PLGrid CORE
advertisement
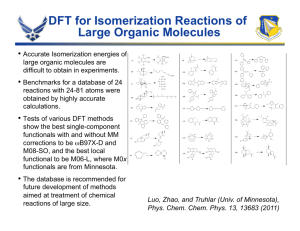
1 PL-Grid: Polish Infrastructure for Supporting Computational Science in the European Research Space Distributed Computing Instrastructure as a Tool for e-Science Jacek Kitowski, Kazimierz Wiatr, Łukasz Dutka, Maciej Twardy, Tomasz Szepieniec, Mariusz Sterzel, Renata Słota and Robert Pająk ACK Cyfronet AGH PL-Grid Consortium PPAM 2015, 7-9.09.2015, Kraków 2 Outline National e-Infrastructure Assumptions and foundations Tool for e-Science e-Infrastructure creation – motivation, background and issues Conceptualization and implementation PLGrid case study Enhancement of Achievements Platforms and Environments – Selected Examples Conclusions 3 e-Infrastructure Creation Motivation and Background Increasing importance of Computational Science and Big Data Analysis Needs: Preventing users from technical problems Expert support for making science Increase of resources Openess for future paradigms Numerically intensive computing Experiments in silico: 1st: Theory 3rd: Simulation Computing and Data for Open Science International collaboration User/platform driven e-infrastructure innovation (e-Science and e-Infrastructure interaction) Computational Science problems: Algorithms, environments and deployment Future and emerging technologies 4th paradigm, distributed, grid and cloud computing, Data Farming 2nd: Experiment 4th Paradigm: Data Intensive Scientific Discovery Data intensive computing Activity initiated by Cyfronet e-Infrastructure Creation 4 Issues Synergistic effort in several dimensions: Meeting user demands in the field of grand challenges applications Activity supported by users with scientific achievements and by well-defined requirements Organizational: horizontal perspective - federation of computer centres supporting the e-infrastructure with different kinds of resources and competences vertical perspective - involvement of computer, computational and domain-specific experts into e-infrastructure operations Technological: different computing hardware and software various middleware environments Meeting user demands Energy awareness Technological Energy awareness: optimal scheduling strategies of computing jobs among federation resources to minimize energy consumption as a whole Organizational 5 PL-Grid Consortium Consortium creation – 2007 a response to requirements from Polish scientists due to ongoing eScience activities in Europe and in the World Aim: significant extension of computing resources and solutions provided to the scientific community PL-Grid Programme Development based on (SWOT analysis): projects funded by the European Regional Development Fund as part of the Innovative Economy Program close international collaboration (EGI, ….) previous projects (5FP, 6FP, 7FP, EDA…) National Network Infrastructure available: Pionier National Project computing resources: Top500 list Polish scientific communities: ~75% highly rated Polish publications in 5 Communities PL-Grid Consortium members: 5 High Performance Computing Polish Centres, representing the Communities coordinated by ACC Cyfronet AGH ACK Cyfronet AGH 42 years of expertise Social Networking Human Resources Infrastructure Resources High Performace Computing Centre of Competence High Performance Networking Rank TOP500 Site System 49 Cyfronet Prometheus VII.2015 Poland HP Apollo 8000 Network Resources Cores Rmax Tflops Rpeak Tflops 41,472 1262.4 1658.9 25,468 266.9 373.9 Zeus 269 Cyfronet Cluster Platform VII.2015 Poland Hewlett-Packard 7 The most powerful HPC Asset (in Poland) Prometheus Cluster (2014/2015) Rpeak = 1658.9 TFlops 1728 servers 41,472 Haswell cores 216 TB RAM (DDR4) 10 PB disks, 180 GB/s HP Apollo 8000 In operation April 2015 Q4 2015 Extensions Rpeak = 483.8 TFlops 504 servers 12,096 Haswell cores RpeakNVIDIA= 256.3 TFlops 144 Nvidia K40 XL In SUMMARY: 2,4 PFlops (with GPU) 49th position on the July 2015 edition of the TOP500 list TOP500, July 2015 Polish Sites 8 System Cores Rmax (TFlop/s) Rpeak (TFlop/s) Prometheus - HP Apollo 8000, Xeon E52680v3 12C 2.5GHz, Infiniband FDR Hewlett-Packard 41,472 1,262.4 1,658.9 Zeus - Cluster Platform SL390/BL2x220, Xeon X5650 6C, 2.660GHz, Infiniband QDR, NVIDIA 2090 Hewlett-Packard 25,468 266.9 373.9 126 TASK, Gdańsk Tryton - HP ProLiant XL230a Gen9, Xeon E5-2670v3 12C 2.3GHz, Infiniband Megatel/Action 17,280 530.5 635.9 135 WCSS, Wrocław BEM - Actina Solar 820 S6, Xeon E52670v3 12C 2.3GHz, Infiniband FDR ACTION 17,280 480.1 635.9 NCNR, Świerk Świerk Computing Centre - Supermicro TwinBlade SBI-7227R/Bull DLC B720, Intel Xeon E5-2680v2/E5-2650 v3 10C 2.8GHz, Infiniband QDR/FDR Format, Bull, Atos Group 17,960 423.2 490.4 NGSC & ICM, ORION - Dell PowerEdge R730, Xeon E52680v3 12C 2.5GHz, Infiniband FDR, AMD FirePro S9150 Dell 16,800 198.8 903.0 University of Warsaw BlueGene/Q, Power BQC 16C 1.600GHz, Custom Interconnect IBM 16,384 189.0 209.7 Rank Site 49 269 155 380 418 Cyfronet, Krakow 10 Family of PL-Grid Projects coordinated by Cyfronet Real Users PL-Grid (2009–2012) Outcome: Common base infrastructure PLGrid PLUS (2011–2015) Assumed Performance Outcome: Focus on users (training, helpdesk…) Domain specific solutions: 13 PLGrid NG (2014–2015) +1500 Tflops +500 Tflops Outcome: Optimization of resources usage, training +8 Tflops Extension of domain specific by 14 PLGrid CORE (2014–2015) Outcome: Competence Center Open Science paradigm (large workflow app., data farming mass comp., ……) End-user services 230 Tflops Summary of Projects Results (up-to-date) Close collaboration between Partners and research communities Development of tools, environments and middleware services, Clouds Integration, HPC, Data intensive, Instruments Development of 27 domain specific solutions Development of IT PL-Grid Infrastructure and ecosystem 12 13 Summary of Projects Results (up-to-date) 26 papers on PL-Grid Project results Facilitation of community participation in international collaboration EGI Council, EGI Executive Board FP7 (VPH-Share, VirtROLL….) EGI-InSPIRE, FedSM, … EGI-Engage, Indico DataCloud, EPOS, CTA, PRACE, H2020…. Publications 700 600 600 500 36 papers on PLGrid Plus Project results 147 authors, 76 reviewers 436 400 300 192 200 121 91 100 54 24 6 3 22 0 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 1 14 Journal Publications (subjective selection) Journal IF Journal IF Journal IF J.Chem.Theor.Phys.Appl. 5.31 J.Chem.Phys. 3,122 Macromolecules 5,927 Phys.Lett. B 6,019 J.Phys.Chem.Lett. 6,687 Astrophys.J.Lett. 5,602 J.High Energy Phys. 6,22 Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys. 4,638 Phys.Rev.Letters 7,728 Astonomy &Astrophys. 4,479 Fuel Processing Techn. 3,019 J.Chem.Theor.Appl. 5,31 Inorganic Chem. 4,794 J.Magn. & Magn. Mat. 2,002 Astrophys.J 6,28 J.Org.Chem. 4,638 Eur.J.Inorg.Chem. 2,965 Chem.Physics 2,028 Optic Lett. 3,179 Chem.Phys.Lett. 1,991 Molec.Pharmaceutics 4,787 Appl.Phys.Lett. 3.515 Phys.Rev.B 3,664 Eur.J.Pharmacology 2,684 J.Comput.Chem. 3,601 Eur.Phys.J. 2,421 Energy 4,159 J.Phys.Chem. B 3,377 Future Gen.Comp.Syst. 2,639 Carbon 6,16 Soft Matter 4,151 J.Phys.Chem. C 4,835 J.Biogeography 4,969 Int.J.Hydrogen Energy 2,93 Crystal Growth & Desing 4,558 Electrochem.Comm. 4,287 Physica B 1,133 J.Magn.&Magn.Mat. 1,892 Conferences: • Cracow Grid Workshop (since 2001) • KU KDM (since 2008) 15 Summary of Projects Results (up-to-date) 200 180 160 # users’ grants (active) 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 6000 Jan/13 Mar/13 May/13 Jul/13 Sep/13 Nov/13 Jan/14 Mar/14 May/14 Jul/14 Sep/14 Nov/14 Jan/15 Mar/15 May/15 Jul/15 Sep/15 ##users users 5000 4000 ALL USERS REGISTERED 3000 2000 INFRASTRUCTURE USERS 1000 EMPLOYEES 0 Summary of Projects Results (up-to-date) Examples of active grants PROTMD (18.9.2015-18.9.2016) – Cyfronet Research on proteins using MD 25 mln hours (2,800 cores) PCJ2015GA (26.8.2015-31.12.2015) – ICM Research on connectome of nematodes using GA 15 mln hours (6,000 cores) PSB (1.3.2015-1.3.2016) – TASK, Cyfronet, ICMM, WCSS New characteristics of DNA in the context of tumor therapy 11 mln hours (1,200 cores) 16 Summary of Projects Results (up-to-date) 17 18 Deployed PLGrid IT Platforms and Tools – selected examples (by Cyfronet) GridSpace A platform for e-Science applications Experiment: an e-science application composed of code fragments (snippets), expressed in either general-purpose scripting programming languages, domain-specific languages or purpose-specific notations. Each snippet is evaluated by a corresponding interpreter. GridSpace2 Experiment Workbench: a web application - an entry point to GridSpace2. It facilitates exploratory development, execution and management of e-science experiments. Embedded Experiment: a published experiment embedded in a web site. GridSpace2 Core: a Java library providing an API for development, storage, management and execution of experiments. Records all available interpreters and their installations on the underlying computational resources. Computational Resources: servers, clusters, grids, clouds and e-infrastructures where the experiments are computed. Contact: E. Ciepiela, D. Harężlak, M. Bubak 19 20 InSilicoLab science gateway framework Goals Complex computations done in non-complex way Separating users from the concept of jobs and the infrastructure Modelling the computation scenarios in an intuitive way Different granularity of the computations Interactive nature of applications Dependencies between applications Summary The framework proved to be an easy way to integrate new domain-specific scenarios Architecture of the InSilicoLab framework: Domain Layer Mediation Layer with its Core Services Resource Layer with different kinds of workers Even if done by external teams Natively supports multiple types of computational resources Including private resources – e.g. private clouds Different kinds of users different kinds of resources Supports various types of computations Contact: J. Kocot, M. Sterzel, T. Szepieniec 21 DataNet collaborative metadata management Objectives Provide means for ad-hoc metadata model creation and deployment of corresponding storage facilities Create a research space for metadata model exchange and discovery with associated data repositories with access restrictions in place Support different types of storage sites and data transfer protocols Support the exploratory paradigm by making the models evolve together with data Architecture Web Interface is used by users to create, extend and discover metadata models Model repositories are deployed in the PaaS Cloud layer for scalable and reliable access from computing nodes through REST interfaces Data items from Storage Sites are linked from the model repositories Contact: E. Ciepiela, D. Harężlak, M. Bubak 22 Onedata transparent access to data A system that provides a unified and efficient access to data stored in organizationally distributed environments. Provides a uniform and coherent view on all data stored on the storage systems distributed across the infrastructure Supports working in groups by creation of an easy-to-use shared workspace for each group. Serves data efficiently Contact: Ł. Dutka Onedata Global Registry 23 Scalarm data farming experiments Scalarm overview Self-scalable platform for parametric studies What problems are addressed with Scalarm ? Data farming experiments with an exploratory approach Adapting to experiment size and simulation type Parameter space generation with support of design of experiment methods Accessing heterogeneous computational infrastructure 75% all submitted tasks Exploratory approach for conducting experiments Supporting online analysis of experiment partial results Integrates with clusters, Grids, Clouds Contact: R. Słota Self-scalability of the management/execution parts Scalarm Graphical User Interface 24 Rimrock access to resources A service which simplifies the management of processes and tasks executed in the PLGrid infrastructure. Rimrock architecture Rimrock features simplicity – non-complicated integration with other applications, scripts and services interactivity – a user can modify working processes based on indirect results universalism – supported by many programming languages versatility – it allows to execute an application in a batch mode or start an interactive application user friendliness – it does not require advanced knowledge (basic information about Bash shell and curl command are sufficient to start using it) Contact: D. Harężlak 25 Cloud Computing The Cloud increases elasticity of research, as scientists can tune the virtual machines to their specific needs. The catalogue of VMs offered by PL-Grid contains many OSs. Cloud platform is also the best and in many cases the only solution for running jobs with legacy software packages. Open Nebula migration to Open Stack, …. Cloud Platform for VPH-Share applications (Atmoshere env.) IaaS, PaaS, STaaS…. Contact: J. Meizner, T. Szepieniec, M. Radecki Cloud environment for VPH-Share app. Portal and Atmosphere 26 Applications Catalog service Objective: to present in one place and in a uniform manner the current offer of the software available in the PLGrid infrastructure, broken down into supercomputing centers, clusters as well as categories and areas of application. Applications Catalog is a system collecting and providing information on the applications, development tools and libraries offered in the PLGrid infrastructure. It allows to search for applications, check the status of their operation, obtain information about changes and updates, as well as it provides documentation and examples of usage. It is designed for all those interested in the use of the applications available in the PLGrid infrastructure. 27 Map-Reduce service Apache Spark 1.5.0 functionality: API, RDD, DataFrame, SQL Backend Execution: DataFrame and SQL Integrations: Data Sources, Hive, Hadoop, Mesos and Cluster Management R Language Machine Learning and Advanced Analytics Spark Streaming 28 29 Summary and Conclusions Three dimensions of development: HPC/GRID/CLOUDs Data & Knowledge layer Network & Future Internet Deployments have the national scope; however with close European links Development oriented on end-users & research projects Achieving synergy between research projects and e-infrastructures by close cooperation and offering relevant services Durability at least 5 years after finishing the projects - confirmed in contracts Future plans: continuation of development Center of Excellence CGW, KUKDM as places to exchange experience and for collaboration between eScience centers in Europe 30 More information Please visit our Web pages: http://www.plgrid.pl/en http://www.plgrid.pl CREDITS! 31 Credits ICM ACC Cyfronet AGH Michał Turała Marian Bubak Krzysztof Zieliński Karol Krawentek Agnieszka Szymańska Maciej Twardy Angelika Zaleska-Walterbach Andrzej Oziębło Zofia Mosurska Marcin Radecki Renata Słota Tomasz Gubała Darin Nikolow Aleksandra Pałuk Patryk Lasoń Marek Magryś Łukasz Flis Special thanks to many domain experts ! … and many others….. Marek Niezgódka Piotr Bała Maciej Filocha PCSS Maciej Stroiński Norbert Meyer Krzysztof Kurowski Tomasz Piontek Paweł Wolniewicz WCSS Jacek Oko Józef Janyszek Mateusz Tykierko Paweł Dziekoński Bartłomiej Balcerek TASK Rafał Tylman Mścislaw Nakonieczny Jarosław Rybicki