 3 Mode.
28.
Click OK to continue.
Also, enable the required features we will use in the rest of this clustering exercise. Navigate
to Configuration -> System -> Settings -> Configure Basic Features.
Enable SSL Offloading and Load Balancing.
Click OK to continue.
Why are we enabling these features again?
When joining a new node to the cluster, the join procedure automatically clears the existing
configuration by executing a “clear ns configuration full” command before joining
the node to the cluster. This mode clears all configuration (including settings and modes enabled)
except the NSIP, default route, and interface settings.
For more information, please see the man page for this command.
> man clear ns configuration
Page 116
Services
Step
29.
Action
Next, we will create a simple load balancing configuration. Let’s start with the server
objects. For this, we will load balance the two Apache servers present on the environment.
Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Servers -> Add.
Enter the following parameters:
Server Name: Apache1
IP Address: 192.168.10.18
Click Create. Do not Close the Window yet! We will be adding additional server objects.
Page 117
Services
Step
30.
Action
In the same window, create another server object for Apache2. Use the following
parameters:
Server Name: Apache2
IP Address: 192.168.10.19
Page 118
Services
Step
31.
Action
Create the corresponding HTTP services for Apache1 and Apache2. Navigate to
Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Services -> Add.
Enter the following parameters:
Service Name: Apache1_svc
Protocol: HTTP
Server: Apache1
Port: 80
Configured Monitor: TCP
Click Create. Do not close the window yet!
Page 119
Services
Step
32.
Action
In the same window, create another service for the Apache2 server. Use the following
parameters:
Service Name: Apache2_svc
Protocol: HTP
Server: Apache2
Port: 80
Configured Monitor: TCP
Click Create and then Close.
Page 120
Services
Step
33.
Action
Lastly, create the virtual server. Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load
Balancing -> Virtual Servers -> Add.
Use the following parameters:
Name: Web_vserver
Protocol: HTTP
IP address: 192.168.10.100
Owner Node: ALL Nodes
Backup Node: ALL Nodes
Bind Apache1_svc and Apache2_svc.
34.
Click Create. Do not click on Close as we are not quite finished.
The application we are load balancing requires persistence to work correctly. Click on the
Method and Persistence tab. In the persistence section, select the following parameters:
Persistence: COOKIEINSERT
Time-out: 0
35.
Leave other parameters with default values. Click Create and then Close.
Save your configuration. Click on the Save icon on the top right corner.
Page 121
Services
Step
36.
Action
From your external workstation, test connectivity by navigating to each external FQDN for
External IP# 1. Use the following credentials:
Username: root
Password: Citrix123
http://your-dashed-fqdn.mycitrixtraining.net/phpmyadmin/ (IP#1)
Did the application work correctly? Are you able to login?
INFO: This Virtual Server are configured as striped entities. This means that any node in the cluster
can process traffic for the configured entity. If a node is not available, the other nodes will be able to
steer packets destined to the backend server through another node in the cluster.
Next, we will configure an additional virtual server entity and assign a particular node to handle
traffic for the application. We will explore the difference between enabling and disabling strict mode.
Continue to the next step.
37. In this exercise, we will use the SharePoint server for a simple load balancing setup. In
XenCenter, ensure that the SharePoint VM is powered ON. If not, start the machine.
Page 122
Services
Step
38.
Action
In the Cluster Configuration Utility, navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management ->
Servers -> Add.
Create a server object for SharePoint. Enter the following parameters:
Server Name: SharePoint
IP Address: 192.168.10.14
Click Create and then Close.
Page 123
Services
Step
39.
Action
Create the service for SharePoint. Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management ->
Load Balancing -> Services -> Add. Use the following parameters:
Name: SharePoint_svc
Protocol: HTTP
IP Address: 192.168.10.14
Configured Monitor: TCP
Click Create and then Close.
Page 124
Services
Step
40.
41.
Action
Finally, create the virtual server. Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load
Balancing -> Virtual Servers -> Add. Use the following parameters:
Click Create and then Close.
Spotted entities are defined by binding them to a nodeGroup. Let’s create a new
nodeGroup that contains only node 0.
GUI Workaround
The NetScaler firmware version used
in the lab does not have the option to
create a NodeGroup from the UI.
This is fixed in an upcoming version;
however, we will use the CLI to work around this display issue in our lab.
On the Site1-Win8Client, use PuTTY to login to the cluster IP: 192.168.10.60. Use
nsroot/nsroot to login.
Create the nodeGroup and bind it to node 0 using the provided commands:
> add nodegroup ng1
> bind nodegroup ng1 -node 0
INFO: Strict mode determines if the system will automatically replace a failed node within the node
group with another node for configuration backup purposes. When creating a new nodeGroup, the
default option is to have STRICT mode disabled. We will toggle this option later to see the effect of
this option.
Page 125
Services
Step
42.
43.
44.
Action
Next, bind the SharePoint virtual server to this node group. From the PuTTY session
execute the following command:
> bind nodegroup ng1 -vserver SharePoint_vserver
We have now configured our Spotted entity. The SharePoint virtual server is only serviced
by node 0. However, strict mode is DISABLED, which means that in the event of a node
0 failure, the system will select the other available node to continue servicing traffic.
Return to the Cluster Configuration Utility and save your configuration by clicking on the
Save icon.
It is time to test our new spotted virtual server. From your workstation, navigate to the
external FQDN for IP#2.
http://your-dashed-fqdn.mycitrixtraining.net (IP# 2)
You should get prompted for HTTP authentication. Login with the following credentials:
Username: TRAINING\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
45.
Did the SharePoint site load correctly?
This site is solely serviced by node 0. Inspect the properties of the nodeGroup. In the
PuTTY session to the Cluster IP, type the following command:
> show nodegroup ng1
ng1
STRICT: NO
Current active node(s): 0
Bound entities count: 1
Backup node: 1
Configurationally bound node(s):
1) 0
Bound LB vserver(s):
1) SharePoint_vserver
Done
>
Note that STRICT mode is disabled.
Page 126
Services
Step
46.
Action
Let’s simulate a node 0 failure. Save your configuration by clicking on the Save icon and
then proceed to shutdown Site1-NetScaler1.
47.
Wait until Site1-NetScaler1 shutdowns completely. Attempt to browse the SharePoint site
from your browser. Is the site responding?
INFO: Since strict mode is DISABLED, traffic destined to this virtual server was taken over by
other available node: Node 1. The system automatically selects a new node to replace the failed one
in order to continue servicing the application.
48. Let’s apply the same test, but now with Strict mode enabled. Power Site1-NetScaler1 back
ON. Wait until it fully initializes and joins the cluster. This process will take about 2-4 mins.
49. Return to the cluster configuration utility on Site1-Win8Client. Since we rebooted the
Cluster Coordinator (CCO) and this node was the current owner of the Cluster IP, the
system will prompt you to re-login.
http://192.168.10.60
Use the following credentials:
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Page 127
Services
Step
50.
Action
In the Cluster configuration utility, check that Site1-NetScaler1 joins the cluster and it is in
ACTIVE status. This process will take about 1-2mins.
To verify this, navigate to Configuration -> System -> Cluster -> Manage Cluster.
Inspect the status of node 0. Click on the Refresh icon to retrieve the latest status.
51.
Click Close to continue.
Set the nodeGroup to STRICT mode. On Site1-Win8Client, open a new SSH session to
the Cluster IP using PuTTY:
52.
Cluster IP: 192.168.10.60
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Enable Strict mode on the nodeGroup. In the CLI, execute the following command:
53.
> set nodeGroup ng1 -strict YES
While in the PuTTY session, save your configuration:
54.
55.
> save config
Done
Browse the SharePoint site to make sure that it still works correctly. From your
workstation, refresh the page and navigate a few links.
Shutdown Site1-NetScaler1. Wait until it fully powers down.
Page 128
Services
Step
56.
57.
58.
Action
Return to the browser. Attempt to navigate the site from your workstation.
Did the site respond?
Since Strict mode is enabled, the system does not replace the failed node. The site will be
unavailable unless at least one node in the nodeGroup is active and operational.
Before you continue to the next exercise, power ON the Site1-NetScaler1 VM.
END OF EXERCISE
Page 129
Services
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
A 2-node cluster is an effective way to reach an Active / Active
configuration in order to fully utilize your hardware.
The cluster configuration is simplified as the configuration coordinator node
replicates all configuration statements to all nodes in the cluster.
A NetScaler cluster can be composed of 2 to 32 nodes.
Which node receives the initial flow and which node contacts the backend
server?
In a link set configuration, the traffic will flow from the CLIENT_IP to the
VIP through the MAC owner. Then, the cluster will select the node that will
process the request (flow processor) and forwards the request to this node
using the backplane interface. Next, the flow processor contacts the backend
server and fetches the response. Through the same backplane interface, this
is returned to the ARP owner who in turn sends it back to the CLIENT_IP.
NodeGroups can be created to bind specific virtual server entities to a
particular set of nodes within the cluster. When an entity is bound to a node
group, the entity becomes a spotted entity.
Traffic can still be received by any node in the cluster depending on the
traffic distribution method being used. If the incoming traffic flow belongs
to a spotted entity, the system will steer the traffic through the backplane
to the nodes in the nodeGroup.
Strict mode determines if the system automatically replaces a failed node
within the nodeGroup for configuration replication purposes.
The Spotted depth is the number of nodes part of a nodeGroup. Depth
can be =>1 to =<n, where n is the number of nodes in the cluster.
Page 130
Services
Challenge Exercise 8: XenMobile and
NetScaler Integration
Overview
XenMobile Device Manager is one of the key components of the Citrix XenMobile Solutions
Bundle. Simpler deployments usually contain a single XDM server; however, for high availability, it is
recommended to have multiple servers. Some of the key functionality for XDM is to provide device
enrollment services and this requires that end-point devices establish an SSL handshake to the XDM
server.
In order to load balance these components, it is required to have an SSL_BRIDGE configuration to
provide simple TCP offloading while still allowing the mobile device to SSL handshake with the
corresponding XDM server.
In this lab, we will configure external access using SSL to this component of the XenMobile solution
bundle. These instructions can be reused to add additional services for a full load-balancing setup.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: XYZ minutes.
Step Action
1.
Return to the Site1-Win8Client VM. If the workstation is locked, login with the following
credentials:
Username: TRAINING\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Page 131
Services
Step
2.
Action
Check that the XenMobile Device Manager (XDM) component was installed by accessing
the XDM console internally.
Open Internet Explorer and navigate to the following URL:
http://192.168.10.13/zdm/
Username: administrator
Password: Citrix123
3.
In the XDM console, click on the Policies tab. The external FQDN for IP# 2 should be
displayed. This tell us that the product was installed and customized for each environment
correctly.
NOTE: The FQDN shown below will be different than the one in your environment.
Please refer back to the Student portal page for a list of external FQDNs assigned to your
lab.
Next, we will allow external access to XDM components. For this we will use the NetScaler
appliance to allow SSL connections to the XDM servers on ports TCP-443 (XenMobile Device
Manager UI) and TCP-8443 (XenMobile device enrollment).
Page 132
Services
Step
4.
Action
NOTE: In the previous exercise, we configured a NetScaler cluster. Before we proceed, we
need to remove the node from the cluster and revert back the original configuration.
On the Site1-Win8Client VM, open a PuTTY session and login to Site1-NetScaler1.
IP: 192.168.10.50
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Execute the following commands to overwrite the current configuration with a pre-loaded
configuration file.
>
>
#
#
5.
rm cluster node 0
shell
cp /var/lab_backup/ns.conf_original_config /nsconfig/ns.conf
reboot
Perform the same configuration override on Site1-NetScaler2. Login using PuTTY.
IP: 192.168.10.55
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
>
>
#
#
6.
7.
rm cluster node 1
shell
cp /var/lab_backup/ns.conf_original_config /nsconfig/ns.conf
reboot
Wait until the appliances fully reinitialize. This process should take between 1-3mins.
We are ready to start the configuration. Open Internet Explorer and navigate to the
NetScaler configuration utility using the default credentials:
http://192.168.10.50
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Page 133
Services
Step
8.
Action
We are greeted by the First Time use wizard. On the System section, add a SNIP:
192.168.10.51. Use the following parameters:
NSIP: 192.168.10.50
SNIP: 192.168.10.51
Hostname: Blank
DNS: 192.168.10.11 (Click Add).
Time Zone: GMT-07:00 PDT-America/Los_Angeles
9.
10.
11.
Click Continue.
On the Manage Licenses section, click Continue as a valid license for clustering is already
installed.
Review the information and click Done.
Since we reverted to a default configuration, we need to enable the necessary features:
Navigate to Configuration -> System -> Settings -> Configure Basic Features
12.
Check Load Balancing and SSL Offloading. Click OK to continue.
Next, we will create the Server Object for XenMobile. Navigate to Configuration ->
Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Servers -> Add. Use the following parameters:
Name: XenMobile
IP Address: 192.168.10.13
Click Create and Close to continue.
NOTE: XenMobile Device Manager (XDM) requires all mobile devices to establish an SSL
handshake directly with the MDM server. We need to configure an SSL_BRIDGE setup in order
for devices to register correctly with the server.
Continue to the next step.
Page 134
Services
Step
13.
Action
Create the SSL_BRIDGE service on TCP port 443. In the NetScaler UI, navigate to
Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Services -> Add.
Use the following parameters:
Service Name: XenMobile_SVC
Server: XenMobile
Protocol: SSL_BRIDGE
Port: 443
Monitor: TCP
Click Create.
Page 135
Services
Step
14.
Action
Device enrollment requires access to an additional TCP port on the XDM server. Add
another service for TCP port 8443:
Service Name: XenMobileEnroll_SVC
Server: XenMobile
Protocol: SSL_BRIDGE
Port: 8443
Monitor: TCP
Click Create and then Close to finish.
Page 136
Services
Step
15.
Action
Next, create the XenMobile virtual server listening on port TCP 443. Use the following
parameters:
Vserver Name: XenMobile_vserver
IP Address: 192.168.10.101
Protocol: SSL_BRIDGE
Port: 443
Monitor: TCP
Service: XenMobile_SVC
Click Create and Close to finish.
Page 137
Services
Step
16.
Action
Lastly, add the XenMobile virtual server listening on port 8443.
Vserver Name: XenMobileEnroll_vserver
IP Address: 192.168.10.101
Protocol: SSL_BRIDGE
Port: 8443
Monitor: TCP
Service: XenMobileEnroll_SVC
Click Create and Close to finish.
INFO: We will now test external access to these components. From your workstation (external
device), navigate to the FQDN for the second public IP address provided. This information is
located in the student portal.
Page 138
Services
Step
17.
Action
From an external browser, enter the corresponding URL for the 2nd Public IP address in the
address bar. Login with the following credentials:
Username: Administrator
Password: Citrix123
You should be able to login without receiving any SSL warnings.
This completes this section. Next, we will configure external access to Exchange 2010 by SSL
offloading with NetScaler.
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
SSL_BRIDGE is required to successfully front-end the XDM component.
Multiple services can be bound to the virtual server in order to provide
redundancy. Use SSLSESSIONID or SOURCEIP persistence depending
on the requirements.
Page 139
Services
Exercise 8 Section 2: Front-ending Microsoft Exchange
deployments with NetScaler
Overview
In order for enforcing mail delivery policies to external mobile devices, the NetScaler appliance needs to
be the front-end device to the internal Microsoft Exchange infrastructure. In this exercise, we will
complete the necessary configuration on the NetScaler appliance as well as the Exchange server for the
deployment to be externally accessible.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: XYZ minutes.
Step Action
1.
In the Site1-Win8Client VM, open a new instance of Internet Explorer and navigate to the
OWA URL to verify that Exchange 2010 was correctly provisioned:
https://ex1.training.lab/owa/
Username: TRAINING\User1
Password: Citrix123
Since this is the first time accessing the user’s mailbox, accept the defaults for language and
time-zone.
If you are able to login to the user’s mailbox, continue with the next step.
Page 140
Services
Step
2.
Action
Go back to the NetScaler Configuration utility already opened in Internet Explorer. Relogin with the following credentials, if the session has expired:
http://192.168.10.50
3.
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
Next, we have to create the Exchange server object. Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic
Management -> Load Balancing -> Servers -> Add. Use the following parameters:
Name: Exchange
IP Address: 192.168.10.15
Page 141
Services
Step
4.
Action
Proceed to create the associated services. On the NetScaler Administration Utility, navigate
to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Services -> Add.
Create the Exchange Service on port 443:
Service Name: Exchange_SVC
Protocol: SSL
Port: 443
Monitor: TCP
Click Create and then Close.
Page 142
Services
Step
5.
Action
Next, let’s create the virtual server used for external access. Navigate to Configuration ->
Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Virtual Servers -> Add
Vserver Name: Exchange_vserver
IP Address: 192.168.10.100
Protocol: SSL
Port: 443
Monitor: TCP
Service: Exchange_SVC
Do not click Create just yet as we need to configure additional parameters.
Continue with the next step.
6.
Since this is an SSL virtual server, we need to bind a server certificate. For this lab, we will
use a production SSL certificate already preloaded in the default configuration. Click on the
SSL settings tab, and bind the wildcard.mycitrixtraining.net certificate.
Click Create and then Close.
Page 143
Services
Step
7.
Action
From your workstation, open a browser instance (Internet Explorer / Firefox / Chrome /
or Safari) and test connectivity to OWA by entering the external URL for IP#1.
https://your-dashed-fqnd.mycitrixtraining.net/owa/
Use the following credentials:
Username: TRAINING\user1
Password: Citrix123
You should be able to login and access the user’s mailbox:
Page 144
Services
Step
8.
Action
Now, we will test connectivity from your mobile device using the ActiveSync protocol.
Add a new Exchange account and configure email access using the following settings:
Since there are many different mobile operating systems, the process might differ from the
screenshots below.
Server: your-dashed-fqdn.mycitrixtraining.net (For IP# 1)
Email: user1@training.lab
Username: user1
Password: Citrix123
Domain: TRAINING
SSL enabled: YES
Port: 443
You should be able to access the user’s mailbox.
NOTE: In Android devices, the device will prompt you to allow the server to control some
of the security features required when setting up a new Exchange account. Click OK to
accept.
9.
To test basic Exchange functionality across different clients, on your external workstation,
go back to the OWA session you previously signed in using the User1 account. Sign out
from that session and log back in with the credentials for User2.
Username: TRAINING\user2
Password: Citrix123
10.
Send an email to user1@training.lab. Verify that you receive this email on your mobile
device.
This concludes with this exercise. Next, we will install and configure the XenMobile
NetScaler connector.
Page 145
Services
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
In order for the NetScaler appliance to interface with the XenMobile Device
Manager API, it uses an intermediary component called XenMobile
NetScaler Connector
The NetScaler leverages a new RESTful API via callout to enforce mail
delivery policies according to the security requirements of the enterprise
Page 146
Services
Exercise 8 Section 3: Installing and configuring XenMobile
NetScaler Connector
Overview
One of the features XM offers is the ability to apply policies to mobile devices. The XenMobile solution
leverages additional components to enforce external mail clients from accessing the Microsoft Exchange
infrastructure in order to retrieve mail according to applied policies. As part of a new component
announced with NetScaler 10.1, the NetScaler appliance can interface with the XDM API through a new
component labeled “XenMobile NetScaler Connector”. XNC provides a device level authorization service
of ActiveSync clients to NetScaler acting as a reverse proxy for the Exchange ActiveSync protocol.
In this exercise, we will focus on installing the XNC component and configuring it properly to continue
with the NetScaler integration configuration.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: XYZ minutes.
Step Action
1.
In XenCenter, select the Site1-XenMobile VM and click on the Console tab. Login with
the following credentials:
Username: TRAINING\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
2.
Page 147
Services
Step
3.
Action
From Site1-XenMobile, execute the XNC installer. This is located in the following path:
\\WIN8CLIENT\c$\citrix\Installers\XncInstaller.exe
4.
Click Next to continue.
Page 148
Services
Step
5.
Action
Accept the default options, agree to the license terms, and click Next to install the
component. Click Next and then Close to finish.
6.
Choose No when prompted to display the release notes.
7.
Click Start and then open the XenMobile NetScaler Configuration utility.
Page 149
Services
Step
8.
9.
Action
In the XNC Configuration utility, select the Web Service tab and configure the listening
address for the XNC service. Click Save and then Start the service.
NOTE: Since we have installed XNC on the XDM host, we do not require encryption as
all the traffic will not be placed on the wire. We will chose HTTP and port 9080 for the
configuration service.
Since XDM users SSL for its API, we need to use a valid FQDN to resolve to server IP.
Open the hosts file located at the following location:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
and add a new entry as follows:
192.168.10.13
your-dashed-fqdn.mycitrixtraining.net
Page 150
Services
Step
10.
Action
Next, we have to define a provider. Go back to the XNC configuration utility, select Config
Providers tab. Click Add and configure a new Provider using the following parameters:
Name: ZDM
Url: https://your-dashed-fqdn.mycitrixtraining.net/zdm/services/MagConfigService
Username: TRAINING\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Click Test Connectivity and Save to continue.
11.
After you save the configuration, the utility prompts you to start the Configuration Service
and Notification Services. Click OK to acknowledge each prompt.
Page 151
Services
12.
13.
Click on Start and select Run. Type services.msc to open the Services management console
and start the XenMobile Configuration Service:
Repeat the same step for XenMobile Notification Service
The next step is to define the type of access to restrict. Since mobile devices use the
ActiveSync protocol, click the Path Filters tab and highlight the Microsoft-ServerActiveSync entry and click on edit:
Page 152
Services
14.
15.
16.
In the Policy option, select Static + ZDM: Block mode to block
NOTE: These policies combine local (aka static) rules with those from ZDM. Block Mode
means that all devices not explicitly identified by the rules will be blocked access to
ActiveSync.
Click Save to finish.
Lastly, we need to allow XDM to report additional information to XNC via its API. From
your workstation, access the XDM console using the following URL:
https://your-dashed-ip.mycitrixtraining.net/zdm/
17.
Username: Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Once logged in, click on the Options link on the top right corner.
Page 153
Services
18.
On the XenMobile Server Options, navigate to the Modules Configurations -> Secure
Mobile Gateway and enable the following filters:
Forbidden Apps: Deny
Implicit Allow / Deny: Allow
Click Close to commit the modifications and Yes to confirm them.
19.
This concludes with this exercise. Next we will configure the necessary callout policy on the
NetScaler to interface XNC in order to determine if a user/device should be
allowed/blocked to access the Exchange infrastructure using ActiveSync.
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
In order for the NetScaler appliance to interface with the XenMobile Device
Manager API, it uses an intermediary component called XenMobile
NetScaler Connector
The NetScaler leverages a new RESTful API via callout to enforce mail
delivery policies according to the security requirements of the enterprise
Page 154
Services
Exercise 8 Section 4: Device enrollment and MDM policy
configuration
Overview
In order to apply ActiveSync policies, the mobile device needs to register with the XDM server. This
requires to install the XenMobile Connect agent on the mobile device and complete the enrollment
process. By default, our XenMobile Device Manager applies the following policies:
Performs a software inventory and reports back to the MDM server
Configures the XenMobile Connect agent to check-in every 2 minutes (Android-only setting)
Sets a 5-digit PIN number requirement (Completed already for Android devices, in our lab we will
add it to the iOS packed in order to get some practice configuring deployment package options)
Offers the user the possibility to install Citrix Receiver and GotoMeeting clients from the App
Store
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: XYZ minutes.
Step Action
1.
First, let’s configure the PIN requirement policy for iOS devices in order for you to get
familiar with the console.
From your workstation, open a browser instance (Internet
Explorer/Chrome/Firefox/Safari) and login the XDM console by navigating to the external
URL corresponding to the 2nd external IP used in the previous exercise.
https://your-dashed-fqdn.mycitrixtraining.net/zdm/
2.
Username: Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Depending on your platform (iOS/Android), labels for packages and other options change.
In the following section, we will list the actions required for each platform.
Page 155
Services
Step
3.
Action
In the XDM console, navigate to the Deployment tab.
For Android: Highlight the Base Android package and click Edit.
For iOS: the name of the package is Base iOS package. Highlight it and Click Edit.
4.
Select the resources link on the left menu to jump to the policies bound to this deployment
package.
Page 156
Services
Step
5.
Action
For Android: Expand the MDM policies, select the Require Pin policy, and click finish to
commit the changes.
For iOS: Expand the Configurations node. Select “Require PIN” and added to the
Resources to Deploy list. Click on Finish to finalize the configuration.
6.
Before sending notifications to mobile devices via email, we need to configure a notification
SMTP server. In the XDM console, click on the Options link on the top right corner.
Page 157
Services
Step
7.
8.
Action
On the Options window, expand Notifications and highlight Notification Server. Select
New -> SMTP server.
Complete the “Create a new SMTP configuration” using the following parameters:
Name: Exchange
Description: Training.lab Exchange
SMTP Server: ex1.training.lab
SMTP port: 25
Secure Channel Protocol: None
No Authentication: Checked
From Name: Administrator
From Email: adminnistrator@training.lab
Click Test Configuration to send a test message to User1. Click Create to commit the
changes and then Close to return to the XDM console.
Page 158
Services
Step
9.
Action
It is time to register our devices with the MDM server. For this, we will send an enrollment
invitation to the User1.
Click on the enrollment tab, select New -> Enrollment invitation
10.
In the General tab, select your device platform (Android / iOS)
For device ownership and enrollment mode select the following defaults:
Device Ownership: Employee
Enrollment Mode: Invitation URL
11.
Click on the User tab. Fill in the User filed with “user1”. Since we are using email for
enrollment invite, leave the Notification section empty.
Page 159
Services
Step
12.
13.
Action
The enrollment invite is create, but will not get sent immediately. In the enrollment tab,
check the box next to the new notification, and click on the Notify button.
Accept the prompt and send the notification:
Page 160
Services
Step
14.
Action
On your device, you should have received an email with the enrollment URL. To make sure
that we download the latest version of the agent, tap on the second link to download the
package from the App Store for your device.
NOTE: The screenshot might change depending on your device/platform/Mobile OS
version. This was tested on a Nexus 7 tablet running Android 4.2.2 and iOS 6.0.2 on iPhone
5.
Android:
iOS:
Page 161
Services
Step
15.
Action
Install the Citrix Mobile Connect agent.
Android:
iOS:
NOTE: Once the application is installed, the device will prompt you to install the Citrix
Mobile Enroll agent.
Page 162
Services
Step
16.
Action
Once installed, open the Connect app on your mobile device and complete the enrollment
process by providing the following information:
Username: user1
Server: your-dashed-fqdn.mycitrixtraining.net (IP# 2)
Password: Citrix123
17.
NOTE: The device will prompt you to install additional profiles (iOS) or active device
administrators (Android). The prompts will be different depending on the platform/OS
version/device type. Accept by installing the required profiles or adding the corresponding
device administrators in order to complete the enrollment process.
In the Citrix Mobile Connect agent, your device should be able to display the applications
pushed as part of the default packages as well as other settings in the configuration node.
For Android, inspect the Apps option and verify the applications appear on the list.
For iOS, open the Connect application and inspect the Configuration -> App Info
option to verify the Connect status. Force a Refresh to check-in with the server.
Page 163
Services
Step
18.
Action
On your workstation, go back to the XenMobile console and inspect the devices tab. Verify
your device was registered.
19.
Check if software inventory was performed on the device. Highlight the device and click
on edit.
20.
Inspect the Software Tab. Verify that all the installed applications show up on the list. We
will use this information later when configuring additional mail policies.
21.
This concludes with this exercise. Next, we will configure the NetScaler to interface with
XNC and allow or deny the user to get their mail.
Page 164
Services
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
A device can be registered in multiple ways. The XDM server is able to
contact the user via SMS or e-mail and send an enrollment URL to
download the package directly from the server or App Store. Alternatively,
this can be completed manually by download the package directly and
completing the enrollment process.
By default no configuration is pushed to the mobile device. In our example,
base packages have been provisioned to perform simple actions on the
mobile device
Page 165
Services
Exercise 8 Section 5: Configuring “Callout” to enforce XDM
mail delivery policies
Overview
In this exercise, we will complete the necessary configuration to leverage the callout feature and interface
with the XNC in order to enforce any mail delivery policies available to the device or user.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: XYZ minutes.
Step Action
1.
In XenCenter, login to Site1-Win8Client. Open Internet Explorer and login to the
NetScaler administration utility with the following credentials:
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
2.
http://192.168.10.50
Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Services. Click on
add to create a new service for the XenMobile NetScaler Connector listening on port
TCP 9080 using the following parameters:
Click Create and Close to commit the changes.
Page 166
Services
Step
3.
Action
Next, we will create the virtual server where we will bind the callout. This virtual server will
not receive live traffic, just callouts when evaluating an ActiveSync request, so we can
disable the directly addressable option.
Navigate to Configuration -> Traffic Management -> Load Balancing -> Virtual Servers.
Click Add and configure a virtual server with the following parameters. Don’t forget to bind
the service created in the previous step.
Click Create and then Close.
Page 167
Services
Step
4.
Action
Now, we will create the HTTP callout. Navigate to Configuration -> AppExpert -> HTTP
Callouts -> Add.
NOTE: Skip to Step 7 if you would prefer to paste in the CLI commands which is easier
than the tricky configuration via the UI!
Create a new callout with the following parameters:
Name: ActiveSyncFilter
Virtual Server: ActiveSyncFilter_vserver
Attribute-based: Checked
Return Type: TEXT
Expression to extract data from Response: HTTP.RES.BODY(20)
Do not click create just yet! We need to define the Request Attributes for the callout to
complete correctly. See next step.
Page 168
Services
Step
5.
Action
In the Create HTTP Callout window, click on configure Request Attributes:
Page 169
Services
Step Action
6. In the Configure HTTP Callout Request Attributes window, configure the callout with
the following parameters:
IMPORTANT: Please note that the user expression below has a SPACE “ “ after the
keyword “Basic”:
It is recommended to type in the values below manually rather than copy and paste.
Name
Method
Host Expression
URL Stem
Expression
GET
“callout.asfilter.internal”
“/services/ActiveSync/Authorize”
user
PARAMETERS
HTTP.REQ.HEADER("authorization").AFTER_STR("Basic
").B64DECODE.BEFORE_STR(":").HTTP_URL_SAFE
Agent
url
resultType
Value
HTTP.REQ.HEADER(“user-agent”).HTTP_URL_SAFE
("https://"+HTTP.REQ.HOSTNAME+HTTP.REQ.URL).B64EN
CODE
“json”
Click OK and OK to commit the changes. Now you can click Create and Close!
Page 170
Services
Step
7.
Action
Here are the equivalent CLI commands for Steps 4-6 above:
add policy httpCallout ActiveSyncFilter
set policy httpCallout ActiveSyncFilter -vServer ActiveSyncFilter_vserver -returnType
TEXT -hostExpr "\"callout.asfilter.internal\"" -urlStemExpr
"\"/services/ActiveSync/Authorize\"" -parameters resultType("json")
url(("https://"+HTTP.REQ.HOSTNAME+HTTP.REQ.URL).B64ENCODE)
user(HTTP.REQ.HEADER("authorization").AFTER_STR("Basic
").B64DECODE.BEFORE_STR(":").HTTP_URL_SAFE)
agent(HTTP.REQ.HEADER("user-agent").HTTP_URL_SAFE) -scheme http -resultExpr
"HTTP.RES.BODY(20)"
Page 171
Services
Step
8.
Action
Next navigate to Configuration -> AppExpert -> Responder -> Policies -> Add.
NOTE: Skip to step 10 to use the CLI rather than UI to create the responder policy and
bind it to the Exchange virtual server.
Configure a Responder policy with the following parameters:
Name: ActiveSyncFilter
Action: Drop
Expression: HTTP.REQ.URL.STARTSWITH("/Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync") &&
HTTP.REQ.HOSTNAME.EQ("callout.asfilter.internal").NOT &&
SYS.HTTP_CALLOUT(ActiveSyncFilter).CONTAINS("deny")
Click Create and then Close.
Page 172
Services
Step
9.
10.
Action
Bind this Responder policy to the Exchange virtual server. Navigate to Configuration ->
Traffic Management -> Virtual Servers. Open the properties of the Exchange_vserver,
select the Policies tab, click on Responder, then Insert Policy, and bind the
ActiveSyncFilter policy.
Click OK to commit the changes.
Here are the equivalent CLI commands for Steps 8-9 above.
add responder policy ActiveSyncFilter "HTTP.REQ.URL.STARTSWITH(\"/MicrosoftServer-ActiveSync\") &&
HTTP.REQ.HOSTNAME.EQ(\"callout.asfilter.internal\").NOT &&
SYS.HTTP_CALLOUT(ActiveSyncFilter).CONTAINS(\"deny\")" DROP
bind lb vserver Exchange_vserver -policyName ActiveSyncFilter -priority 100 gotoPriorityExpression END -type REQUEST
Page 173
Services
Step
11.
12.
Action
Go back to your mobile device and try to get your mail, you should be successful. Next we
will create a blacklist application policy to restrict the existence of some packages in order
for the user to be able to access their mailbox.
This concludes with this exercise.
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
All the components of the solution use an API to exchange information
about the status of users and devices. This information can be used on the
NetScaler to enforce security policies based on the device actions.
Page 174
Services
Exercise 8 Section 6: Configuring MDM policies to enforce
email security for ActiveSync enabled devices.
Overview
In this exercise, we will configure MDM policies to determine device compliance based on the software
packages installed on the device. This information will be made available to the NetScaler appliance via the
XNC API in order to enforce email security policies.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: XYZ minutes.
Step Action
1.
On your external workstation, open the XDM console by navigating to the following URL
which corresponds to your external IP #2:
https://your-dashed-fqdn.mycitrixtraining.net/zdm/
2.
Username: Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Click on the Policies tab. Expand App Policies and highlight Applications Access
Policies.
Page 175
Services
Step
3.
Action
Click on New Applications Access Policy and create a new policy with the following
parameters:
For Android:
Name: Android App Black List
Access Policy: Forbidden
OS type: Android
4.
For iOS:
Name: iOS App Black List
Access Policy: Forbidden
OS type: iOS
Click on New app and enter the following information:
For Android:
App Name: Instagram
App package name: com.instagram.android
For iOS:
App Name: Instagram
App bundle ID: com.burbn.instagram
Click Create and Create again to commit the changes.
NOTE: This application will be used to determine if the device is in compliance. This lab
requires that you install/uninstall the application multiple times to test for the policy. If you
would like to use another application, please note the package name exactly as it appears in
the software inventory list.
Next, we will need to modify the deployment package to enforce this rules during the next agent
check-in. This will determine the device compliance and modifies the SMG status flag.
Page 176
Services
Step
5.
Action
Click on Deployment tab, highlight the package for your platform, click edit, and navigate
to the Resources option.
6.
Expand Application Access Policy and select the App Black List for your platform as a
Resource to Deploy. Click Finish to commit deploy the package.
7.
Return to the Policies tab. In the Application Access Policy settings, tick the checkboxes
for each App Black List and click on Apply App List.
Page 177
Services
Step
8.
Action
Package deployment may take a few minutes as it will be completed during the next agent
check in. If you would like to force an agent check-in, open the Citrix Mobile Connect
application on your mobile device and complete the below instructions for each platform:
For Android:
Tap on the Configuration -> Connection Status option to force an agent check-in.
For iOS:
Tap on the Configuration -> Refresh option to force a policy refresh.
Page 178
Services
Step
9.
Action
In a few minutes, the devices will report its status to the XDM server. Go back to the
XDM console and navigate to the Devices tab. Expand ActiveDirectory -> training.lab
and highlight the Training Users container.
You will see that the devices are now flagged as blocked for the SMG status:
Page 179
Services
Step
10.
Action
Go back to your mobile device and attempt to access the user’s mailbox. You should be
denied access.
Android mail client:
iOS mail client:
Page 180
Services
Step
11.
Action
To verify the configuration, let’s inspect the dynamic policies and logs in XNC. On the
Site1-XenMobile VM, open the XenMobile NetScaler Configuration Console and Click
on the Policies tab.
12.
13.
In the upper right corner click on Refresh to get the latest policies from XDM.
Expand the ZDM (deny) node. You should see the list of devices on the deny list
according to the SMG status being reported.
14.
Click on the Log tab. Select All Actions from the menu and click Go. The XNC log should
display the latest attempts from any device connecting through the NetScaler.
Page 181
Services
Step
15.
16.
17.
18.
Action
From your mobile device, attempt to access the user’s mailbox. You should receive the
same denied message. Go back to the XNC Console log and Click go. New requests should
appear on the list.
Now, on your mobile device, proceed to uninstall Instagram and force and agent check-in.
Wait a few minutes and inspect the SMG status on the XDM console. The system should
have cleared the flag as the device is back in compliance.
Attempt to access the user’s mailbox. The mail client should be able to perform a full
refresh.
Congratulations, you have concluded this challenge exercise!
Page 182
Services
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
XNC queries the XenMobile Device Manager API to build a dynamic policy
set.
The NetScaler appliance uses this information to enforce email restriction
rules.
Page 183
Services
Challenge Exercise 9: DataStream Kerberos
Authentication using Microsoft SQL
Overview
Kerberos is a computer network authentication protocol which works on the basis of "tickets" to
allow nodes communicating over a non-secure network to prove their identity to one another in a secure
manner. It has been considered as the most secure and widely used, but most complex authentication
system. In order to get Constrained Delegation to work a user account has to be created. This account
must have the rights to do the Protocol Transition and Delegation. Essentially, this is the account that has
the rights to request a Kerberos Ticket on behalf of a user logging into the NetScaler and then provide this
ticket to the services behind the NetScaler appliance.
Exercise 9 Section 1: Active Directory Configuration
The tasks for Section 1 are:
Create KCD User account:
Enable the Delegation tab for KCD User Account
Creating the Keytab file
Add the Services
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: 20 minutes.
Step Action
1.
Select the Site1-AD.training.lab virtual machine and click the Console tab.
2.
Click the Send Ctrl+Alt+Del button on the bottom left of the screen.
3.
Login as…
Username: TRAINING\administrator
Password: Citrix123
Page 184
Services
Step
4.
Action
Double-click the Active Directory Users and Computers shortcut on the desktop.
5.
The Active Directory Users and Computers window pops up. Right-click the Users
node and go to New > User.
6.
Configure the user account as follows:
First name: KCDUser
Full name: KCDUser
User logon name: kcduser
Click Next.
Page 185
Services
Step
7.
8.
9.
10.
Action
Configure the following:
Password: Citrix123
Confirm password: Citrix123
User must change password at next logon: Unchecked
Password Never Expired: Checked
Click Next, then Finish.
Right-click the newly created account and select Properties.
NOTE: There is no Delegation tab.
Next we must enable the Delegation tab.
Close the account properties window by clicking OK.
Within the Site1-AD.training.lab virtual machine, open a command prompt.
Page 186
Services
Step
11.
Action
Add both SPNs for the MSSQLSvc. At the command prompt, enter the following
commands:
setspn -A MSSQLSvc/kcdvserver.training.lab training\kcduser
setspn -A MSSQLSvc/kcdvserver.training.lab:1433 training\kcduser
NOTE: In this example training is the domain and kcduser is the user account we just
created. The end result is to register the kcduser account with these SPN:
MSSQLSvc\kcdvserver.training.com
MSSQLSvc\kcdvserver.training.com:1433
12.
This will enable the Delegation tab in the kcduser properties.
Now you should see the Delegation tab enabled in the properties of the account.
NOTE: In order for the Delegation tab to appear, Active Directory needs to be running at
a minimum of Windows 2003 functional level.
Page 187
Services
Step
13.
Action
Open another command prompt and enter the following command:
ktpass /princ host/kcdvserver.training.lab@TRAINING.LAB
/ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL /mapuser training\kcduser /pass
Citrix123 /out C:\kcdvserver.keytab
14.
Switch to the Site1-Win8Client virtual machine. Login with the following credentials:
15.
Username: TRAINING\administrator
Password: Citrix123
Click on the folder icon to open Windows Explorer.
Page 188
Services
Step
16.
Action
Navigate to \\ad\c$ and copy the kcdvserver.keytab file to the local c:\.
17.
On the desktop of the Site1-Win8Client virtual machine, launch WinSCP.
Page 189
Services
Step
18.
Action
Configure the session as follows and click Login:
File protocol: SFTP
Host name: 192.168.10.50
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
19.
Copy the kcdvserver.keytab file from the local C:\ to the NetScaler
/flash/nsconfig/krb directory.
Page 190
Services
Step
20.
Action
Merge the recently copied keytab into the running keytab file by using the ktutil command:
root@ns#
ktutil:
ktutil:
ktutil:
21.
22.
23.
ktutil
rkt /nsconfig/krb/kcdvserver.keytab
wkt /etc/krb5.keytab
q
Verify the running keytab file information includes the new SPN. Execute the following
command:
root@ns# klist -k /etc/krb5.keytab
Keytab name: WRFILE:/etc/krb5.keytab
KVNO Principal
---- ------------------------------------------------------------------------1 dummy@DUMMY.COM
2 NS$@TRAINING.LAB
...
...
2 cifs/ns.TRAINING.LAB@TRAINING.LAB
2 cifs/ns.TRAINING.LAB@TRAINING.LAB
3 host/kcdvserver.training.lab@TRAINING.LAB
root@ns#
Select the Site1-AD.training.lab virtual machine.
Navigate to the properties of the KCDuser account and click the Delegation tab.
Page 191
Services
Step
24.
25.
Action
Click Add.
Note: The “Kerberos only” options will not work since they do not enable Protocol
Transition and Constrained Delegation.
Click on Users or Computers. Search for the SQL1 computer account and click on Check
Names. Verify that the KCDuser account is correct and then click OK.
NOTE: Constrained Delegation does not support services hosted in other domains even
though there is a trust relationship to those domains.
Page 192
Services
Step
26.
27.
Action
Because we are setting up Constrained Delegation to SQL Server, the MSSQLSvc is
selected. Use the Ctrl key to add both MSSQLSvc “Services” on the SQL1 server and click
OK.
Active Directory Configuration is now complete.
Page 193
Services
Exercise 9 Section 2: SQL Server Configuration
In this section, we will create a login with the authentication as Windows. SQL Windows Authentication
requires both client and server to be part of a windows domain. For login, the client will get the Kerberos
ticket for SQL Server from AD and send the same ticket to SQL Server for authentication instead of the
username and password. Windows authentication support on NetScaler enables Microsoft SQL Load
Balanced/Content Switched virtual server to authenticate the client and authenticate itself on behalf of the
client to the backend server, and pass on the requests/responses coming from client/server to
server/client respectively. There is no need to add a database user on NetScaler.
Step by step guidance
Create a login with Windows Authentication
Estimated time to complete this lab: 5 minutes.
Step Action
1.
Select the Site1-SQLServer virtual machine and click the Console tab.
2.
3.
Click the Ctrl+Alt+Del button on the bottom left of the screen. Login with the following
credentials:
Username: TRAINING\administrator
Password: Citrix123
Launch the SQL Server Management Studio shortcut on the desktop.
Page 194
Services
Step
4.
5.
Action
Click Connect to accept the default Windows Authentication setting and click Connect.
Expand the Security node and right-click on the Logins node. Click New Login…
Page 195
Services
Step
6.
Action
Click the Search button next to the Login name text box.
7.
In the “Enter the object name to select” field, type training\kcduser and click Check
Names.
8.
The kcduser account created is found. Click OK
Page 196
Services
Step
9.
10.
Action
Click OK to accept the newly created Login.
Close SQL Server Management Studio and logout of the Site1-SQLServer virtual
machine.
Page 197
Services
Exercise 9 Section 3: Kerberos NetScaler Configuration
In this section, we will perform the necessary steps to configure the NetScaler to support Constrained
Delegation. The steps include:
Add service to host running Microsoft SQL
Creating a load balanced virtual server
Binding the Microsoft SQL service to the load balanced virtual server
Creating the KCD account and database profile
Add DNS name server
Joining NetScaler to the Windows domain
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: 15 minutes.
Step Action
1.
Select the Site1-Win8Client virtual machine again.
2.
Open Internet Explorer and browse to http://192.168.10.50
3.
Login as…
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
4.
Navigate to Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Services and click Add.
Page 198
Services
Step
5.
6.
7.
Action
Add server object that is called exactly the same as the NETBIOS name of the SQL server:
Click Create and then Close.
Configure the following options and click Create:
Service Name: SQL1_svc
Protocol: MSSQL
Server: SQL1
Port: 1433
Configured Monitors: TCP
Click Close and select the Virtual Servers node.
Page 199
Services
Step
8.
Action
Click Add and configure the following:
Name: SQLAuth
Protocol: MSSQL
IP Address: 192.168.10.121
Port: 1433
Click the checkbox under the Active column to bind the SQL1 service to the virtual server.
9.
10.
Click Create and Close.
Enable the AAA feature. Right-click on AAA-Application Traffic and select Enable
Feature.
Navigate to Security > AAA-Application Traffic > KCD Accounts and click Add.
Page 200
Services
Step
11.
12.
Action
Click Add. Enter the following configuration::
Name: kcdaccount1
Keytab File Path: /nsconfig/krb/kcdvserver.keytab
Click Create and Close.
The SPN is retrieved from the keytab file.
Page 201
Services
Step
13.
14.
Action
Go back to the Virtual Servers list. Double-click the SQLAuth virtual server and select the
Profiles tab.
Click New… next to the Database Profile dropdown arrow.
Configure the following and click Create:
Name: kcd1
KCD Account: kcdaccount1
Click Create and OK on the virtual server properties page.
Page 202
Services
Step
15.
Action
Navigate to Traffic Management > DNS > Name Servers and click Add.
16.
Enter the IP address 192.168.10.11 and click Create.
17.
18.
19.
20.
Click Close.
Select the DNS Suffix node.
Enter the suffix training.lab and click Create.
The suffix is added. Click Close.
Page 203
Services
Step
21.
Action
Launch PuTTY from the desktop and connect to the NetScaler management IP:
IP: 192.168.10.50
Username: nsroot
Password: nsroot
22.
Type the following command:
ping training.lab
Note: NetScaler must be able to resolve the domain before you join it to the Windows
domain.
Page 204
Services
Step
23.
24.
25.
Action
Navigate to Security > AAA-Application Traffic > Kerberos Domain Join
Click the “+” to add a profile/action.
Configure the following settings and click Create:
Name: nego_act
Domain Name: TRAINING.LAB
User Name: Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Confirm Password: Citrix123
Click Create and OK on the Kerberos Domain Join window.
Page 205
Services
Exercise 9 Section 4: Setup Validation
In this section, we will verify that all of the configuration was done correctly and test authentication to the
virtual server backend.
Estimated time to complete this lab: 5 minutes.
Step
1.
2.
3.
Action
From the Site1-Win8Client virtual machine, bring up the PuTTY session from the taskbar.
At the command prompt type ‘shell’ and hit the Enter key.
Type the following command:
/opt/likewise/bin/kinit -k -t /nsconfig/krb/kcdvserver.keytab -f
'host/kcdvserver.training.lab@TRAINING.LAB'
NOTE: This command verifies the client can contact the KDC authentication service for a
Ticket Granting Ticket. This should return without giving any messages.
Page 206
Services
Step
4.
Action
Type the following command:
/opt/likewise/bin/t_s4u kcduser@TRAINING.LAB
MSSQLSvc/sql1.training.lab:1433 /nsconfig/krb/kcdvserver.keytab
NOTE: This command verifies the client can get a KCD ticket for the backend server. If
the above commands run without issue, then KCD should work. Otherwise, configuration
changes may be required at NetScaler or Active Directory.
The command output similar to the following:
5.
6.
Close PuTTY session.
Select the AD.training.lab virtual machine.
Logon as…
Username: TRAINING\Administrator
Password: Citrix123
Page 207
Services
Step
7.
Action
Create a new DNS record for the SQLAuth vserver. Open the DNS console and create a
new A record on the training.lab zone:
User the following parameters:
Name: kcdvserver
IP Address: 192.168.10.121
Page 208
Services
Step
8.
9.
Action
We are going to test Kerberos Connectivity from the Domain Controller. This VM already
has SQL Server client tools installed. From AD.training.lab, launch SQL Server Manager
Studio from the desktop.
Connect to the Virtual Server FQDN. Configure the connection using the provided
parameters. Click Connect:
Server type: Database Engine
Server name: kcdvserver.training.lab
Authentication: Windows Authentication
Page 209
Services
Step
10.
Action
The connection is made to SQL1 via the load balanced virtual server using Constrained
Delegation.
11.
To verify the client is using Kerberos authentication, run the following query to check the
auth_scheme parameter. Click on New Query and enter the following SQL statement:
SELECT auth_scheme FROM sys.dm_exec_connections WHERE session_id
= @@spid ;
12.
Congratulations! You have configured successful Kerberos authentication using the
NetScaler appliance. Close SQL Server Management Studio.
Page 210
Services
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for this exercise are:
The KCD account is used to extract the SPN from the keytab file.
NetScaler reads the keytab file and extracts the SPN listed within the file.
The Kcdverserver.keytab file has to be copied under /nsconfig/krb/. If the
file is not found in this location, NetScaler will reject it.
The Database Profile can be used with Load Balanced and Content
Switching virtual servers.
For Constrained Delegation to work, NetScaler should be a member of the
Windows domain.
Page 211
Services
Optional Exercise 10: NetScaler 10.1 Quiz
Overview
In this section, there are multiple quiz-like questions. Some are new and some you will be able to answer
them easily if you worked through the above exercises. If you get stuck, the answer sheet is at the end of
this section. No peeking in advance!
For this quiz, please logon to Site2-NetScaler from Site2-Win8Client.
Step by step guidance
Estimated time to complete this lab: 20 minutes.
Step Action
1. In NetScaler 10.1, a new built-in monitor was introduced for checking the health of servers.
Navigate to Configuration > Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Monitors >
Add.
2.
What is it?
What are the two parameters under Special Parameters tab?
1. X
2. Y
This is a screenshot of COOKIEINSERT Persistence from NetScaler 10.0:
This has changed in NetScaler 10.1.
What is the new option?
Page 212
Services
Step
3.
Action
This is the output of a CLI command from NetScaler 10.0:
> stat lb vserver SF_vserver ?
-detail
-fullValues
-logFile <input_filename>
-ntimes <positive_integer>
-sortBy Hits [<sortOrder>]
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Run the same command on the NetScaler 10.1 CLI and see how this is different?
In NetScaler 10.0 the Gateway feature was called Access Gateway (Enterprise Edition).
What is the new name for the Gateway feature in NetScaler 10.1?
What are the six nodes in the revamped NetScaler 10.1 GUI?
In the Netscaler 10.1 GUI, where is the new home for the Responder feature?
Answer: ‘Notify When Expires’ is now enabled by default
In the NetScaler 10.0 CLI, the following option is available to view the statistics of a Load
Balanced Virtual Server:
> stat lb vserver SF_vserver
Virtual Server Summary
SF_vserver
9.
vsvrIP port
192.168.20.110
Protocol
443
State
SSL
Health
DOWN
0
What is different with the same option in NetScaler 10.1?
Support for the SPDY protocol is a new enhancement on Load Balancing on NetScaler 10.1.
How do you enable this protocol on a new HTTP Load Balanced Virtual Server?
Page 213
Services
Step Action
10. The HTTP Callout feature has been enhanced in NetScaler 10.1. Here is a screenshot from
NetScaler 10.0. Compare with the same in NetScaler 10.1.
What is different?
What are the two new options?
Page 214
Services
Step
11.
Action
A new Policy Expression option has been added in NetScaler 10.1. This expression could
be used with the Rewrite feature.
Here is a screenshot of the equivalent in NetScaler 10.0. What is the new option?
12. Under NetScaler Gateway there is a new option called KCD Accounts
Do you have any idea what KCD stands for?
13. In NetScaler 10.0 there is a feature called CloudBridge, this has been moved under the
System node in NetScaler 10.1 and it was given a new name.
What is this “new” name?
14. There is a new checkbox option for DNS in NetScaler 10.1 when creating a new DNS
Zone. Can you figure it out from this NetScaler 10.0 screenshot:
Bonus Question, what’s the second new option?
Page 215
Services
Step Action
15. Observe the new Virtual Server Health option. This exercise is to guess what value for the
Health Threshold needs to be entered so that when only one Service is up the virtual server
goes down.
To get started navigate to Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Virtual Servers.
Select SF_vserver and click Open. Click Advanced tab and scroll down until you can see
Health Threshold near the bottom:
This is where you will need to enter a value and click OK.
To bring a service down you need to return to the Services tab. You should see two monitors
bound:
Select SF2-XenDesktop and click Open
Click Disable, then OK at the Wait Time dialog box and OK again at Configure Service
dialog. This should bing the SF2-XenDesktop service down.
Now check the % Health colum under Virtual Servers:
Does the virtual server stay up or go down?
Page 216
Services
Step Action
16. Navigate to System > System Information > Statistics
Is there an option for services?
17. Navigate to Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Add
Select TFTP from the drop down list.
What is the port number that is populated by default?
18. There is a new option in NetScaler 10.1 when using Datastream load balancing of Microsoft
SQL Servers.
Here is a screenshot of NetScaler 10.0:
What is different in NetScaler 10.1?
19. Datastream for Microsoft SQL Server allows Windows based authentication in NetScaler
10.1. Using the answer from question #18 above, what option do you think is needed for
this?
Page 217
Services
Step Action
20. Advanced Policy Expressions have been enhanced in NetScaler 10.1.
The following expression exists in NetScaler 10.0:
HTTP.REQ.BODY(100)
This will return 100 bytes of data from the body of a HTTP Request.
If we expand this to a new nested expression available in NetScaler 10.1:
HTTP.REQ.BODY(HTTP.REQ.CONTENT_LENGTH)
What do you think this particular expression does?
21. There’s a new feature in NetScaler 10.1 called AppQoE. If the first part stands for
‘Application Quality of’, what does the last ‘E’ stand for?
A. End-user
B. Experience
C. Enterprise
Page 218
Services
Hints
1. It’s the at the bottom of the Type drop-down list
2. Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Virtual Servers > Add > Method and Persistence
> Persistence
7. Traffic Management > SSL > Certificates > Add
9. System > Profiles > HTTP Profiles
10. AppExpert > HTTP Callouts > Add
11. AppExpert > Rewrite > Policies > Add > Expression > CLIENT.TCP.
12. Click KCD Accounts, the answer is in the GUI!
14. Hint: Traffic Managhement > DNS > Zones > Add
18. Traffic Management > Load Balancing > Virtual Servers > Add. Set protocol to MSSQL, go
to Profiles
19. Same as Hint #18
20. Hint: AppExpert > Rewrite > Policy > Expression. Enter
HTTP.REQ.CONTENT_LENGTH. Click Evaluate. Make sure HTTP Request is selcted as
Flow Type. Click Sample and select POST Request. Click Evaluate. This should return the
value 11.
Summary
Key
Takeaways
The key takeaways for these exercises are:
There are over 200 new features included in NetScaler 10.1
Page 219
Services
Revision History
Revision
Change Description
1.0
Original Version
1.1
Updated topology diagrams
Updated By
Date
Andrew Sandford
and David Jimenez
05/02/2013
David Jimenez
05/13/2013
About Citrix
Citrix Systems, Inc. (NASDAQ:CTXS) is the leading provider of virtualization, networking and software as a service
technologies for more than 230,000 organizations worldwide. It’s Citrix Delivery Center, Citrix Cloud Center (C3)
and Citrix Online Services product families radically simplify computing for millions of users, delivering applications
as an on-demand service to any user, in any location on any device. Citrix customers include the world’s largest
Internet companies, 99 percent of Fortune Global 500 enterprises, and hundreds of thousands of small businesses
and prosumers worldwide. Citrix partners with over 10,000 companies worldwide in more than 100 countries.
Founded in 1989, annual revenue in 2008 was $1.6 billion.
http://www.citrix.com
© 2013 Citrix Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Citrix®, Citrix Delivery Center™, Citrix Cloud Center™,
XenApp™, XenServer™, NetScaler®, XenDesktop™, Citrix Repeater™, Citrix Receiver™, Citrix Workflow
Studio™, GoToMyPC®, GoToAssist®, GoToMeeting®, GoToWebinar®, GoView™ and HiDef Corporate™ are
trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc. and/or one or more of its subsidiaries, and may be registered in the United States
Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other trademarks and registered trademarks are property of
their respective owners.
Page 220