Chemical Bonding
advertisement

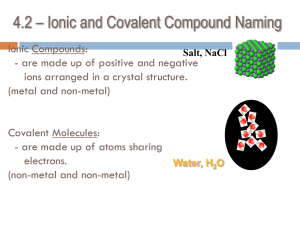
Chemical Bonding Ionic Bonding • Ions are atoms that have lost or gained one or more electrons, resulting in a positive or negative charge • Cation = a positively charged ion • Anion = a negatively charged ion • Elements in the vertical column families develop the same ionic charges: • Metals tend to lose electrons (form cations). • Non-metals tend to gain electrons (form anions). • Metal cation + Non-metal anion = ionic compound. • Are the following ions, cations or anions? • Chlorine ion • Magnesium ion • Oxygen ion Naming Binary Ionic Compounds • A binary ionic compound is a compound composed of a metal cation and a non-metal anion. • The first part of the name identifies the positive ion, which is the metal cation. • The second part of the name identifies the negative ion, which is the non-metal anion. • The name of the non-metal ion always ends with the sufix –ide. Elements in Ionic Compound Name of Ionic Compound magnesium and phosphorus magnesium phosphide sodium and chlorine sodium chloride calcium and bromine calcium bromide aluminum and oxygen aluminum oxide Writing the chemical formulas for binary ionic compounds • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Write the symbols with the metal first: Write the charge above each symbol. Cross over the numbers, not the charges. Never write a subscript 1. Write the formula, reduce if possible. aluminum oxide • Practice: Elements in Ionic Compound Ions Name Chemical Formula potassium and bromine K+1 and Br-1 potassium bromide KBr magnesium and chlorine Mg+2 and Cl-1 magnesium chloride MgCl2 aluminum and sulphur Al+3 and S-2 aluminum sulphide Al2S3 calcium and oxygen Ca+2 and O-2 calcium oxide CaO magnesium and bromine Mg+2 and Br-1 magnesium bromide MgBr2 calcium and iodine Ca+2 and I-1 calcium iodide CaI2 aluminum and oxygen Al+2 and O-2 aluminum oxide Al2O3 potassium and chlorine K+1 and Cl-1 potassium chloride KCl magnesium and nitrogen Mg+2 and N-3 magnesium nitride Mg3N2 sodium and phosphorus Na+1 and P-3 sodium phosphide Na3P Multivalent Metals • Multivalent metals have more than one ion charge listed on the periodic table. • For example, copper can form ions with a +1 or +2 charge. • Cu+1 = copper (I) • Cu+2 = copper (II) • Cu3N = Cu+1N-3 = copper (I) nitride • Practice: Chemical Formula Name SnS2 tin (IV) sulphide Fe2O3 iron (III) oxide FeF3 iron (III) fluoride Cr3P2 chromium (II) phosphide Multivalent Metals Practice: Chemical Formula Name SnS2 FeO copper(II) oxide Cu3N Cu2O mercury(II) chloride Answers SnS2 tin(IV) sulphide FeO iron(II) oxide CuO copper(II) oxide Cu3N copper(I) nitride Cu2O copper(I) oxide HgCl2 mercury(II) chloride Molecular Compounds • Molecular compounds are formed when atoms of two or more different elements SHARE electrons • A covalent bond is formed when electrons are shared between atoms. • For example, water (H20) Diatomic molecules • Elements that have two atoms joined by one or more covalent bonds to form a molecule • H2, O2, Br2, F2, I2, N2, Cl2 oxygen molecule Characteristics of Molecular Compounds What is the difference between a molecular formula and structural formula? • A molecular formula is a chemical formula – it shows the number of atoms of each element. • A structural formula shows the arrangement of the atoms that make up a molecule. water = H2O glucose = C6H12O6 Binary molecular compounds • Binary molecular compounds are compounds composed of two non-metals joined by one or more covalent bonds. • For example: carbon dioxide (CO2) Steps to naming a binary molecular compound: Prefix Number 1. How many atoms of the 1st element? Write the correct prefix. Never use the prefix mono- for the 1st element. mono- 1 di- 2 tri- 3 2. How many atoms of the 2nd element? Write the tetracorrect prefix. penta3. Write the suffix –ide to the 2nd element. hexa- 4 hepta- 7 octa- 8 For example: N2O4 = dinitrogen tetraoxide 5 6 Practice: Chemical Formula Name NO2 bromine monochloride PCl3 disulphur dinitride CCl4 diphosphorus hexoxide CO Answers: Chemical Formula Name NO2 nitrogen dioxide BrCl bromine monochloride PCl3 phosphorus trichloride S2N2 disulphur dinitride CCl4 carbon tetrachloride P2O6 diphosphorus hexoxide CO carbon monoxide Ionic Compounds with Polyatomic Ions • A polyatomic ion is an ion that is composed of more than one atom. • A ternary compound is a compound composed of three different elements. • For example: calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2, each molecule is composed of 1 calcium atom, 2 oxygen atoms, and 2 hydrogen atoms. • Naming compounds with polyatomic ions follows the same rules as other ionic compounds: 1. Write the cation 1st (e.g. calcium, Ca+2) 2. Write the anion 2nd (e.g. hydroxide, OH-) Common Polyatomic Ions Charge Name +1 -1 -2 -3 Chemical Formula ammonium (NH4 ) + hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) (HCO3 ) - hydroxide (OH ) - nitrate (NO3 ) - nitrite (NO2 ) - chlorate (ClO3 ) - carbonate (CO3 ) –2 sulphate (SO4 ) –2 sulphite (SO3 ) –2 peroxide (O2 ) –2 phosphate (PO4 ) –3 phosphite (PO3 ) -3 Practice: Name Chemical Formula calcium carbonate CaCO3 ammonium sulphate (NH4)2SO4 Mg3(PO3)2 potassium sulphate calcium nitrate Fe2(SO3)3 sodium phosphate LiOH cobalt(II) phosphate Answers: Name Chemical Formula calcium carbonate CaCO3 ammonium sulphate (NH4)2SO4 magnesium phosphite Mg3(PO3)2 potassium sulphate K2SO4 calcium nitrate Ca(NO3)2 iron(III) sulphite Fe2(SO3)3 sodium phosphate Na3PO4 lithium hydroxide LiOH cobalt(II) phosphate Co3(PO4)2 So what are all of these compounds? • sodium chloride • zinc oxide • calcium carbonate • calcium hydroxide So what are all of these compounds? • nitrogen dioxide • dinitrogen tetraoxide • phosphorus trichloride • sodium nitrite Naming Acids • Binary acids are composed of hydrogen and a non-metal • To name a binary acid: – 1. Wire the root of the non-metal name. – 2. Add the prefix hydro- to the root name. – 3. Add the ending –ic acid to the root name. For example: HF(aq) = hydrofluoric acid HCl(aq) = hydrochloric acid HI(aq) = hydroiodic acid • Oxoacids are composed of hydrogen, oxygen, and another element. • To name an oxoacid: – 1. Write the name of the anion, without the –ate or –ite ending. – 2. If the anion name ended in –ate, replace it with –ic at the end of the name. – 3. If the anion name ended in –ite, replace it with –ous at the end of the name. – 4. Add the word acid. For example: H2SO4(aq) = sulphuric acid H2SO3(aq) = sulphurous acid H3PO4 (aq) = phosphoric acid H2CO3 (aq) = carbonic acid Naming Bases • Many bases are ionic compounds composed of metal ions and hydroxide ions. They are named the same way as other ionic compounds. • For example: – NaOH = sodium hydroxide – Ca(OH)2(aq) = calcium hydroxide