Weathering and Soil Formation
advertisement

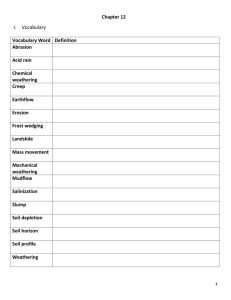
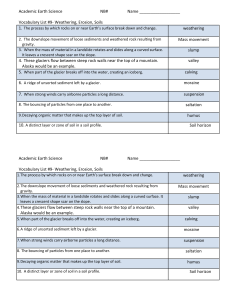
Weathering and Soil Formation Chapter 6 WARM-UP #1 •The breaking down of rocks and other materials at Earth’s surface is ANSWER • weathering. WARM-UP #2 •Freezing and thawing cause ANSWER • Ice wedging VOCABULARY •Weathering •Erosion •Uniformitarianism weathering and erosion • Weathering – the process that breaks down rock and other substances at the Earth’s surface. • Erosion – forces of erosion carry the pieces away…..weathering and erosion work together to break down and carry away rocks on Earth’s surface. vocabulary •Uniformitarianism – principles that operate today operated in the past WARM-UP #3 •Which is a cause of chemical weathering? ANSWER • Acid rain WARM-UP #4 •Mechanical weathering is faster in a climate that is ANSWER • warm VOCABULARY •Mechanical weathering •Abrasion •Ice wedging MECHANICAL WEATHERING • Mechanical weathering – weathering where the rock is broken into smaller pieces….each piece is still the same composition….mechanical weathering is a slow process EXAMPLES • Freezing and thawing, release of pressure, plant growth, actions of animals, abrasion • Abrasion – grinding away of rocks by rock particles carried away by wind, water, ice, or gravity • Ice wedging – water seeps into cracks – expands when it freezes – ice is like a wedge that breaks the rock apart WARM-UP #5 •When dead plants and animals decay, they form ANSWER • humus WARM-UP #6 •A solid layer of rock under the soil is called ANSWER • bedrock VOCABULARY •Chemical weathering •Oxidation •Permeable Chemical weathering • Process that breaks down rock through chemical changes………..causes are the action of water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, living organisms, and acid rain. VOCABULARY • Oxidation – when iron combines with oxygen in the presence of water………….rust • Permeable – rock that is full of tiny holes…allows water to seep through easily….permeable rocks will weather quickly when exposed to chemical weathering. WARM-UP #7 •In the United States, most of the eastern states are covered with ANSWER • Forest soil WARM-UP #8 •Living things that break down dead organisms are called ANSWER • decomposer VOCABULARY •Soil •Bedrock •Humus VOCABULARY • Soil – loose weathered material on Earth’s surface where plants can grow • Bedrock – solid layer of rock below the soil • Humus – decayed organic material in soil WARM-UP #9 •Soil fertility is a measure of ANSWER how good soil is for growing plants. WARM-UP #10 •Farmers leave dead plants in their fields in the soil conservation method called ANSWER • conservation plowing. VOCABULARY •Fertility •Loam •Soil horizon VOCABULARY • Fertility – measure of how well the soil supports plant growth • Loam – soil made up of equal parts of sand, clay and silt • Soil horizon – is how the soil develops into layers ………the layers differ in color and texture WARM-UP #11 • The movement of rock pieces and other materials on Earth’s surface is called ______________________ ______. ANSWER • erosion WARM-UP#12 • The kind of weathering that breaks rocks into smaller pieces is _____________weathering. ANSWER • mechanical VOCABULARY •Topsoil •Subsoil •Litter •Decomposers TOPSOIL AND SUBSOIL • Topsoil – is horizon A ….crumbly, dark brown soil that is a mixture of humus, clay and other mixtures • Subsoil – is horizon B….clay and other particles washed down from horizon A…little humus LITTER AND DECOMPOSERS • Litter – is what is left of the plant before it adds to humus…..leaves, roots, and the plant itself when it dies. • Decomposers – organisms that break down the remains of dead organisms into smaller pieces and digest them with chemicals. WARM-UP#13 • The scraping of rock by windblown pieces of rock is called _________________________ _. ANSWER • abrasion WARM-UP#14 •The material on Earth’s surface in which plants can grow is ___________________. ANSWER • soil VOCABULARY • Sod – thick masses of tough roots at the surface of the soil……..keeps the soil in place and held onto moisture. • Natural resource – anything in the environment that humans use WARM-UP #15 •The B horizon is also called _____________ . ANSWER • subsoil WARM-UP #16 •In ______________ weathering, the makeup of rock changes. ANSWER • chemical VOCABULARY • Dust Bowl – ruined farmland on Oklahoma and parts of the surrounding states…..caused by years of droughts and lots of plowing tuned the top soil to dust and it blew away. • Soil Conservation – management of the soil to prevent it’s destruction. WARM-UP #17 •Different kinds of rock weather at different ___________. • rates WARM-UP #18 •The last layer of soil to form is the _____ horizon. • C PLOWING • Contour Plowing – plow the fields along the curve of the slope….slows runoff and preserves the soil from erosion. • Conservation Plowing – disturb the plant cover and soil as little as possible…dead weeds and stalks are left in the ground to help return soil nutrients. CROP ROTATION • Farmers plant different crops in the field each year………helps maintain the nutrients in the soil WARM-UP #19 •Loss of _____________ causes soil to lose its fertility. • topsoil WARM-UP #20 • One way to keep soil fertile is to grow a __________________ kind of plant every year. • different