Stuart-Middleton-DVD-PPT - Manukau Institute of Technology
advertisement

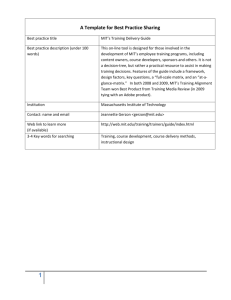
THS : Questions and Answers Dr Stuart Middleton Manukau Institute of Technology EdTalkNZ www.stuartmiddleton.co.nz www.edtalknz.com 1 NZ’s leaking education pipeline • • • • • 20% 30,000 4,000 4500 80% Disappeared from education by age 16 Secondary Truants each day Excluded each year (unless MOE intervenes) Leave primary but fail to enter secondary Youth appearing in the Youth Court have left or are absent from school • 48% Successfully complete a postsecondary qualification that they start • 17,000 – 25,000 NEETS 15-19 year olds Not in Employment, Education and Training – Annual cost in excess of $NZ1 billion Shared Issues New Zealand Australia Great Britain Canada United States of America 3 The Pattern Unease socially and politically with education Unprecedented levels of disengagement Social Disengagement Issues Inactive Disconnect between education and the economy Skill Shortage Youth - Physical - Virtual - Unintended NEET (15 – 19) Not in Employment Education or Training Some big factors outside the education system 6 Mum and Dad’s Generation Primary / Basic / Elementary Education Academic / General Secondary Education HERDSA 2009 Higher and Further Education The Baby Boomers’ Generation Primary / Basic / Elementary Education Academic / General Secondary Education Other HERDSA 2009 Higher and Further Education 1970’s into the 1980’s Primary / Basic / Elementary Education EEEE Academic / General Secondary Education Higher and Further Education Other Other Opportunities: Employment / On-the-job Training / Teaching / Nursing / Accountancy / Night Class / Apprenticeships / Offices / Unskilled and Low Skilled Employment HERDSA 2009 1970’s into the 1980’s Primary / Basic / Elementary Education EEEE Academic / General Secondary Education Higher and Further Education Other Other Opportunities: Employment / On-the-job Training / Teaching / Nursing / Accountancy / Night Class / Apprenticeships / Offices / Unskilled and Low Skilled Employment HERDSA 2009 1980’s into the 1990’s Primary / Basic / Elementary Education EEEE Academic / General Secondary Education Higher and Further Education Grew HE and FE Downwards Other • • • • Other Opportunities: Employment / On-the-job Training / Teaching / Nursing / Accountancy / Night Class / Apprenticeships / Offices / Unskilled and Low Skilled Employment HERDSA 2009 Level 1-3 Courses Polytechnics PTE’s “Doing a Course” As we go into the 21st Century Primary / Basic / Elementary Education EEEE Academic / General Secondary Education Higher and Further Education Growing HE Downwards Level 1-3 Courses Polytechnics PTE’s “Doing a Course” Other Opportunities: Employment / On-the-job Training / Teaching / Nursing / Accountancy / Night Class / Apprenticeships / Offices / Unskilled and Low Skilled Employment The Disengaged 12 Growth of secondary schooling 70.00% 60.00% 50.00% 40.00% 30.00% 20.00% Cohort Growth 10.00% Cohort Retention 0.00% 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 -10.00% -20.00% -30.00% 13 The big issue: disengagement 1. Physical Disengagement – actually not being at school 2. Virtual Disengagement – at school but not getting qualifications 3. Unintended Disengagement – Good intentions, right moves, but little or no success post-secondary. 14 What has created disengagement in NZ? 1. A series of opportunities for young people been stripped from our education system a) Uncritical acceptance of the value of increased general academic secondary education; b) Removal of vocationally / technical oriented options; c) The delaying of both the decision about pathways and the actual entry into the workforce. 2. Failure to respond to increasing diversity 3. Uncritical acceptance that more is better. 15 Some questions emerge. . . . . . • Is secondary school as it is the best learning environment for all students? – No, without a doubt • Are we are keeping students in the school system past the point of disengagement? – Yes, that is clear • Can we engage students in pathways that offer a future that holds increased rewards? – Only if we change 16 Some answers emerge Issue • Disengagement Answer • Change what we are doing to keep students in education • Get new pathways to students earlier • Provide wider options earlier • Lack of focus • Provide clear vocational options • Basic skills • Teach in new and integrated ways • Qualifications • Focus on Access and Equity as outputs not inputs Logical relationships • • Positioning the responses • 12 years old and 14 years old are critical points Tertiary High School • A programme at a polytechnic (MIT) offered collaboratively with secondary schools (Counties Manukau) • Schools / parents / MIT identify students in Year 10 who have potential but are unlikely to succeed in a school setting • Selected students enter the THS in Year 11 • Complete their secondary schooling (= NCEA Level 3) and a two year Career and Technical Education qualification (diploma / Year 1-2 of a degree, etc) 18 Students targeted for the programme are likely to be: • • • • • underperforming and likely to fail at school; pose a potential threat of disengagement; likely to finish school with little or no qualifications; at risk educationally but not yet in risk interested in a career path that is appropriate to an institute of technology; • will be reflective of the communities of Counties Manukau • from a low decile school and/or a low income family; • likely to be a First Generation Student 19 Programme Overview • The THS is a hybrid tertiary / secondary programme • There is a mix of MIT qualifications / NCEA • High levels of credit bearing activities • Based on the New Zealand Curriculum • An alternative pathway through senior secondary into postsecondary • Students will be “in school” not “at school” 20 21 22 23 Key Concepts • The engagement with scheduled MIT courses will increase over time during the programme • Key component in the success of the programme will be FLEXIBILITY • Decreasing individual support will be determined by individual students’ needs as they progress from Years 1 to 4 24 Programme Overview 1 @ Programme Centre • Developing Work and Personal Skills (DWPS) including Personal Pathway Plan • Literacy Support: x 3 (Literacy, Numeracy, Digital) including MIT Course support • Structured Self-Directed Activities (SDA) including possible involvement with origin school 25 Programme Overview 2 @ MIT Campus • Year 1 to contain two programmes 1st Semester: to inform student choice (Preparing for Trades and Professions = PTPs) 2nd Semester: to provide focused discipline experiences (Specifically designed MIT staircase courses or existing MIT entry level programmes) • Years 2, 3 & 4 All students enrolled in selected MIT qualifications 26 MIT Component : Year 1 • 1. Preparing for Trades and Professions (PTP) Construction Automotive / Fabrication Early Childhood Introduction to Business Visual Arts Sports Leadership Nursing & Health Hospitality • 2. Focused discipline experiences New discipline focused courses to provide career pathways or Existing MIT Qualification(s): including entry level and Foundation pathway programmes 27 The shifting programme balance Special features • • • • • • • “College knowledge” emphasis in literacy, numeracy and technology High levels of supervision and monitoring Personal development related to their school All CTE qualification classes are normal scheduled MIT classes CTE support programme alongside the MIT classes All work activity in the programme is credit bearing Students will get NCEA Level 3 and the CTE Qualification (and possibly an Associate Degree) 29 Principles: Collaboration • The Tertiary / Secondary Programme does not take students out of school; it keeps them “in school” but not “at school”. • collaborative project - a polytechnic (MIT), government agencies (MOE and TEC) and a consortium of about 25 secondary schools • Secondary teachers will work alongside tertiary teachers 30 Principles: Student Focus • agreed set of criteria. • integrated and socialised into the tertiary institution. • both “secondary” and “tertiary” • ongoing contact with their secondary school. • programme of personal growth and development • dual enrolled 31 Principles: Programme • vocational and technical orientation • • all work will becredit bearing • • MITqualification in normal scheduled MIT classes. 32 Principles: Pastoral Care • emphasis on monitoring progress, monitoring attendance and supporting learning. 33 Some learnings • The THS is as much a challenge for MIT as it is for schools • The THS required new programmes to be developed: – Year 1 – Year 2 – PTPs Certificate in Tertiary Pathways Level 1 – 60 credits Level 2 60 credits In development now (2 x 60 credit courses Level 3) written for each of eight MIT departments • The THS demands a new relationship secondary / tertiary • The THS is one answer to the question “How can we make a difference for disengaging students?” 34 “. . . . . looking at the stars” • Start with the end in mind • The THS has led to changes that two years ago seemed out of reach: – – – – Dual enrolment Dual funding Under 16-year olds legally and fulltime in tertiary New approaches to curriculum in the senior school 35 “The hallmark of our age is the tension between aspirations and sluggish institutions.” John W Gardner And finally ………. • Making changes is not an option – it is what we have to do. • Start small and become great. • Don’t look for more resources – use what you have differently ($ and people). • Work with the willing. • Put the learner at the centre – that solves most issues. 36 Ina te mahi he rangatira Stuart Middleton Executive Director Manukau Institute of Technology EdTalkNZ www.stuartmiddleton.co.nz www.edtalknz.com 37