Aqueous Solutions
advertisement

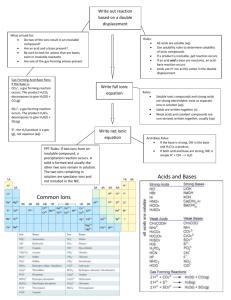
Aqueous Solutions Ionic Reactions • General Rules for dissolution (dissociation) of ionic compounds – Only 1 cation and 1 anion are formed – Monoatomic ions = subscripts become coefficients for the ions – Polyatomic ions = only subscripts outside of parentheses become coefficients – Charges of all ions must add up to zero (because compounds are neutral Examples of Ionic Compounds dissolving in water • NaBr (s) Na+(aq) + Br- (aq) • Cr(NO3)3 (s) Cr3+ (aq) + 3 NO3- (aq) Practice • • • • • • • K2S (s) FeCl3 (s) MgBr2 (s) AlCl3 (s) Na2Cr2O7 (s) (NH4)2S (s) K3PO4 (s) Answers • • • • • • • K2S (s) 2 K+ (aq) + S2- (aq) FeCl3 (s) Fe3+ (aq) + 3 Cl- (aq) MgBr2 (s) Mg2+ (aq) + 2 Br- (aq) AlCl3 (s) Al3+ (aq) + 3 Cl- (aq) Na2Cr2O7 (s) 2 Na+ (aq) + Cr2O72- (aq) (NH4)2S (s) 2 NH4+ (aq) + S2- (aq) K3PO4 (s) 3 K+ (aq) + PO43- (aq) Will it dissolve in water? • Soluble: Alkali metals, NH4+, ClO3-, ClO4-, acetates, NO3-, and strong acids _____________________________________ • Strong Acids = HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO3, HClO4 • All other acids are weak Will it dissolve in water? Sometimes Soluble: • Cl-, Br-, I- except with Ag+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ • Sulfate except with Hg22+, Pb2+, Ca2+, and Ba2+ Will it dissolve Insoluble: • CO32-, CrO42-,Cr2O72-, PO43-, P3- except with Alkali Metals and ammonium • S2- except with Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and ammonium • OH- and O2-except with Alkali Metals and ammonium (slightly soluble with Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+) Will a rxn occur? • Chemical Driving Force 1. Formation of water is the strongest driving force 2. Formation of a precipitate (insoluble compound) 3. Formation of a covalent compound. Many of these are organic acids or gases » » » » H2CO3 (aq) CO2 (g) + H2O (l) H2SO3(aq) SO2 (g) + H2O (l) NH4OH NH3 (g) + H2O (l) H2S (aq) H2S (g) Practice: Formation of water • HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) • CaO (s) + 2 HCl (aq) Practice: Predicting Products Solubility Rules • Always Soluble: Alkali metals, NH4+, ClO3-, ClO4-, acetates, NO3-, and strong acids • Cl-, Br-, I- except with Ag+, Hg22+, and Pb2+ Practice Reactions • KCl + Pb(NO3)2 Practice: Predicting Product Solubility Rules • Always Soluble: Alkali metals, NH4+, ClO3-, ClO4-, acetates, NO3-, and strong acids • Sulfate except with Ag+, Hg22+, Pb2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+ Practice Reaction • Na2SO4 + Ba(NO3)2 Practice: Formation of a Gas Gases From Aqueous Soln Practice Reaction • • • • • K2SO3 + HNO3 H2CO3 (aq) CO2 (g) + H2O (l) H2SO3(aq) SO2 (g) + H2O (l) NH4OH NH3 (g) + H2O (l) H2S (aq) H2S (g) Practice: Formation of a Gas Gases from Aqueous Soln: Practice Reaction: • • • • • HCl + CaCO3 H2CO3 (aq) CO2 (g) + H2O (l) H2SO3(aq) SO2 (g) + H2O (l) NH4OH NH3 (g) + H2O (l) H2S (aq) H2S (g) Equations • Molecular Equation = show chemical formulas HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) Equations • (Complete) Ionic Equation = – show ions for strong electrolytes – insoluble compounds (precipitates), gases, and covalent compounds are written as molecules H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + H2O (l) Equations • Net Ionic Equation = Only show substances that are not present on both reactant and product sides. • Ex: (Complete) Ionic Equation H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + H2O (l) • Ex: Net Ionic Equation H+(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O (l) Net Ionic Equations • Allows chemists to identify active components of the reaction. Ions not included are considered “spectator ions” H+(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O (l) • So Na+ and Cl- are spectator ions Net Ionic Equations • If all ions cancel on reactant and products side, then there is no driving force and therefore no reaction will occur • Ex: Will potassium chloride and sodium nitrate react? Will potassium chloride and sodium nitrate react? • Molecular Equation KCl (aq) + NaNO3 (aq) NaCl (aq) + KNO3 (aq Will potassium chloride and sodium nitrate react? • Molecular Equation KCl (aq) + NaNO3 (aq) NaCl (aq) + KNO3 (aq) • (Complete) Ionic Equation K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Na+(aq) + NO3-(aq) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) Will A Reaction Occur? • Potassium sulfate is mixed with Barium nitrate Potassium Sulfate with Barium Nitrate K2SO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2 KNO3 (aq) Potassium Sulfate with Barium Nitrate K2SO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2 KNO3 (aq) 2K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Ba2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Potassium Sulfate with Barium Nitrate 2K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Ba2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Net Ionic Equation: SO42-(aq) + Ba2+(aq) BaSO4(s)